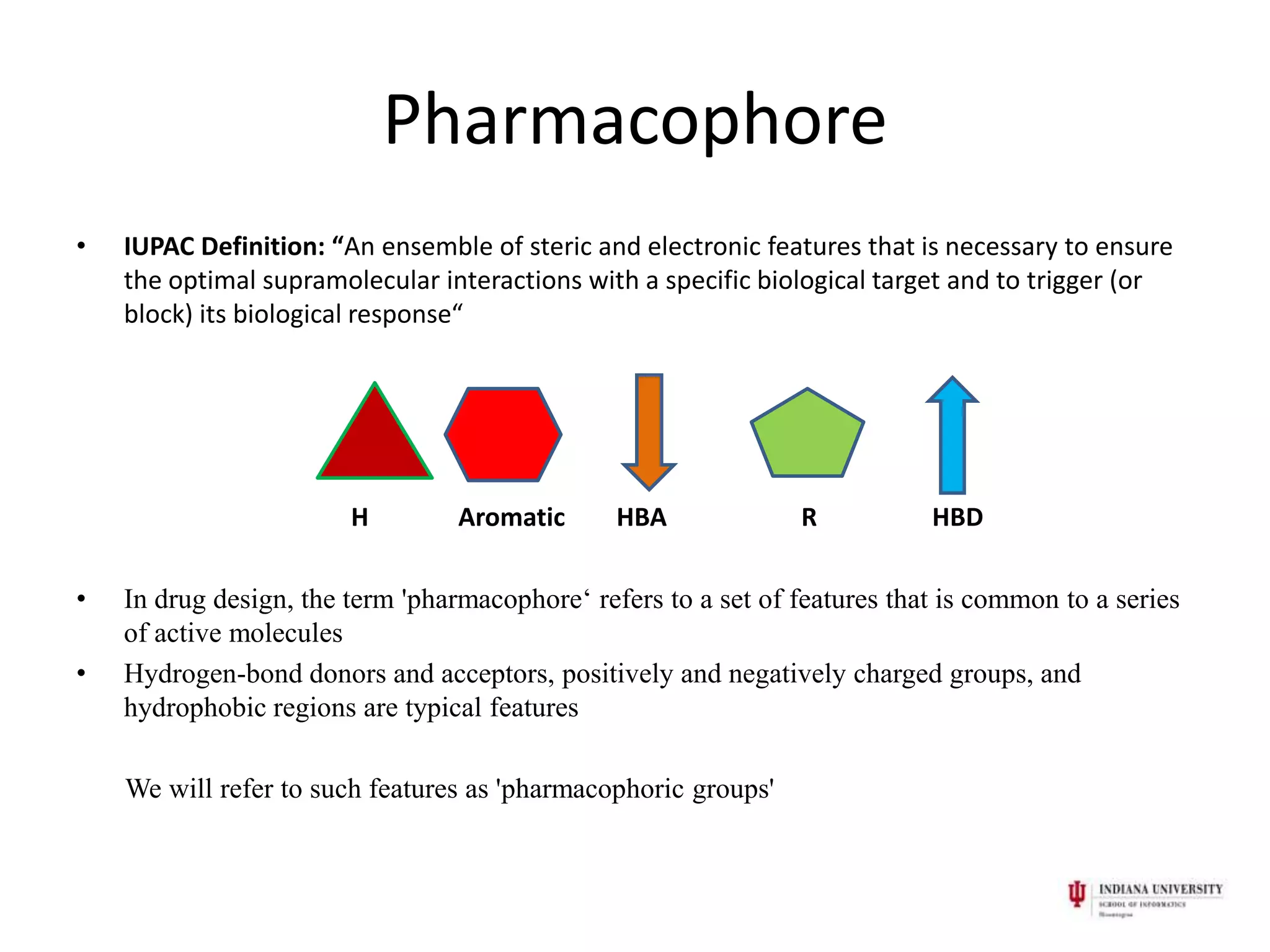
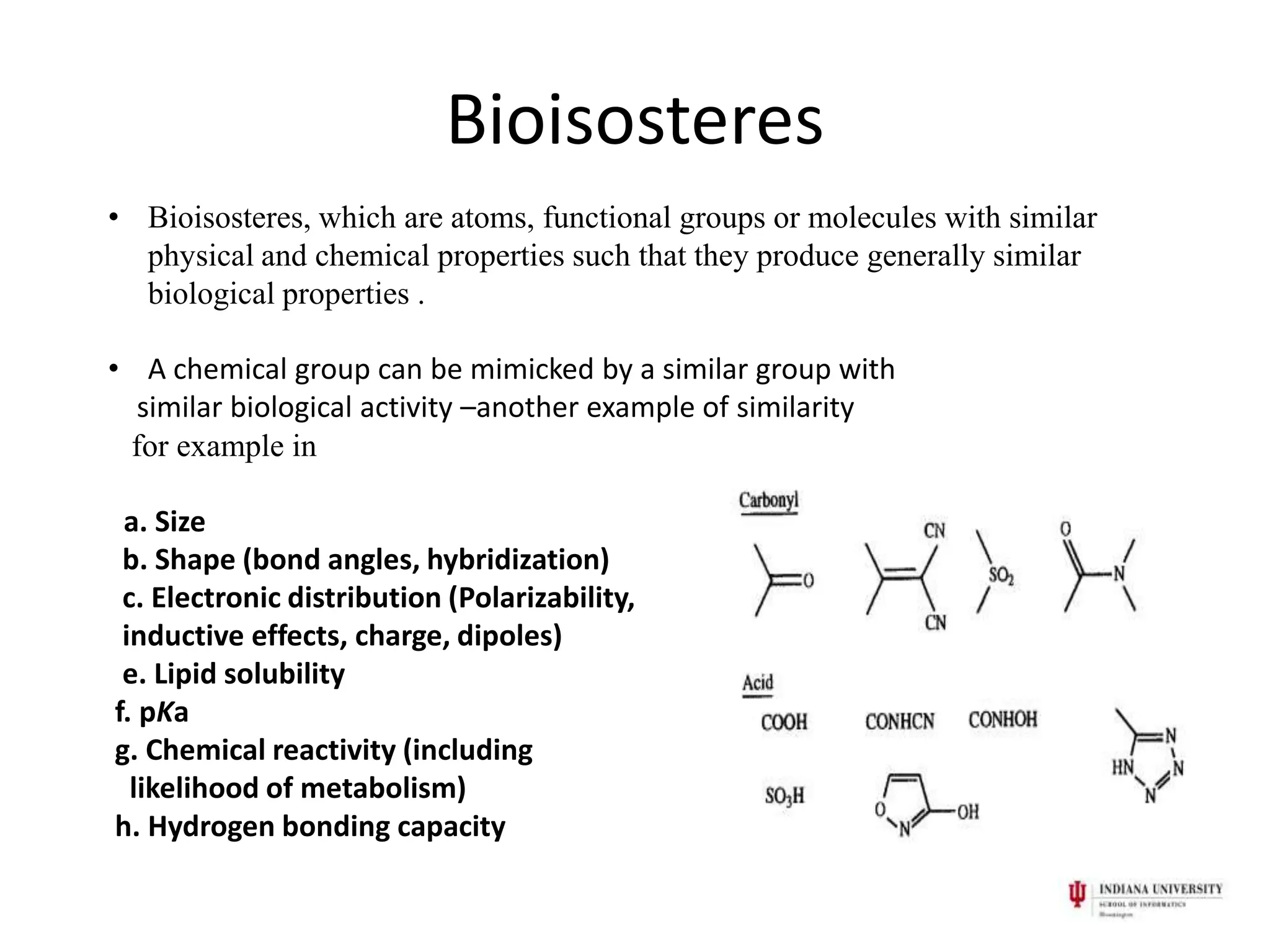
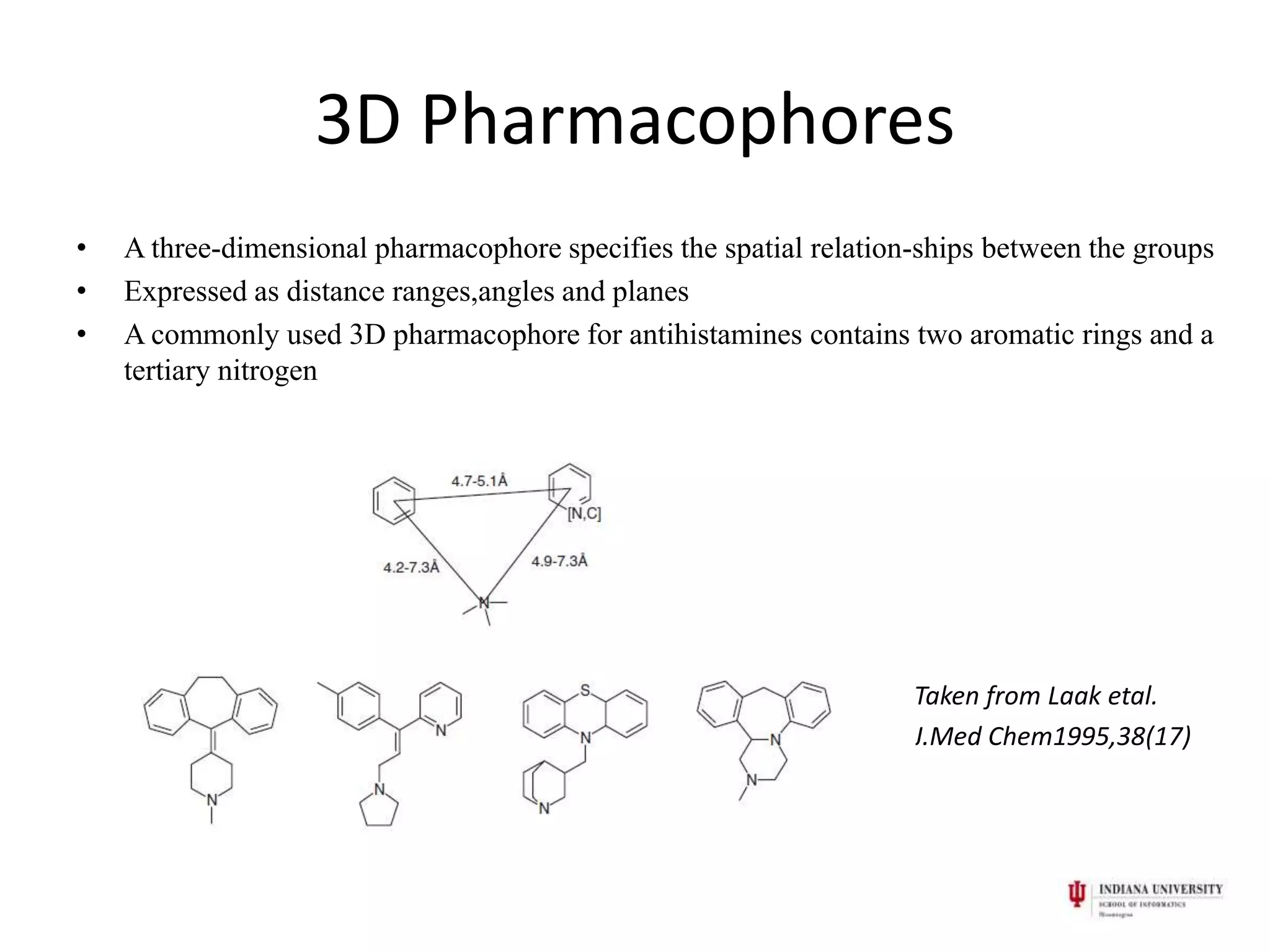
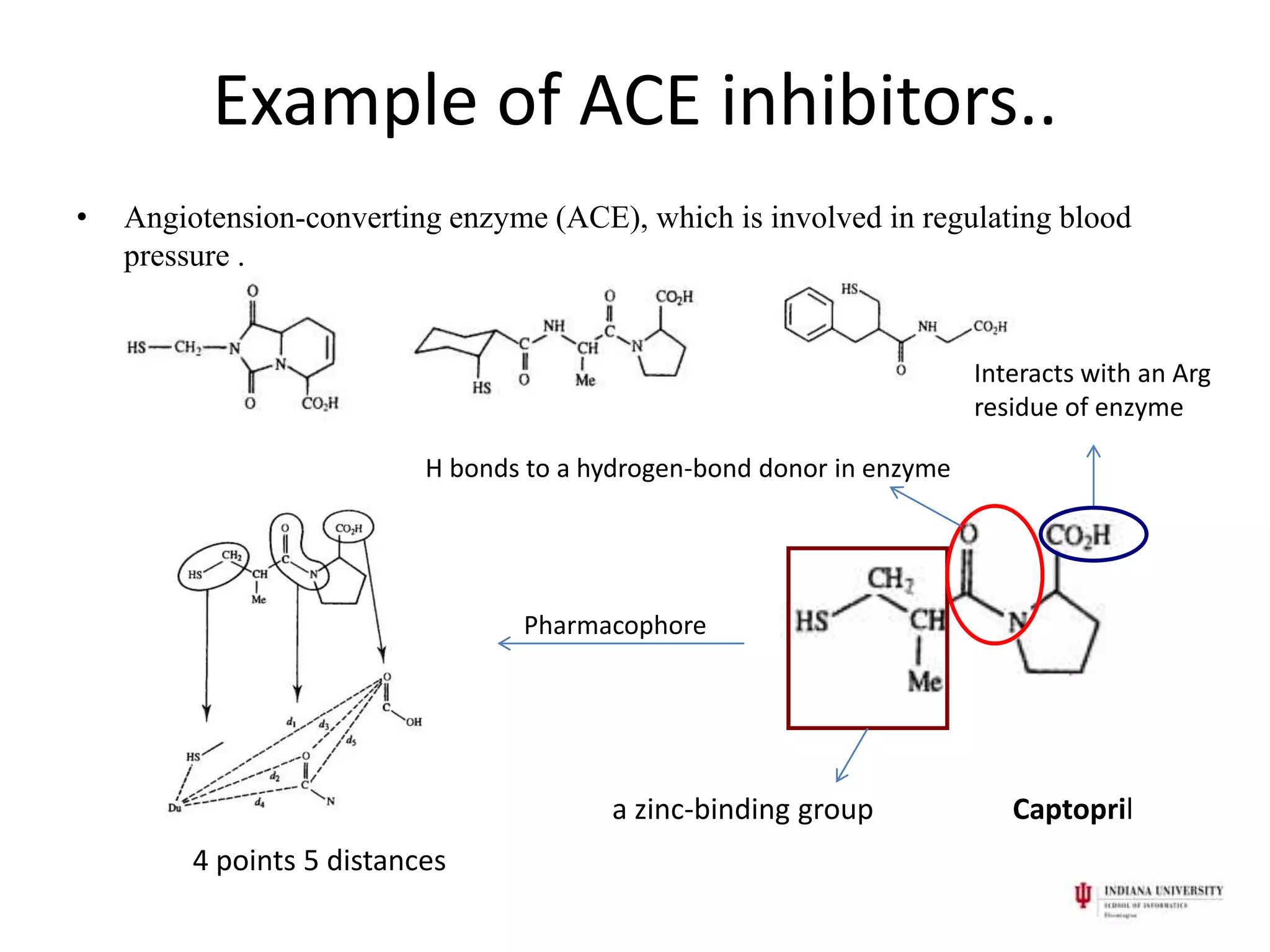
