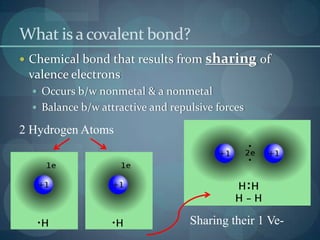
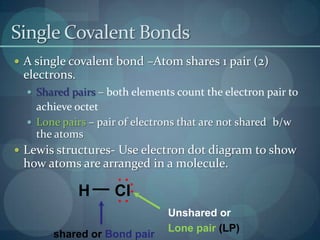
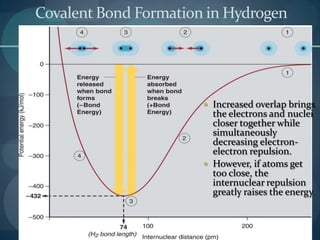
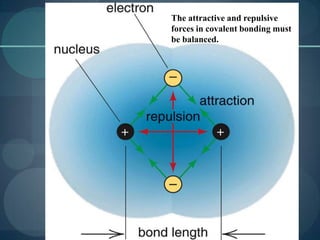
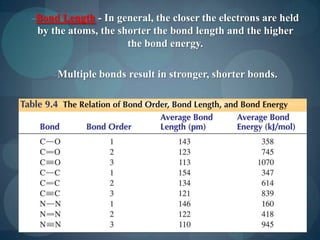
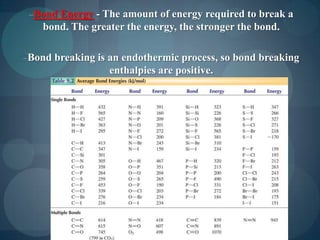
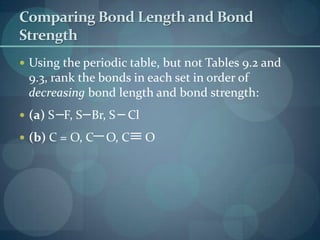
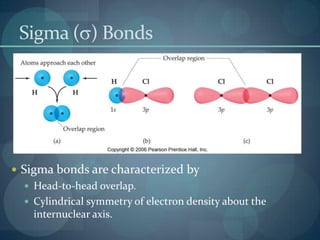
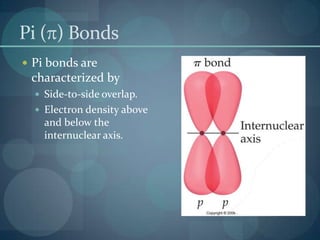
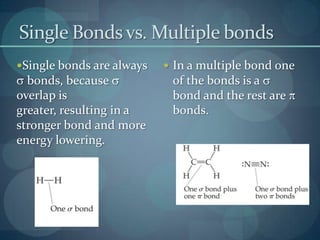
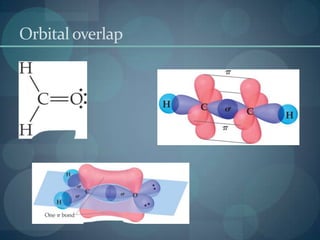
This document discusses different types of chemical bonds including ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and the factors that determine bond strength. It defines ionic bonds as electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions, and covalent bonds as the sharing of valence electrons between nonmetals. Bond length and bond energy are inversely related, with shorter, stronger bonds forming from increased orbital overlap and multiple bonds. Lewis structures are used to represent electron arrangements in molecules using dots or lines to indicate bonding and non-bonding electron pairs.