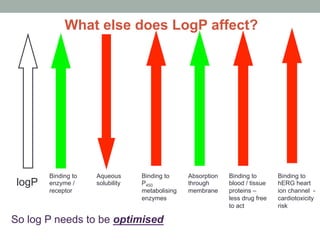
This document discusses types of chemical data including data on drugs, agrochemicals, fragrances, food additives, and natural products. It focuses on drug data such as chemical properties, adverse events, toxicology, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). LogP is discussed as a measure of solubility, with examples of how it is calculated from molecular fragments and corrections. Molecular descriptors that can predict properties are also introduced, including topological, geometrical, electronic, and hybrid descriptors. Finally, some freely available tools for calculating molecular descriptors are listed.



![Partition coefficients
1-Octanol is the most frequently used lipid phase in pharmaceutical research.
This is because:
§ It has a polar and non polar region (like a membrane phospholipid)
§ Po/w is fairly easy to measure
§ Po/w often correlates well with many biological properties
§ It can be predicted fairly accurately using computational models
Xaqueous
Xoctanol
P
Partition coefficient P (usually expressed as log10P or logP) is defined as:
P =
[X]octanol
[X]aqueous
P is a measure of the relative affinity of a molecule for the lipid and aqueous phases in
the absence of ionisation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicaldata-150908014948-lva1-app6891/85/Chemical-data-5-320.jpg)