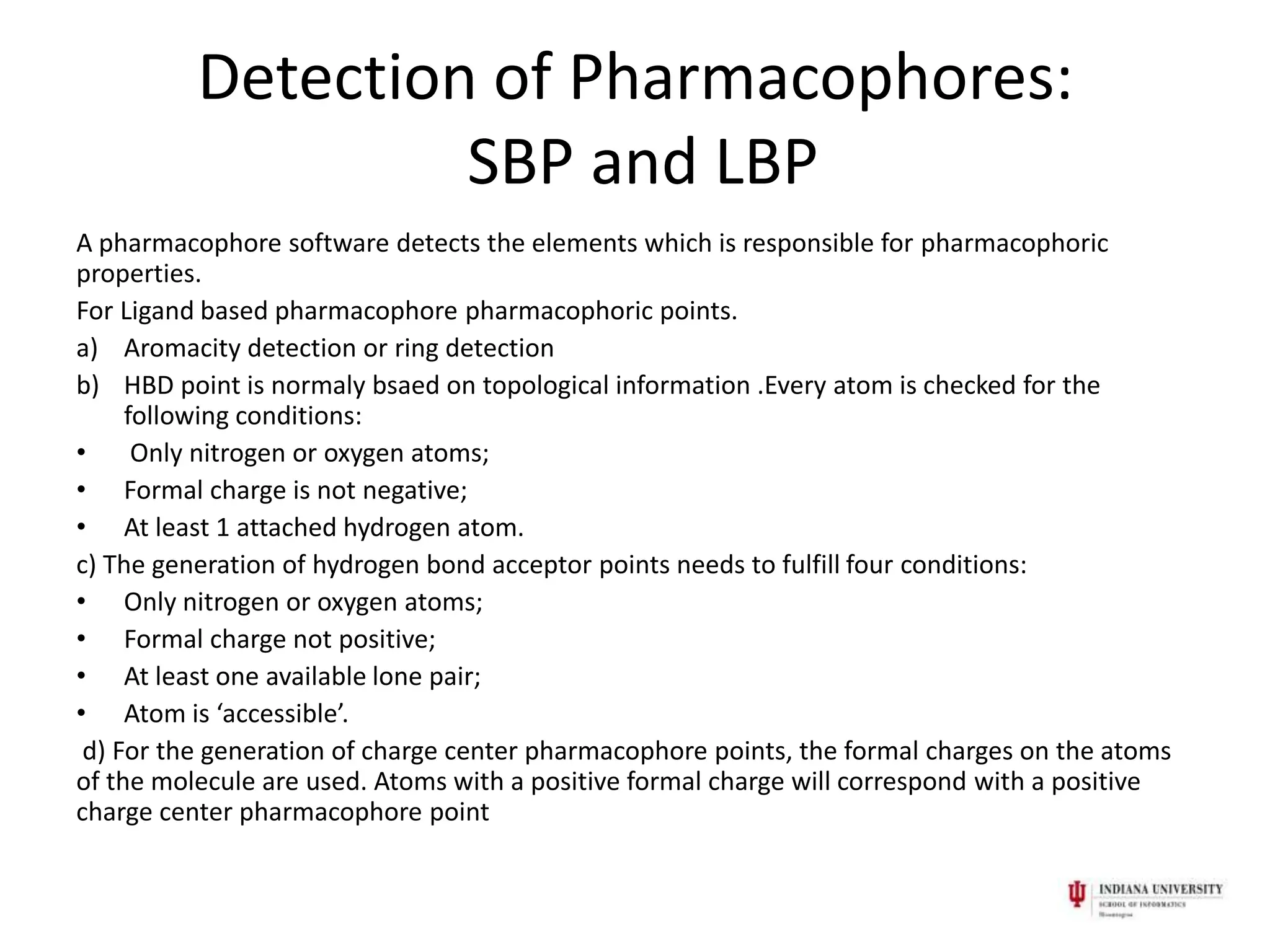
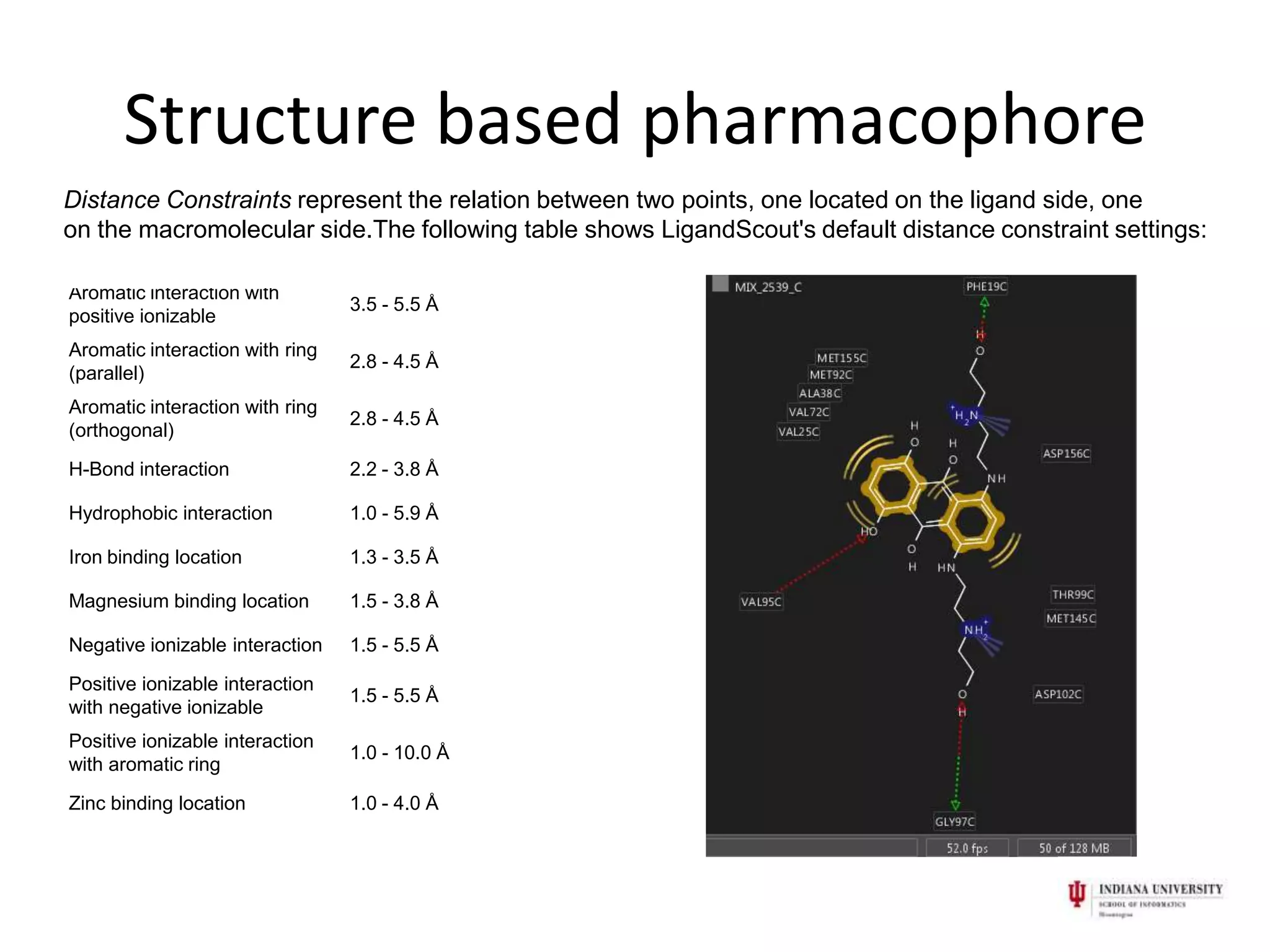
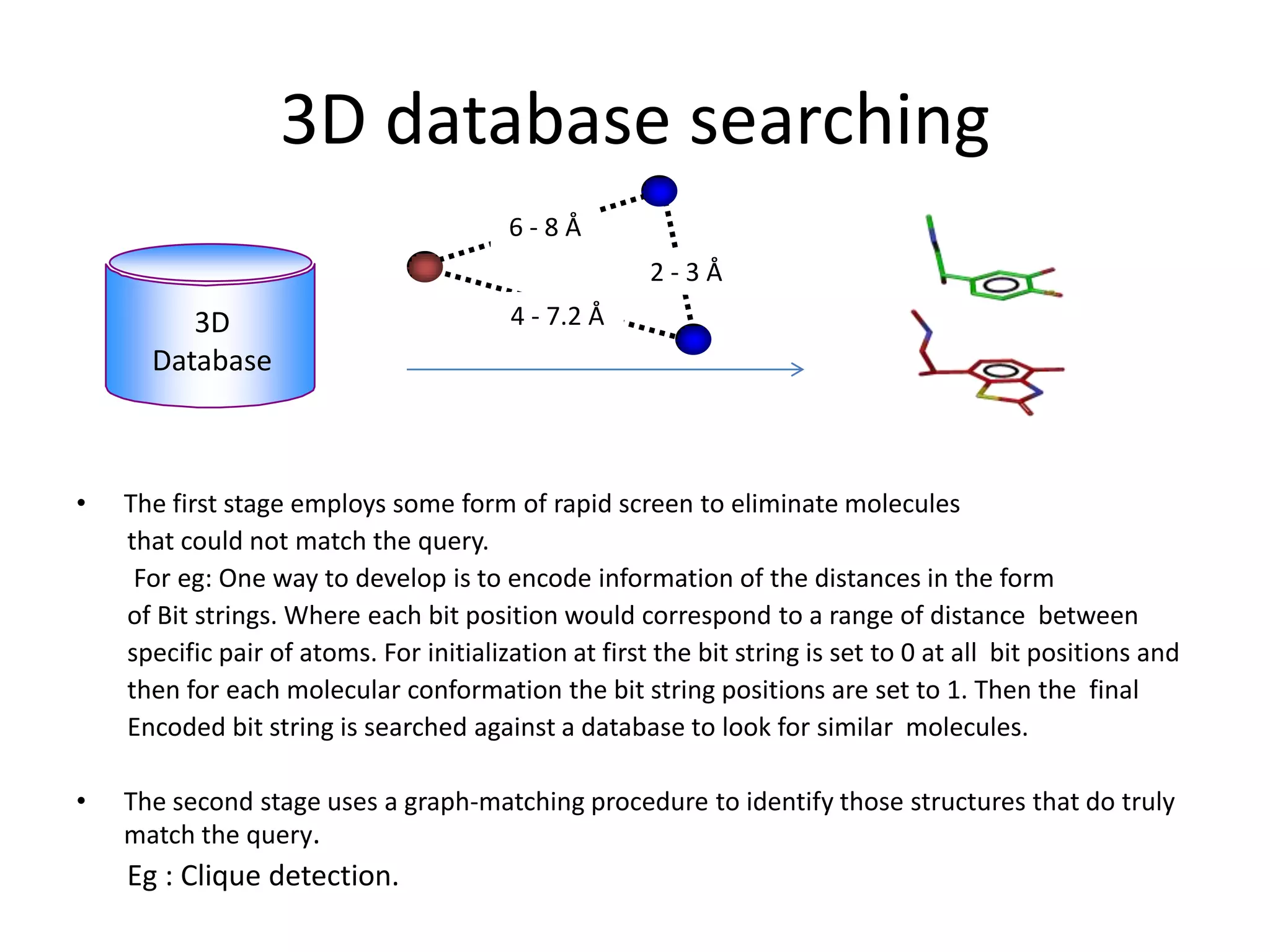
