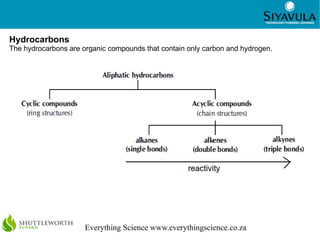
The document discusses organic chemistry and organic molecules. It defines organic molecules as those containing carbon and notes that all living things contain organic compounds. It describes the unique bonding properties of carbon that allow it to form many complex structures found in organic compounds. Finally, it discusses several classes of organic compounds like hydrocarbons, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and their properties and reactions.