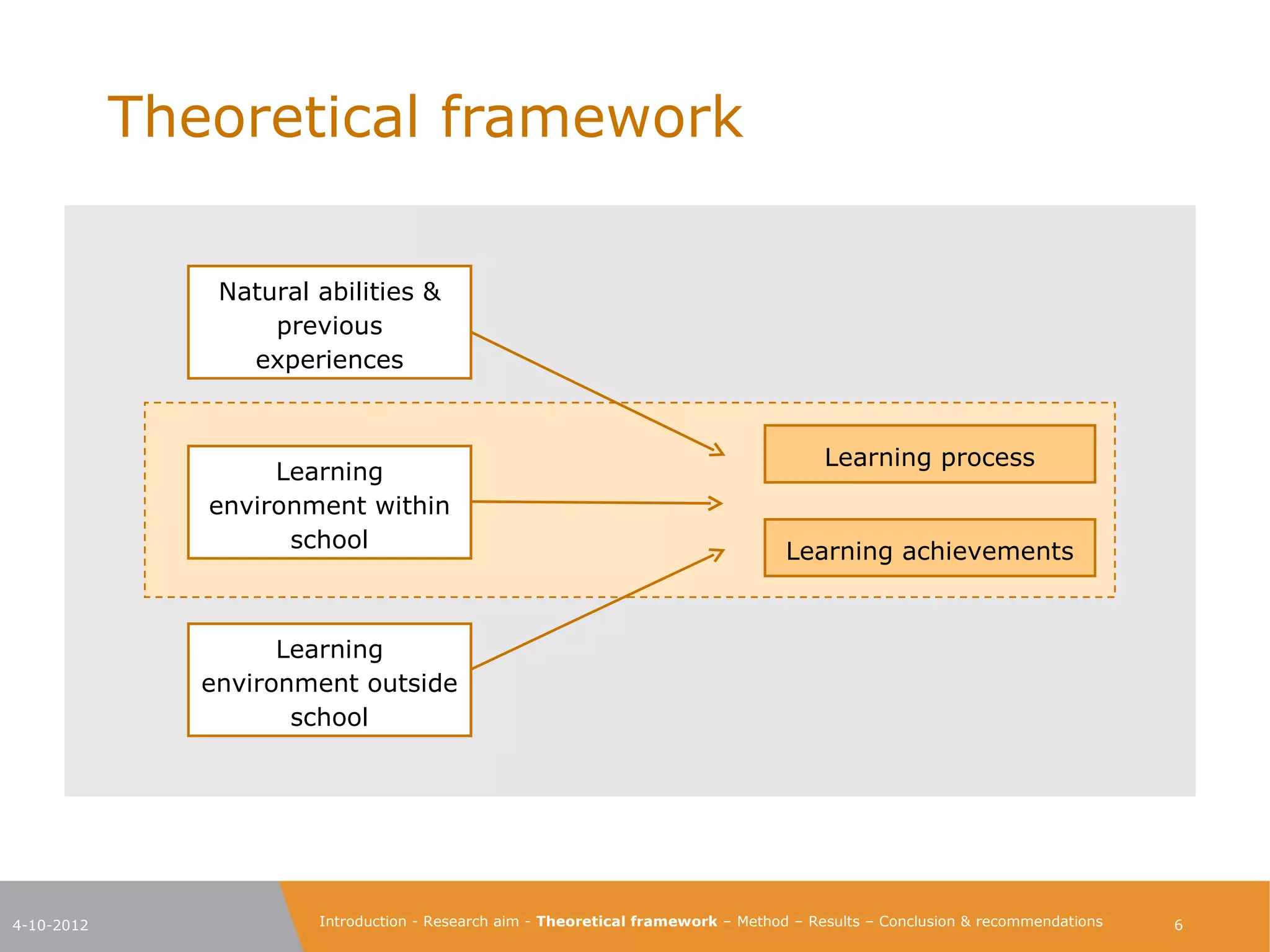