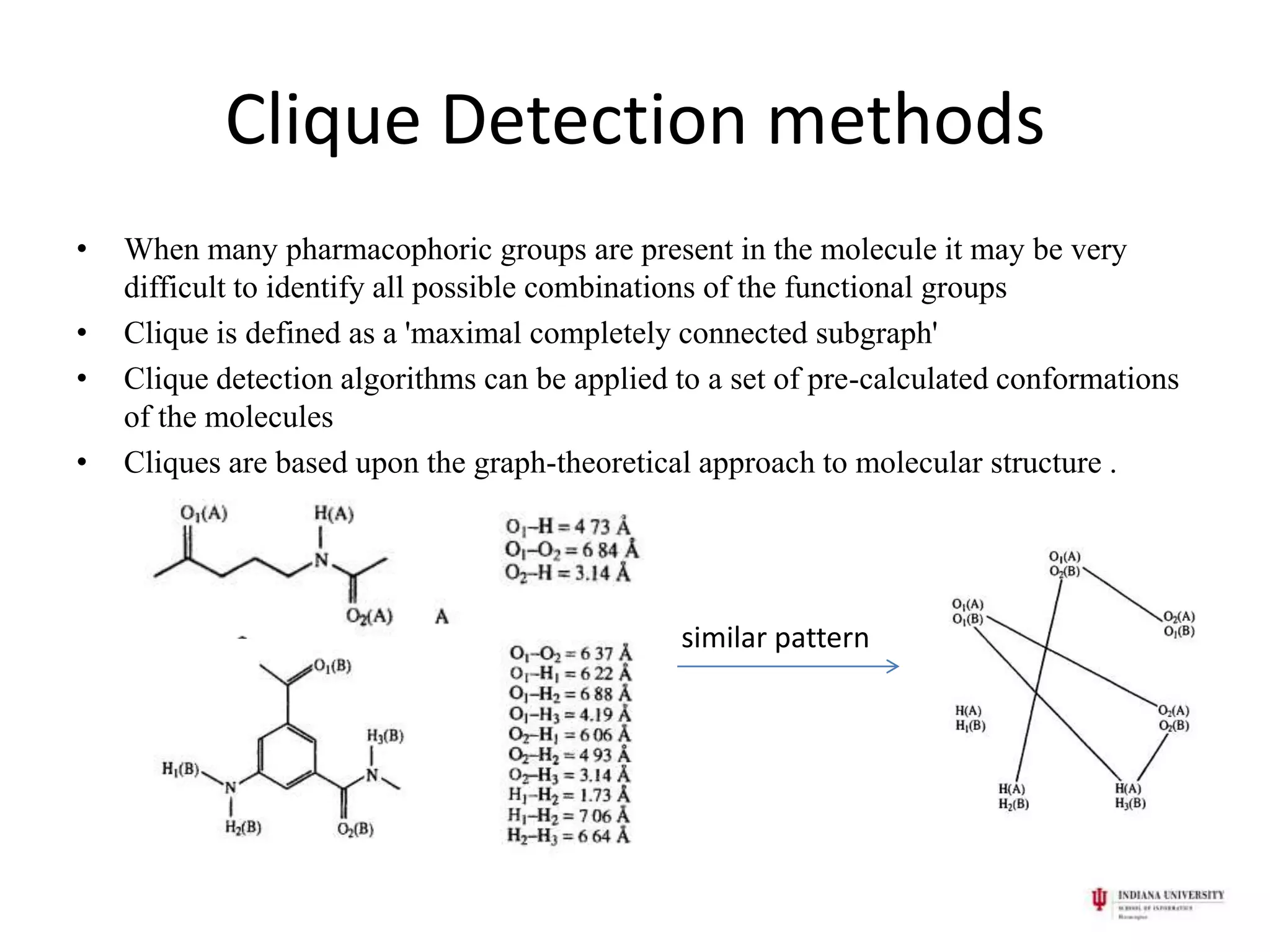
1) Pharmacophores are sets of steric and electronic features common to active drug molecules that interact with biological