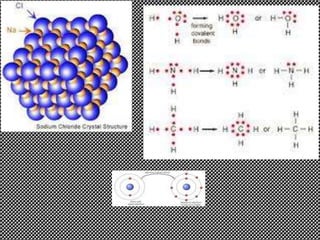
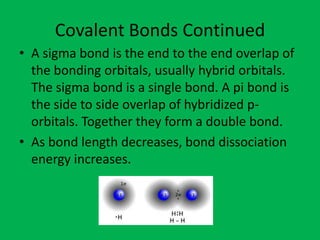
Ionic bonds form between oppositely charged ions through electrostatic attraction. The strength of ionic bonds increases with greater charge separation, resulting in higher melting points. Ionic solids do not conduct electricity. Covalent bonds form when atoms share pairs of electrons. Ionic and covalent bonding allow for the formation of stable chemical substances containing two or more atoms.