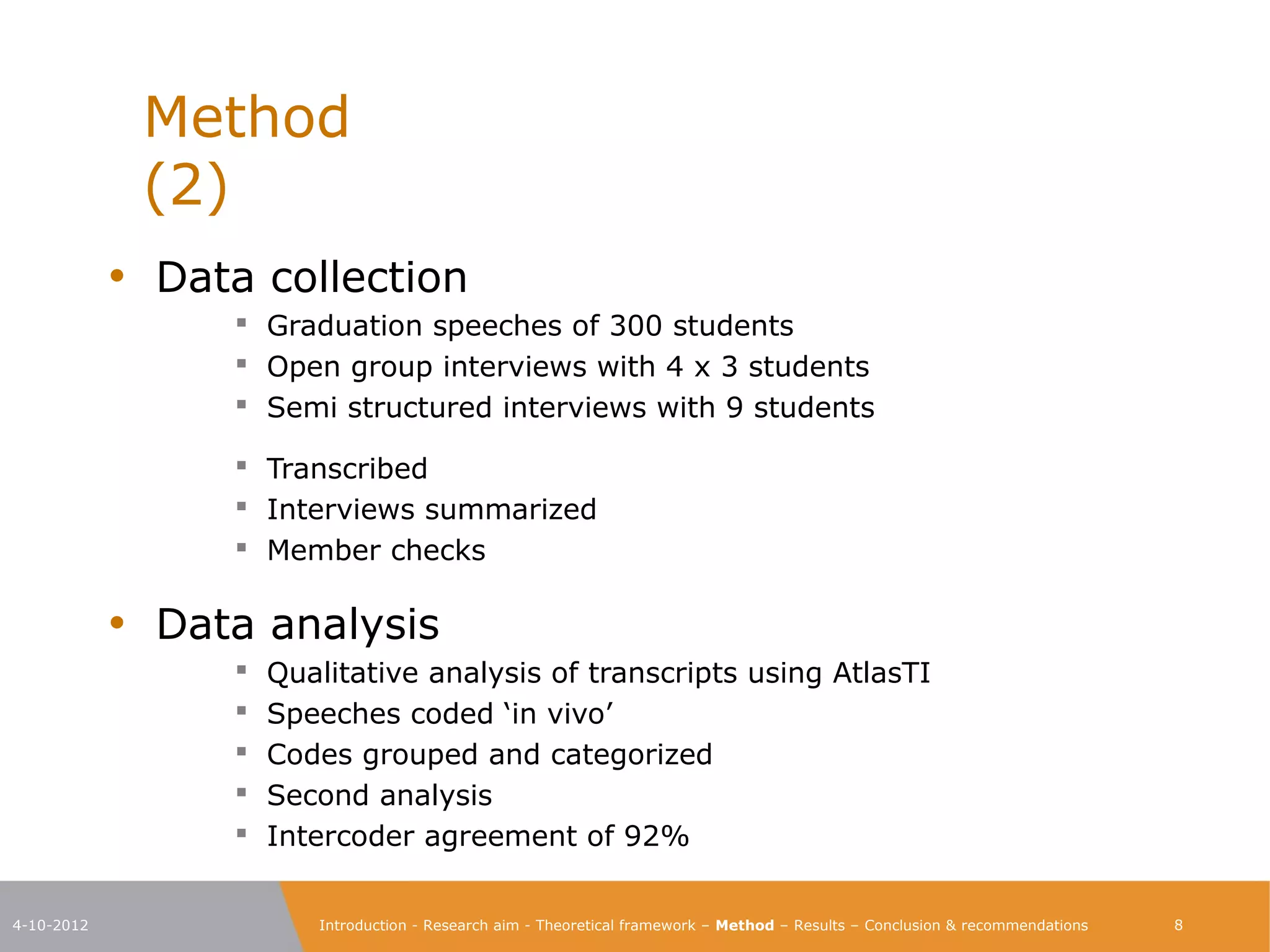