targets in a specific way. They include features like hydrogen bond donors/acceptors and hydrophobic regions.
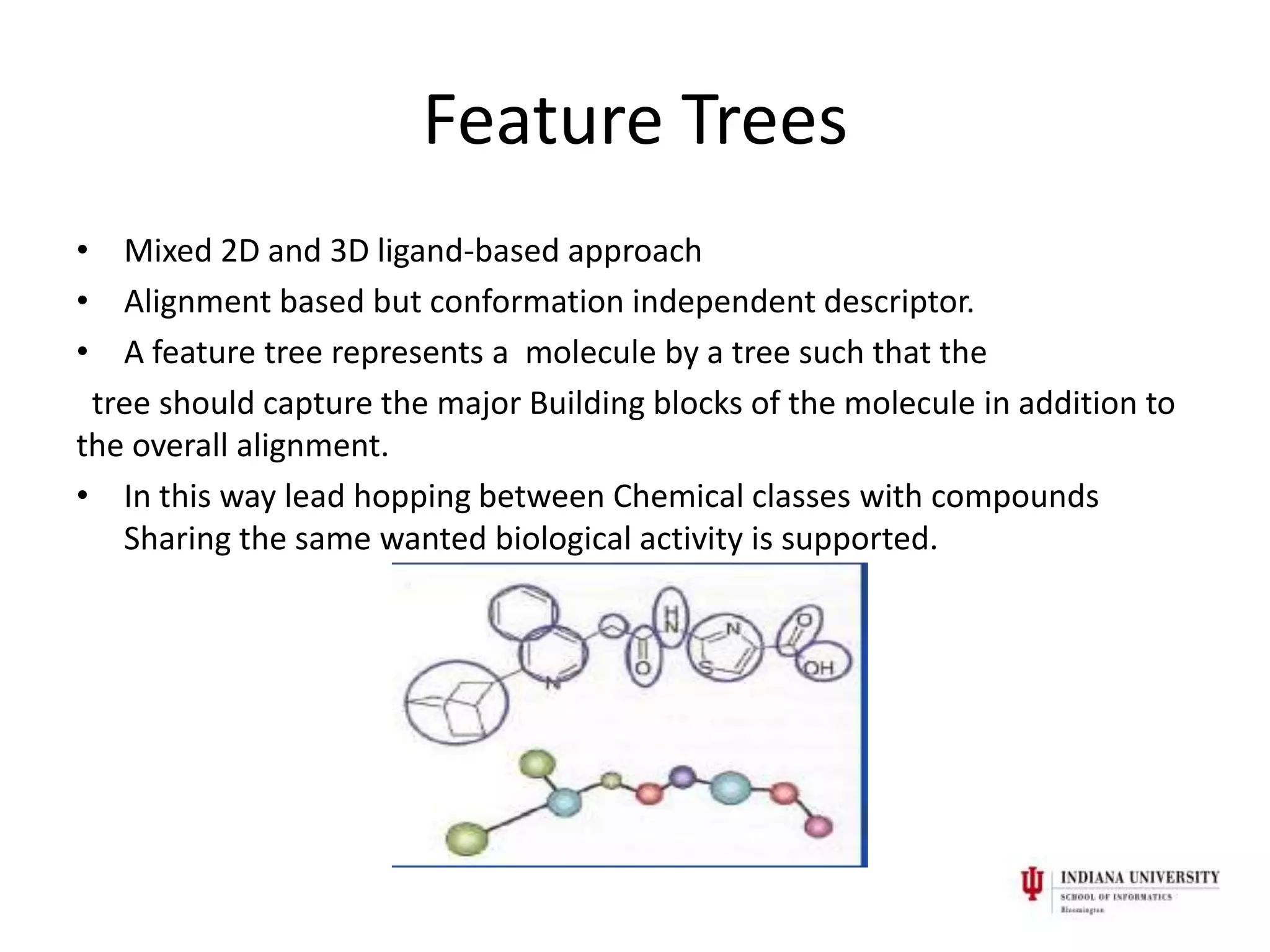
