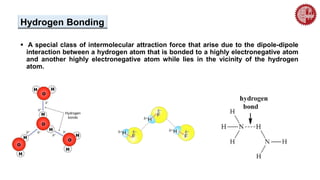
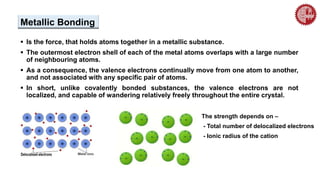
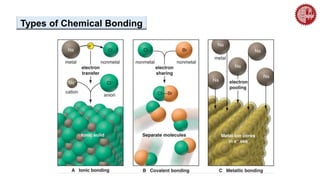
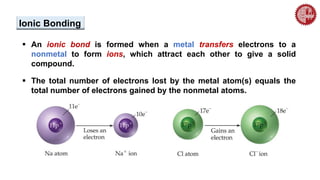
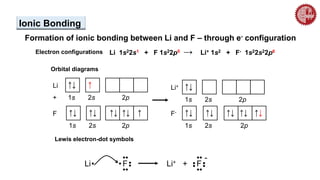
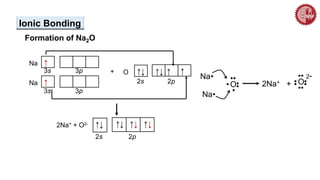
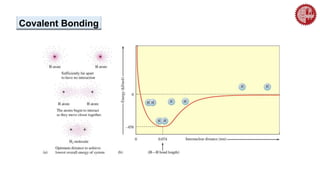
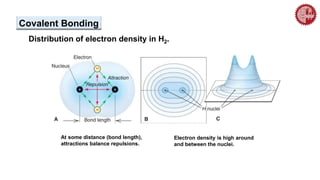
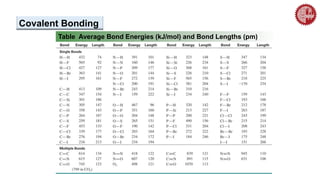
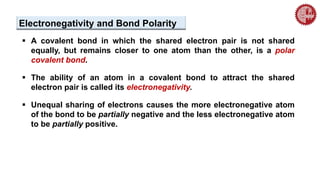
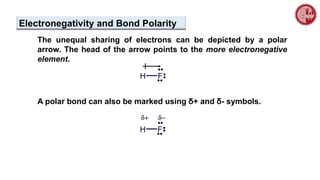
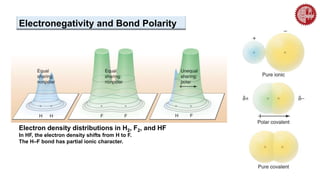
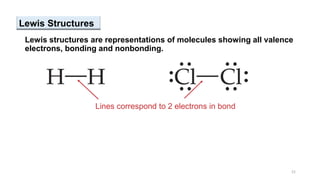
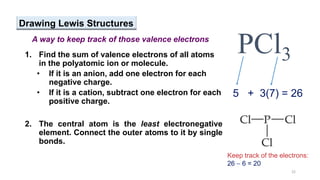
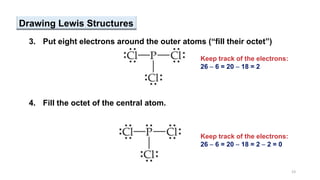
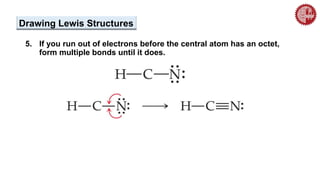
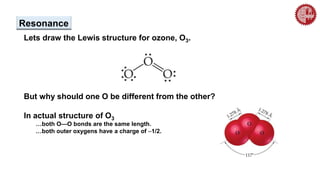
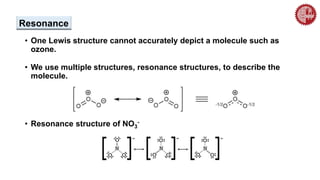
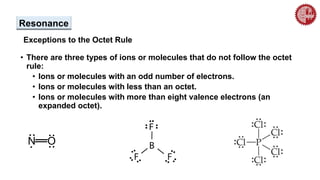
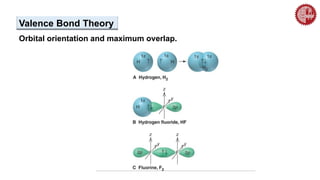
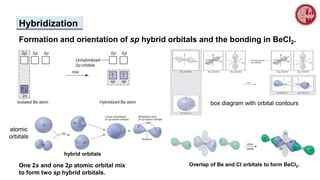
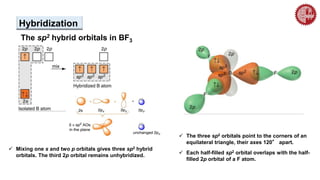
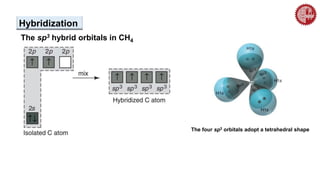
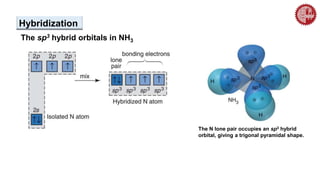
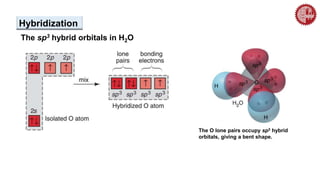
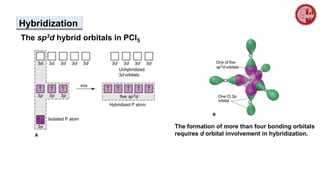
