The document discusses several key physicochemical properties that influence a drug's biological activity, including:
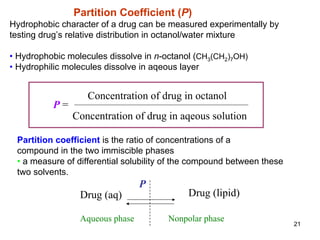
1. Partition coefficient, which measures a drug's relative solubility in water vs. lipid and predicts its distribution in the body.
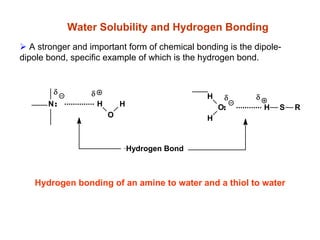
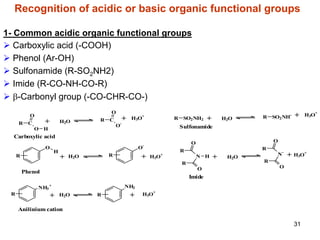
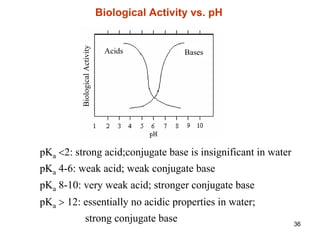
2. Acidity and basicity, with ionization affecting absorption, transport, binding, and elimination. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation calculates the percentage of a drug in its ionized and unionized forms.
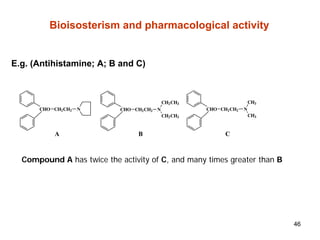
3. Steric factors like a drug's bulk, size, and shape, which can either hinder or help its interaction with receptors and enzymes. A drug's physicochemical properties are crucial to its ability to reach biological targets.














![35
Handerson Hasselbalch Equation
pH = pKa + log
[A-]
[HA]
pH = pKa + log
[B]
[BH+]
*Weak acid
*Weak base
¾ For calculating the percentage of drug existing in ionized or
unionized form at a given pH
Weak acids: pH > pKa ; [A-] > [HA] , (ionized > unionized)
Weak bases: pH > pKa ; [HA] > [A-] , (unionized > ionized)
¾ pH = pKa ; [HA] = [A-] , (unionized = ionized)
HA H
+
+ A
Ka
H
+
+ B
BH+ Ka
CH3COOH CH3COO + H+
NH4 + H2O NH3 + H3O+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20-240224070946-606a46ef/85/20-physicochemical-properties-determination-1-pdf-20-320.jpg)
![37
pH = pKa + log
[A-]
[HA]
B = A-
A = HA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20-240224070946-606a46ef/85/20-physicochemical-properties-determination-1-pdf-22-320.jpg)