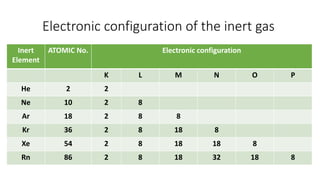
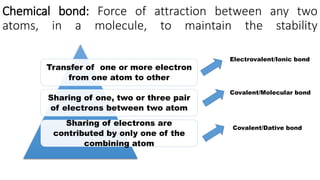
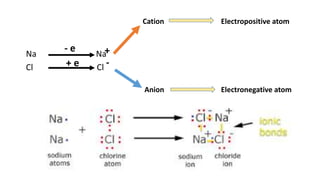
1) Ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred from one atom to another, giving the atoms opposite charges and forming ions.
2) The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged cation, while the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged anion.
3) Ionic bond formation requires one atom to have a low ionization potential and the other a high electron affinity, so there is an overall decrease in energy when electrons are transferred.