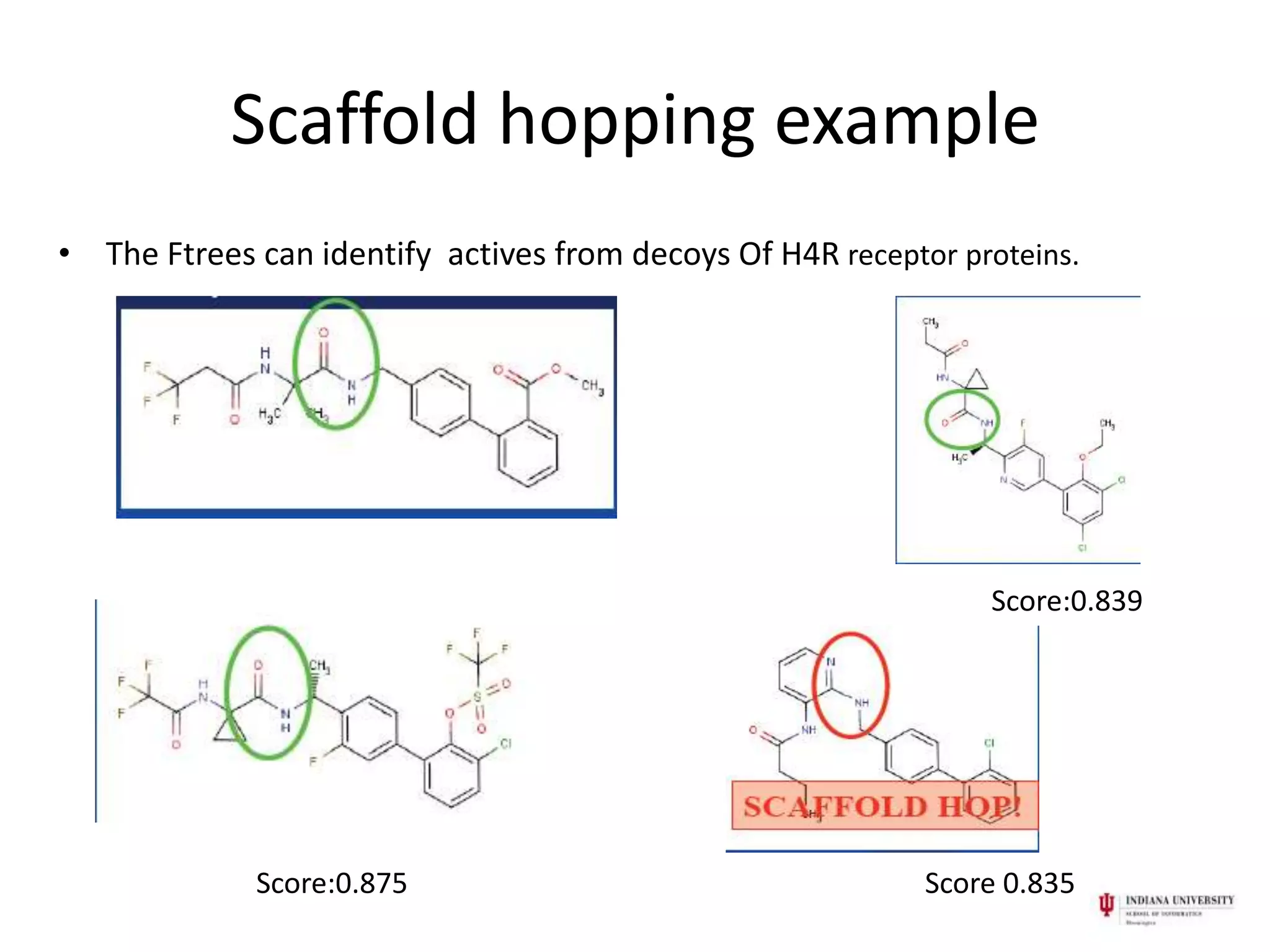
2) Feature trees (Ftrees) are a ligand-based approach that represents molecules as trees to capture major building