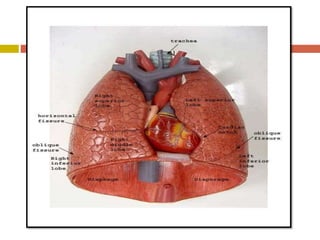
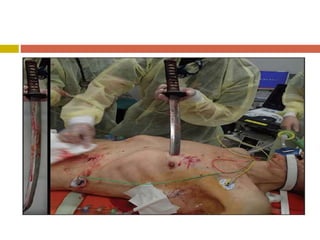
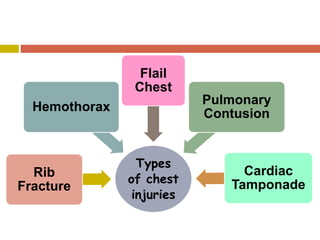
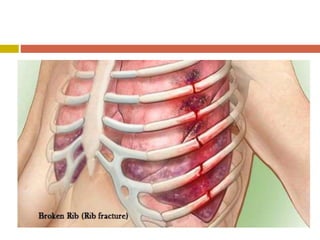
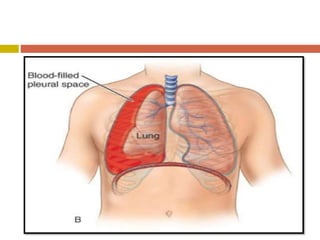
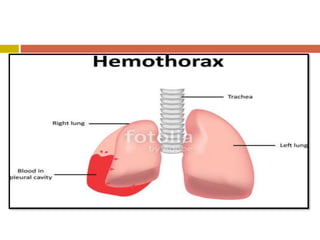
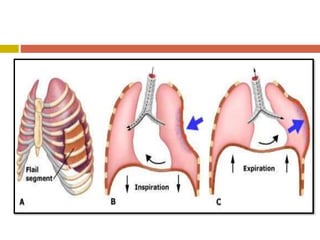
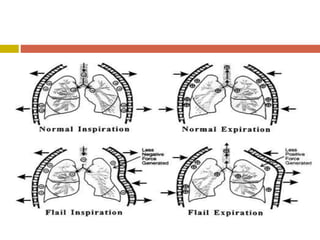
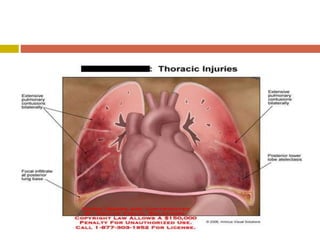
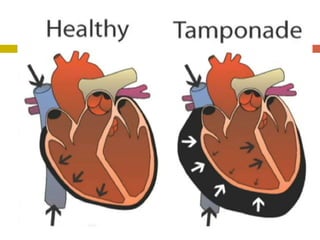
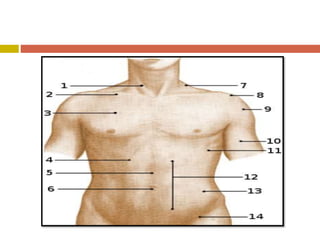
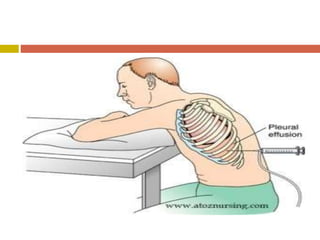
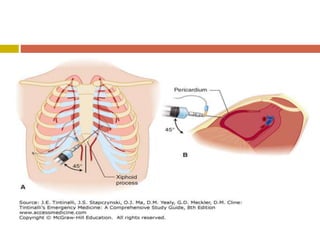
Chest injuries can be life-threatening and result from blunt or penetrating trauma. The document defines a chest injury as any injury affecting the ribs, heart, lungs, blood vessels, trachea or esophagus. Common causes include motor vehicle accidents, falls, and assaults. Types of chest injuries include rib fractures, hemothorax, flail chest, pulmonary contusion, and cardiac tamponade. Diagnostic evaluation involves history, physical exam, x-ray, CT scan and monitoring for symptoms like respiratory distress, decreased breath sounds, and chest pain. Management focuses on resuscitation, stabilizing the chest wall, draining fluids, addressing fractures, and monitoring for complications.