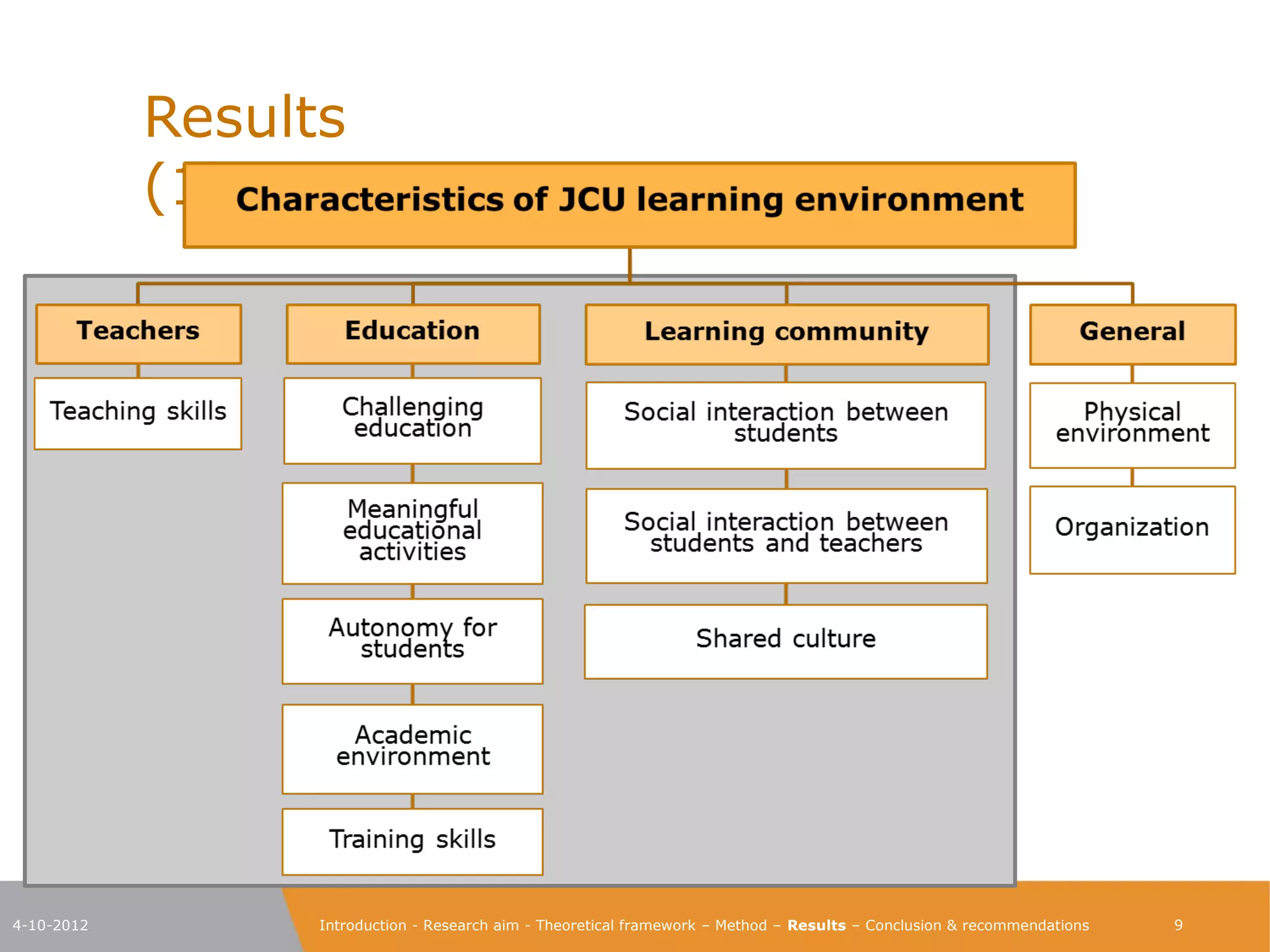