blocks and overall alignment in a conformation-independent way, supporting "lead hopping" between chemical classes.
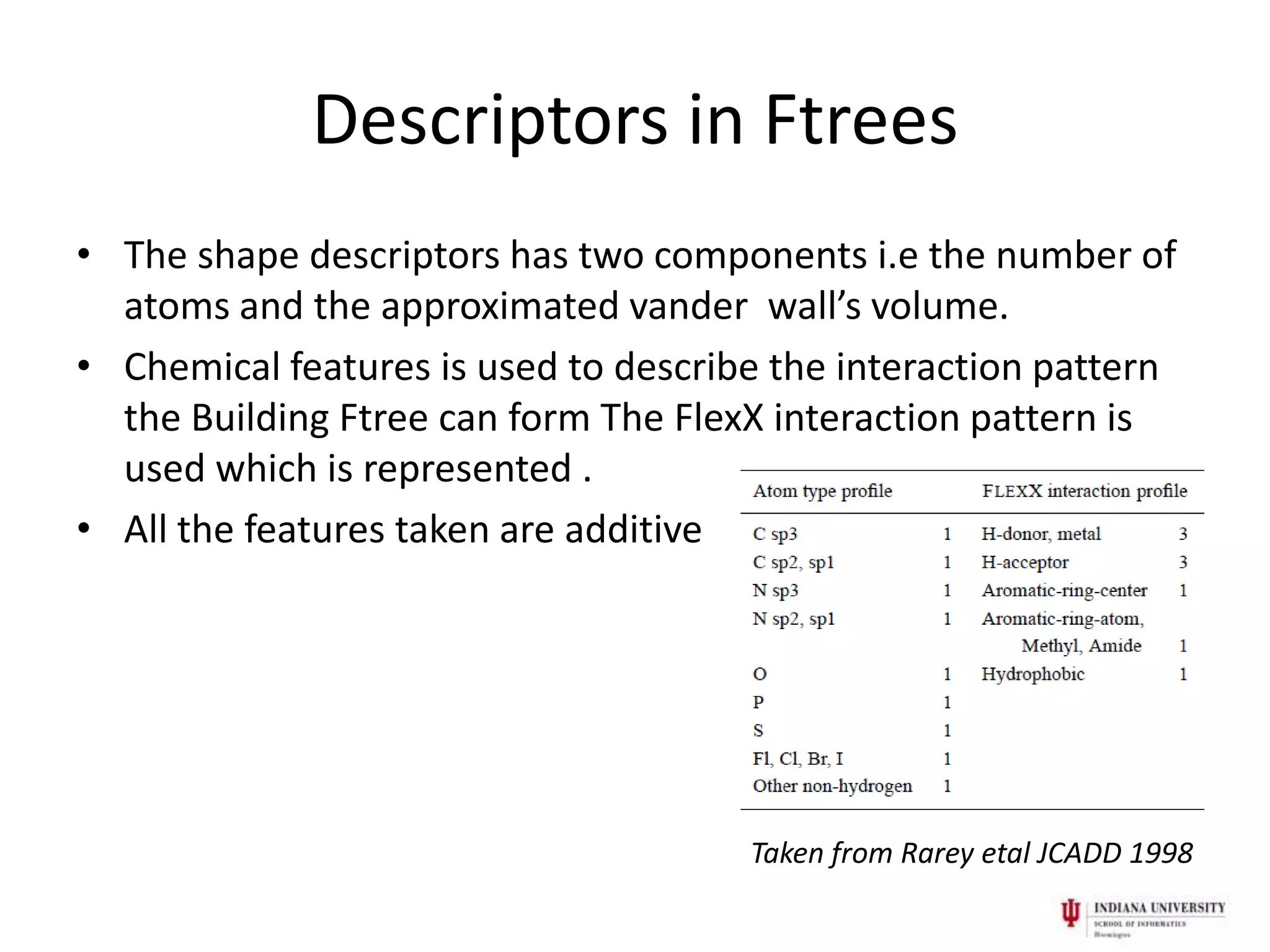
