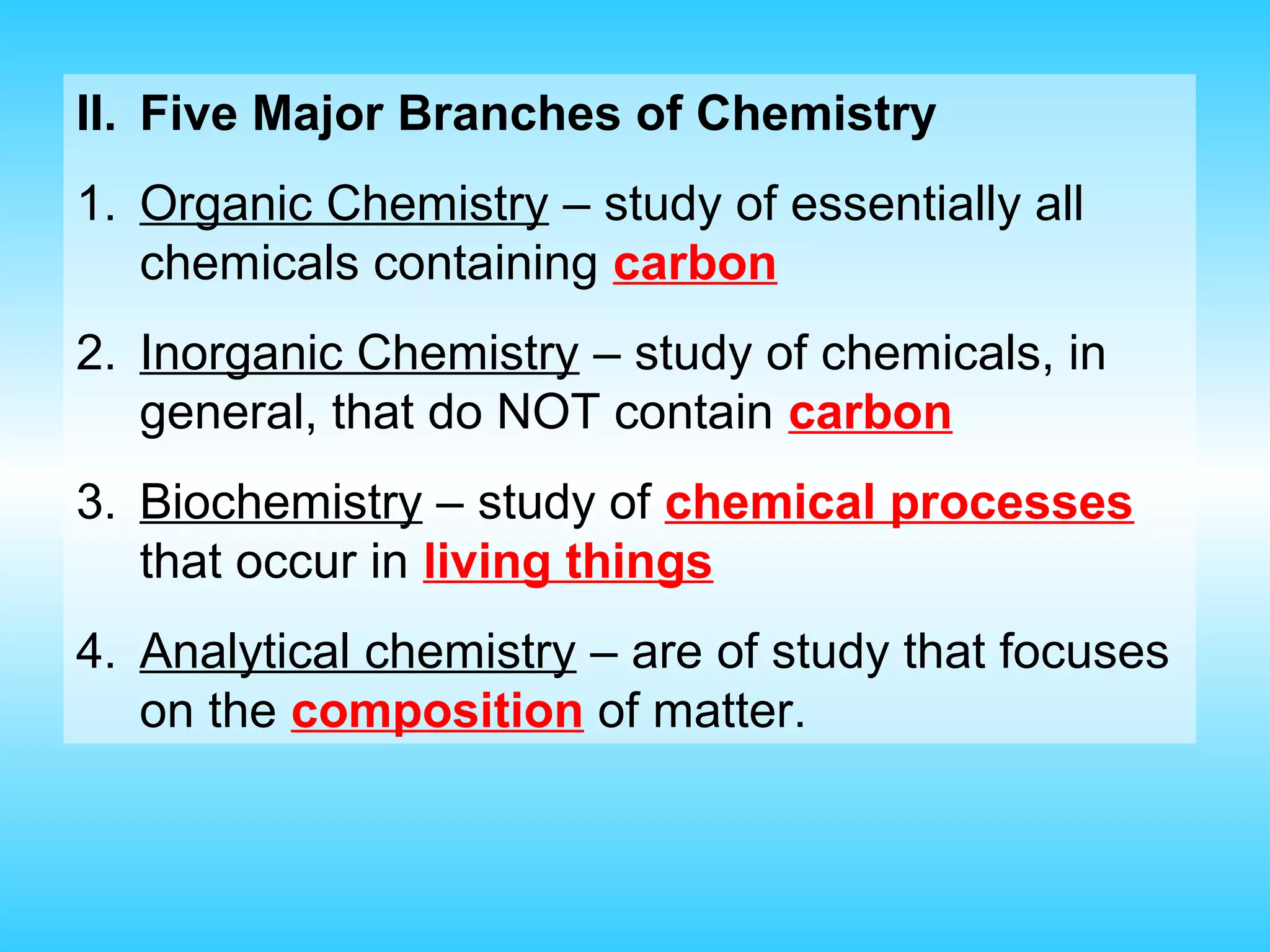
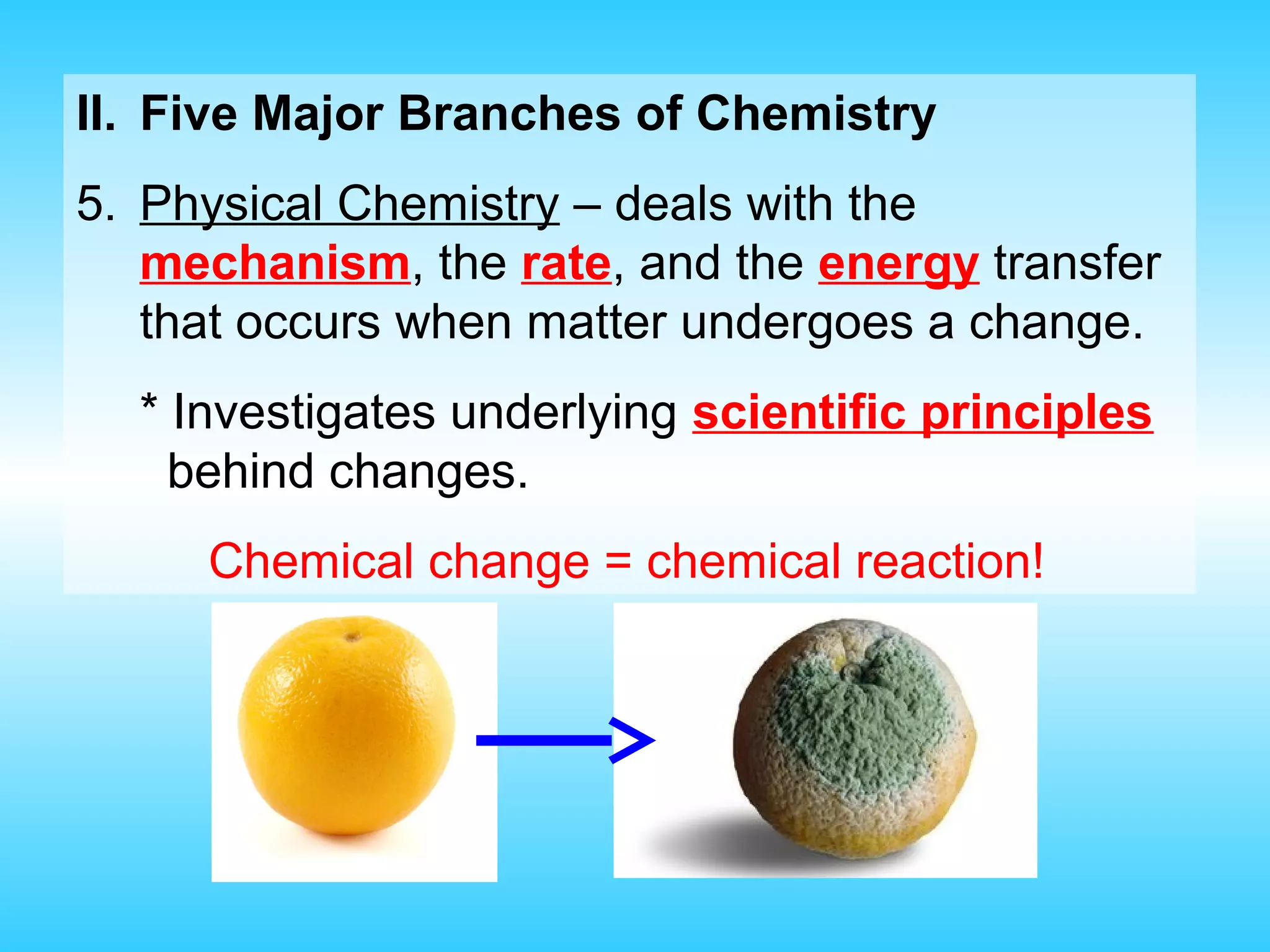
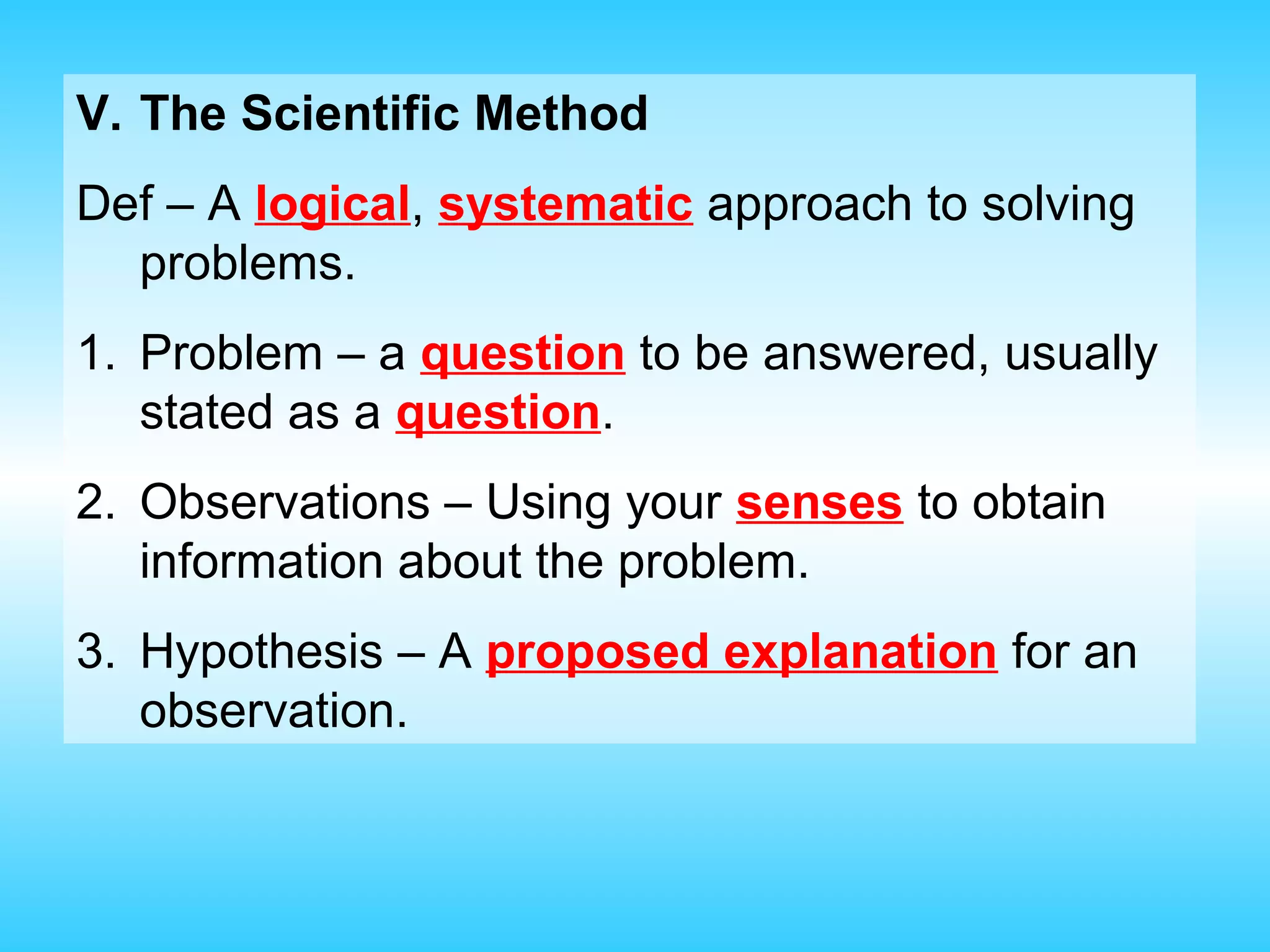
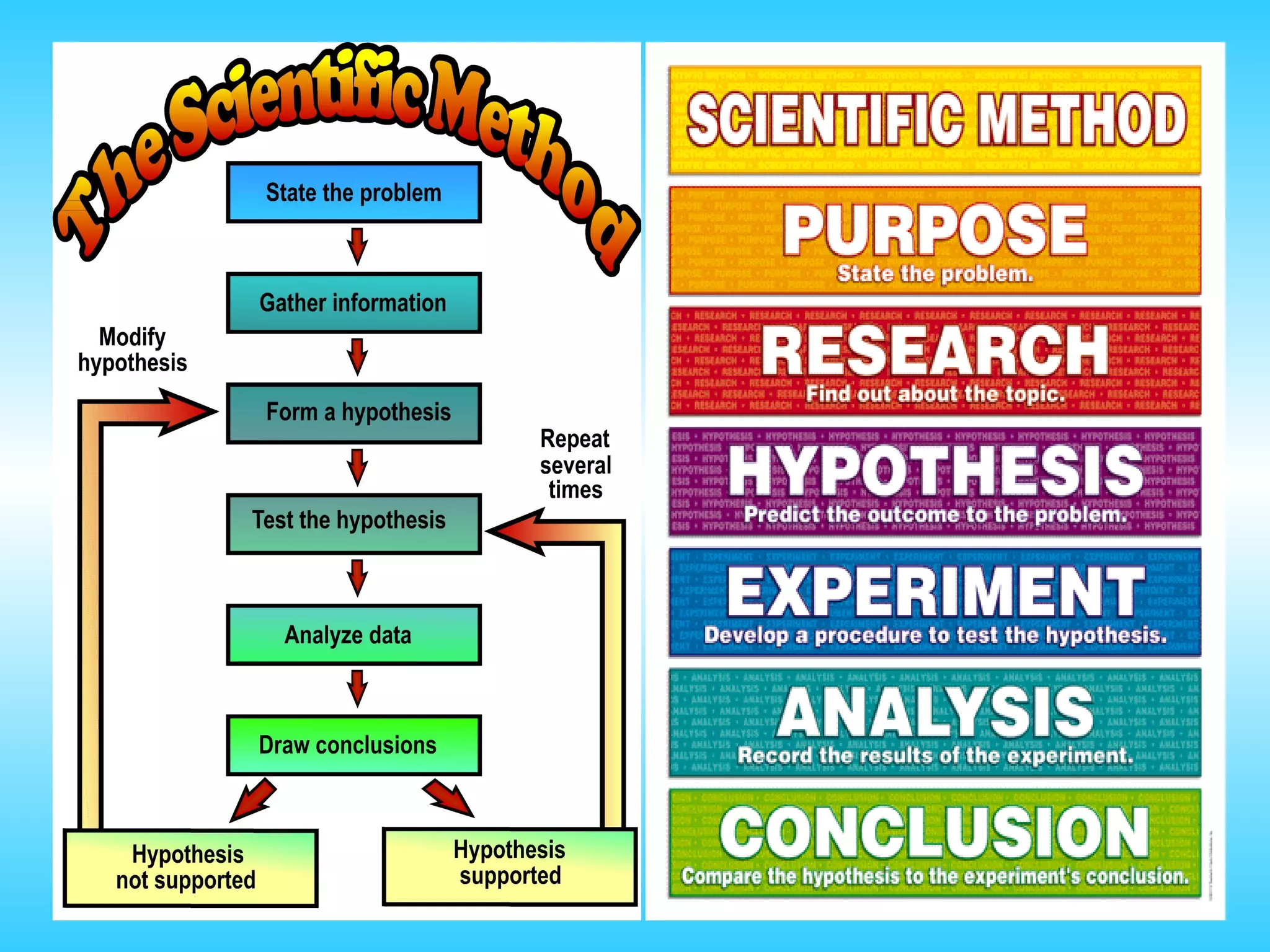
Chapter 1 provides an introduction to chemistry, defining it as the study of matter and its changes, with examples of matter and non-matter. It outlines five major branches of chemistry—organic, inorganic, biochemistry, analytical, and physical—and differentiates between pure and applied chemistry. Additionally, the chapter emphasizes the importance of chemistry in various fields such as agriculture, medicine, and environmental science, and introduces the scientific method as a systematic approach to problem-solving.