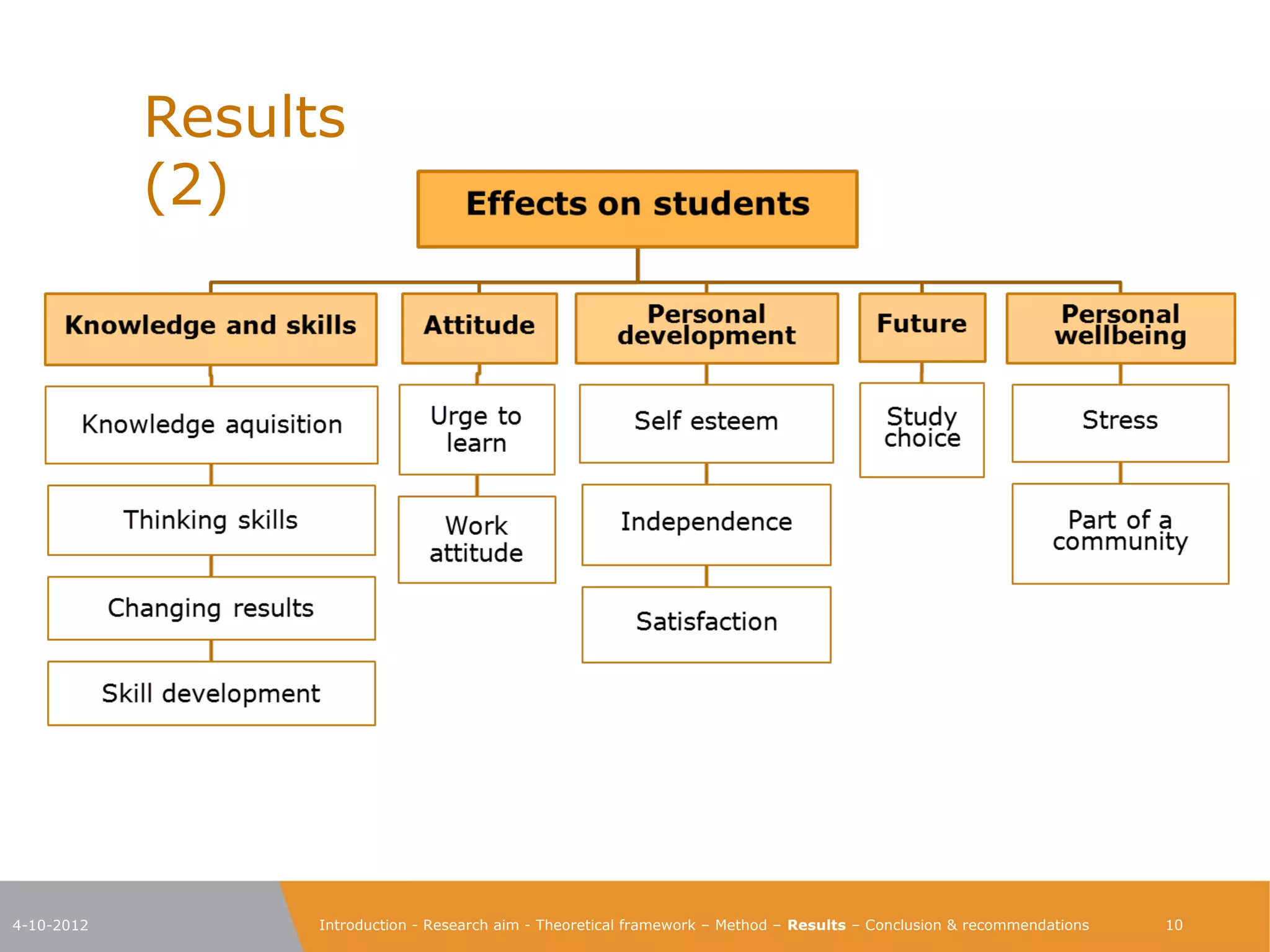