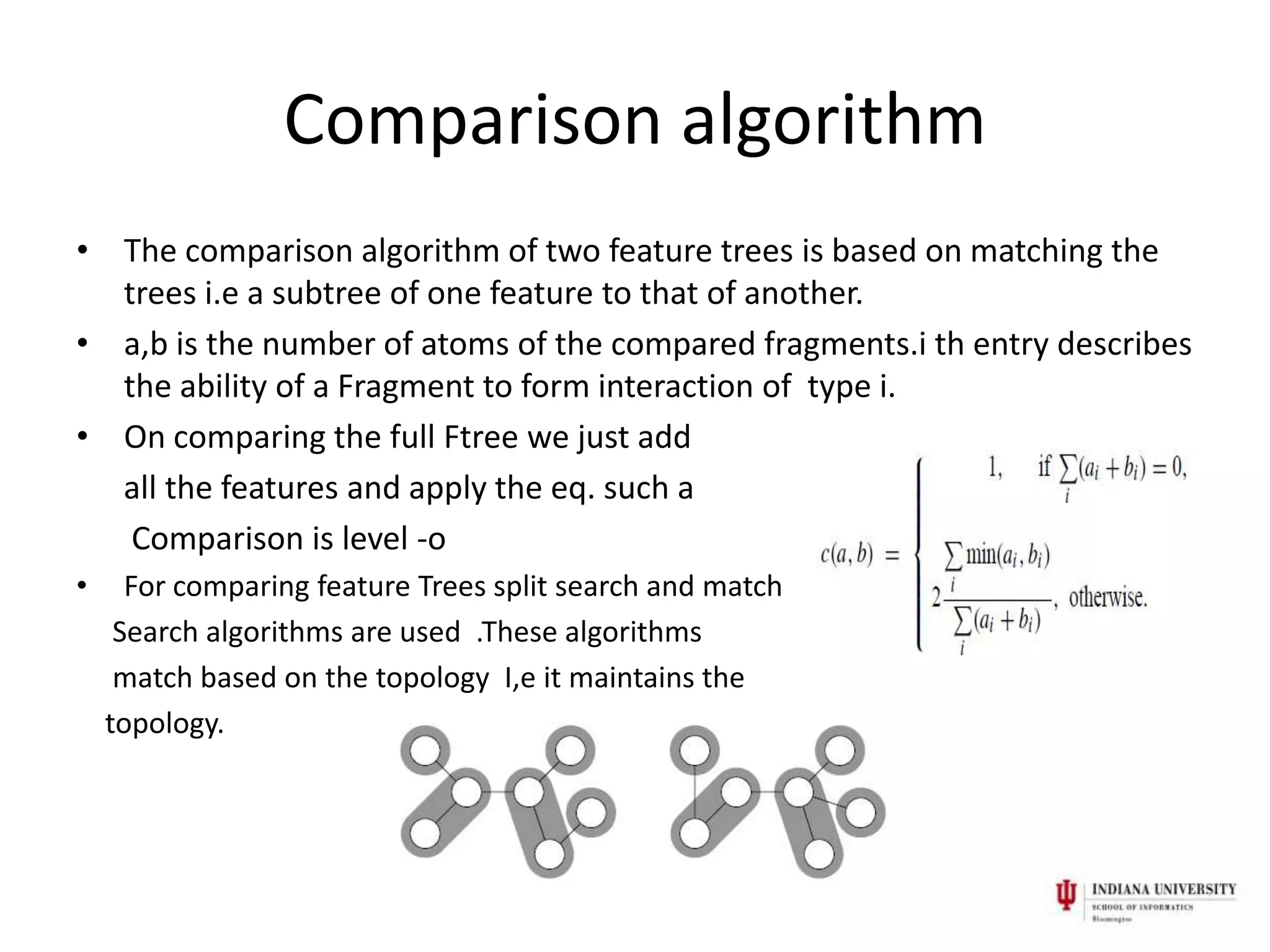
3) Ftrees describe molecular fragments as nodes labeled with shape and chemical descriptors. Molecules are compared by matching subtrees using topology-preserving search algorithms. This allows identification of actives from different chemical scaffolds.