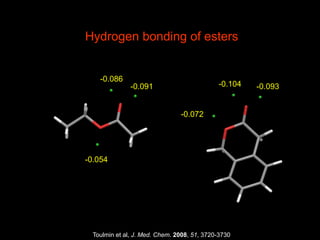
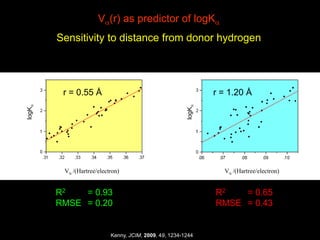
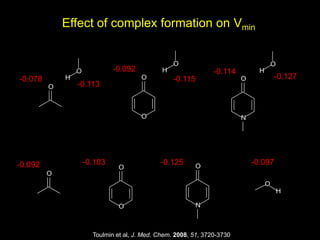
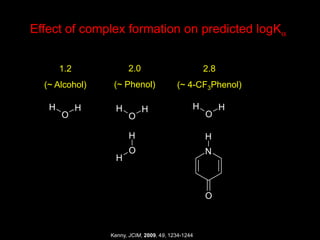
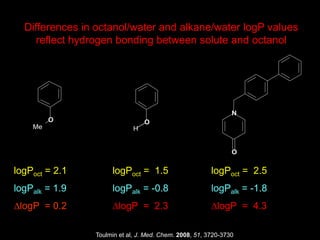
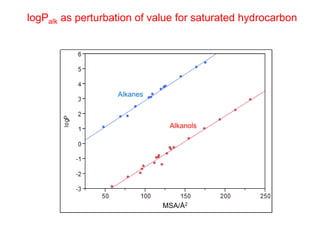
The document discusses the importance of lipophilicity in molecular design, particularly in drug discovery and development, outlining challenges faced by the pharmaceutical industry such as unpredictable toxicity and difficulties in measuring unbound drug concentrations. It emphasizes that hydrogen bonding is a significant determinant of lipophilicity and highlights alternatives to the octanol/water partitioning system, suggesting the relevance of alkane/water systems. Key findings include the correlation of molecular electrostatic potential with hydrogen bond properties and the implications for drug affinity and permeability.