This document provides an overview of chemical bonding. It defines a chemical bond as a force of attraction between atoms or ions that holds atoms together in molecules or compounds. Atoms form bonds to achieve stable electron configurations. There are three main types of bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic. Ionic bonds form through the transfer of electrons between metals and nonmetals. Covalent bonds form through the sharing of electrons, usually between nonmetals. Metallic bonds involve the pooling of electrons between metal atoms. The document further explores bond formation and properties.











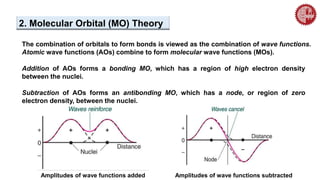
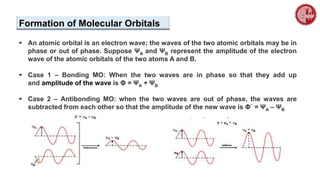
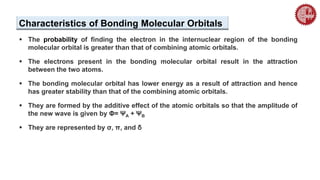
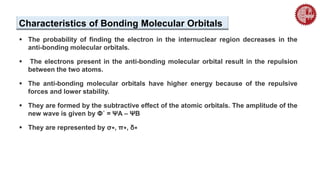

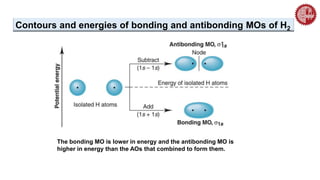
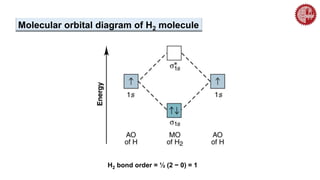
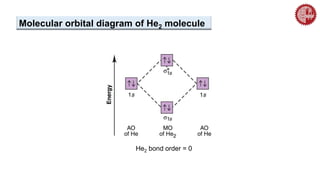
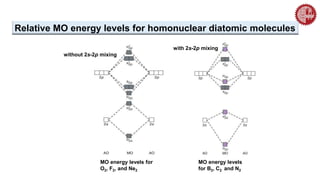
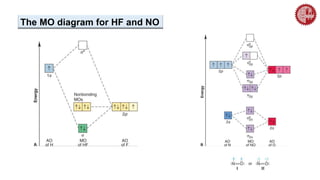
![ A MO diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and
number of electrons in each MO.
The MO diagram also shows the AOs from which each MO is formed.
Bond order is calculated as follows:
½[(no. of e– in bonding MO) – (no. of e– in antibonding MO)]
2. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalbonding-dr-220907052026-5154f9f5/85/Chemical-Bonding-Dr-Mahbub-pptx-53-320.jpg)