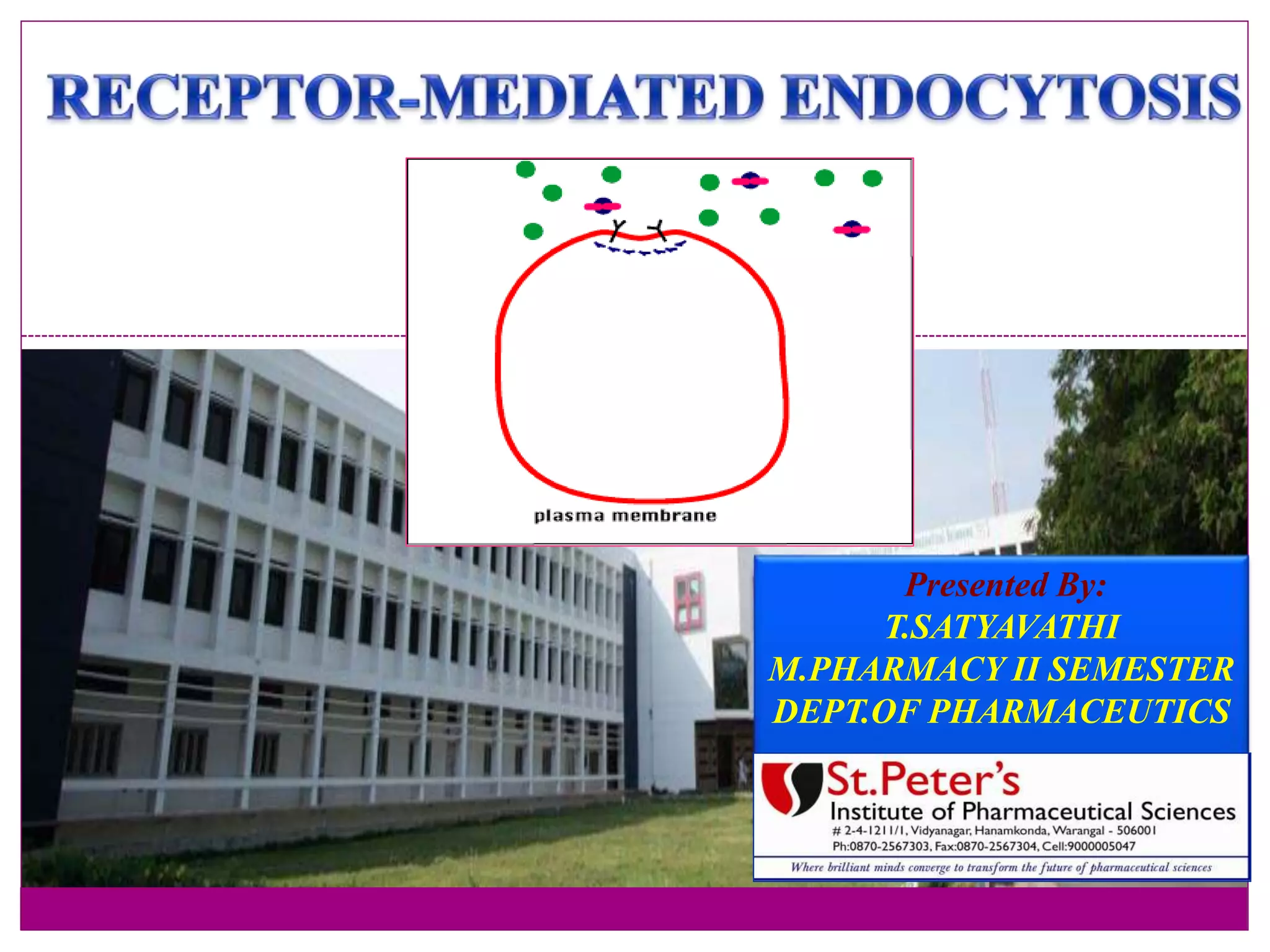
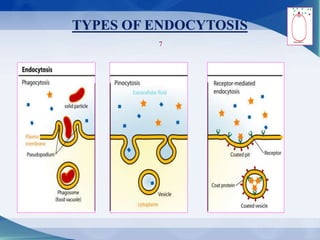
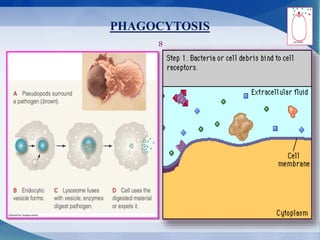
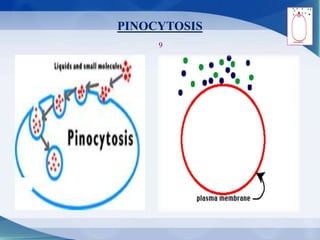
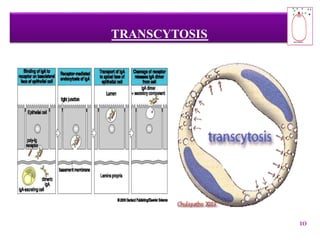
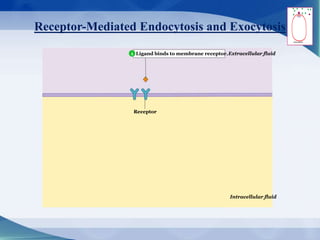
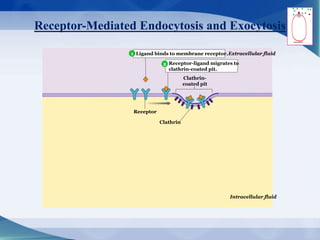
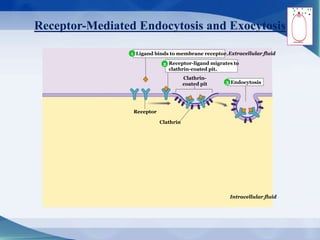
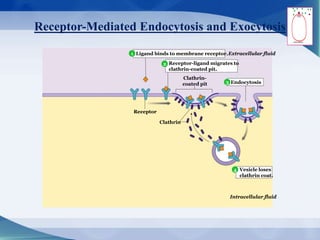
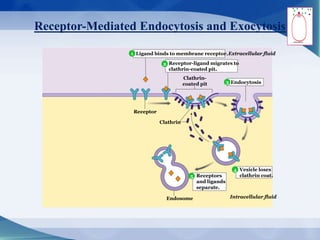
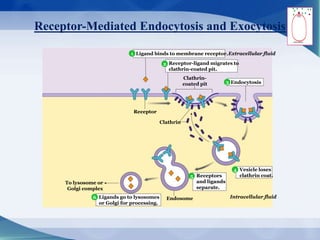
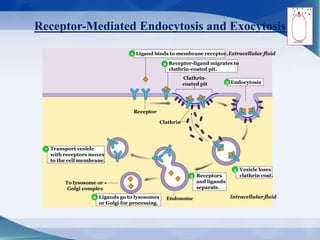
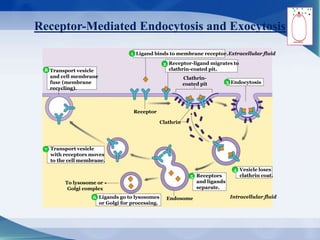
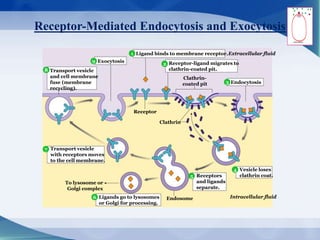
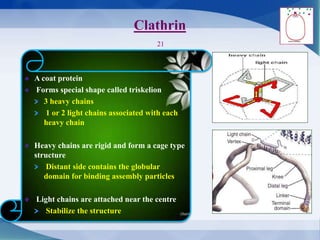
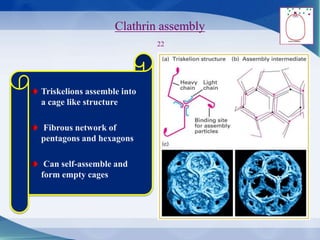
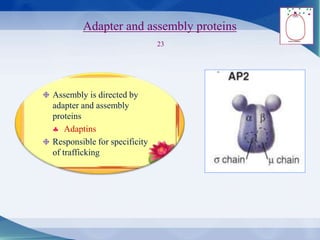
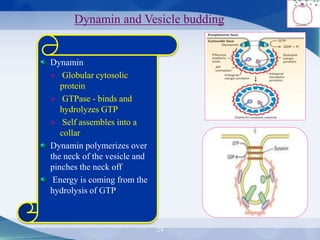
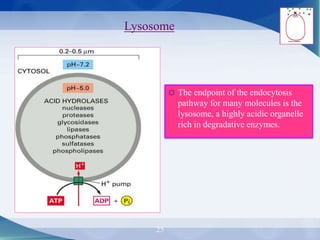
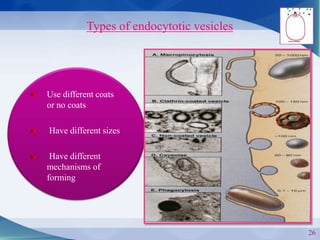
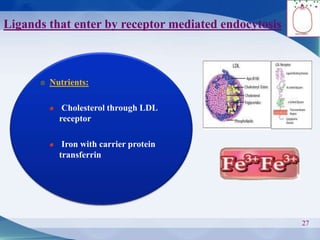
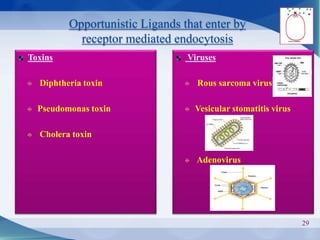
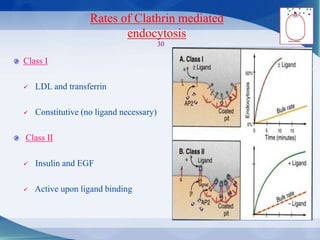
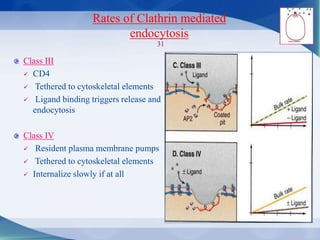
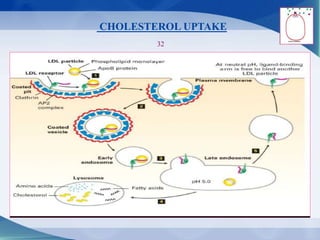
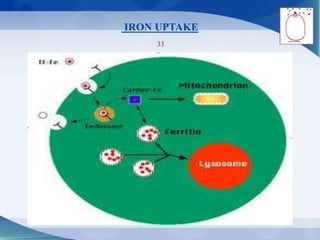
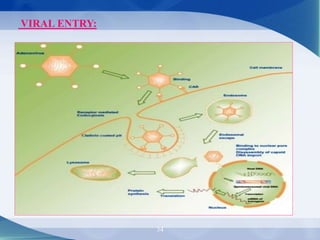
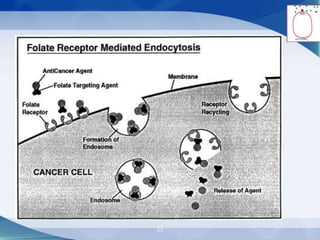
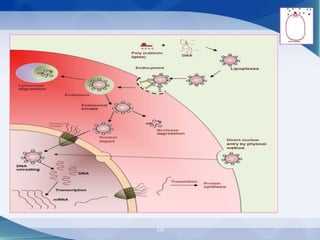
The document discusses receptor-mediated endocytosis and exocytosis, detailing the role of receptors in cellular communication and the specific mechanisms involved in the uptake of molecules like LDL and iron. It covers various types of endocytosis, including phagocytosis and pinocytosis, and emphasizes the importance of clathrin-coated pits in concentrating surface receptors for efficient internalization. Conclusively, receptor-mediated endocytosis is crucial for cells to selectively internalize necessary substances.