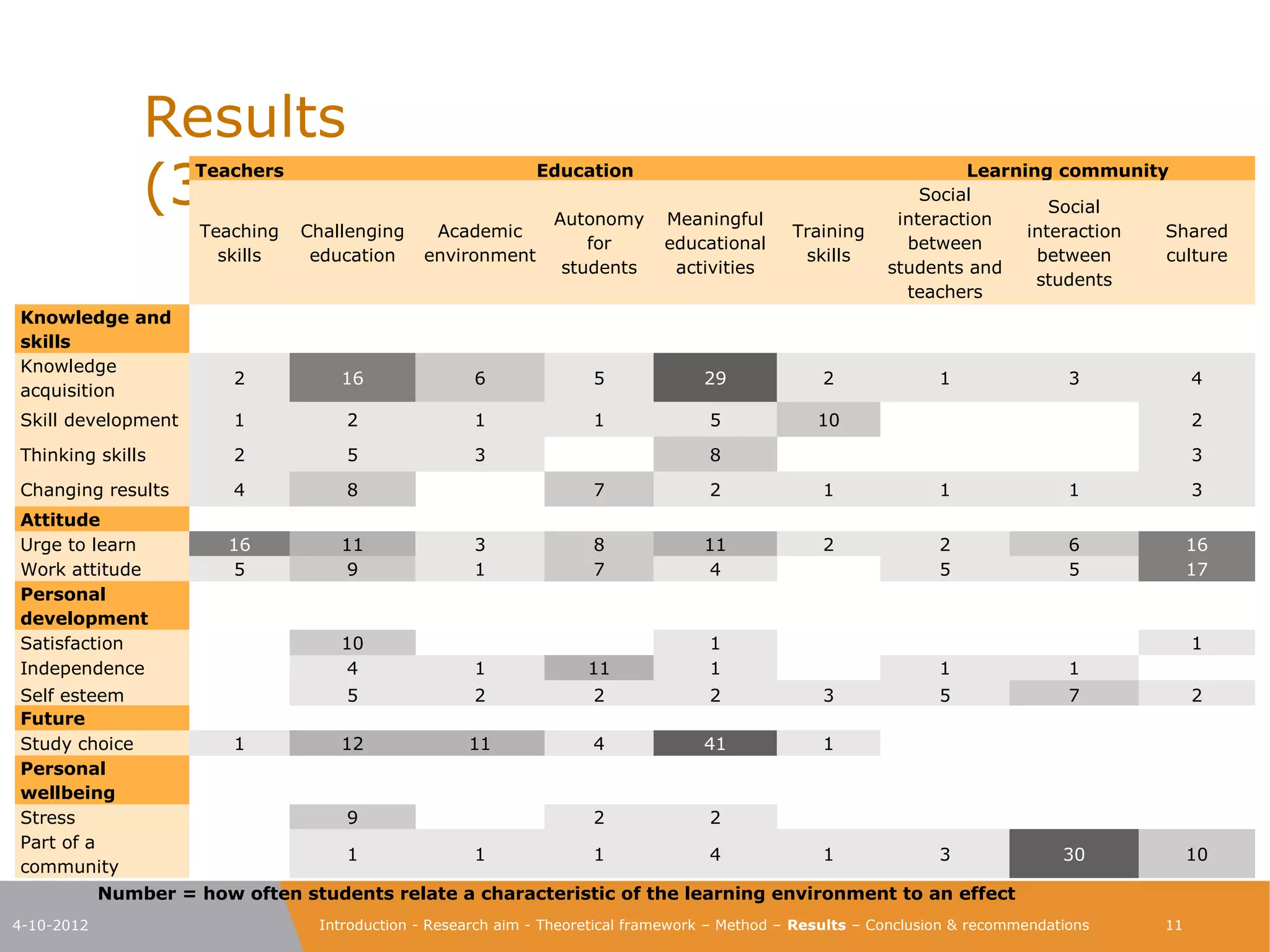
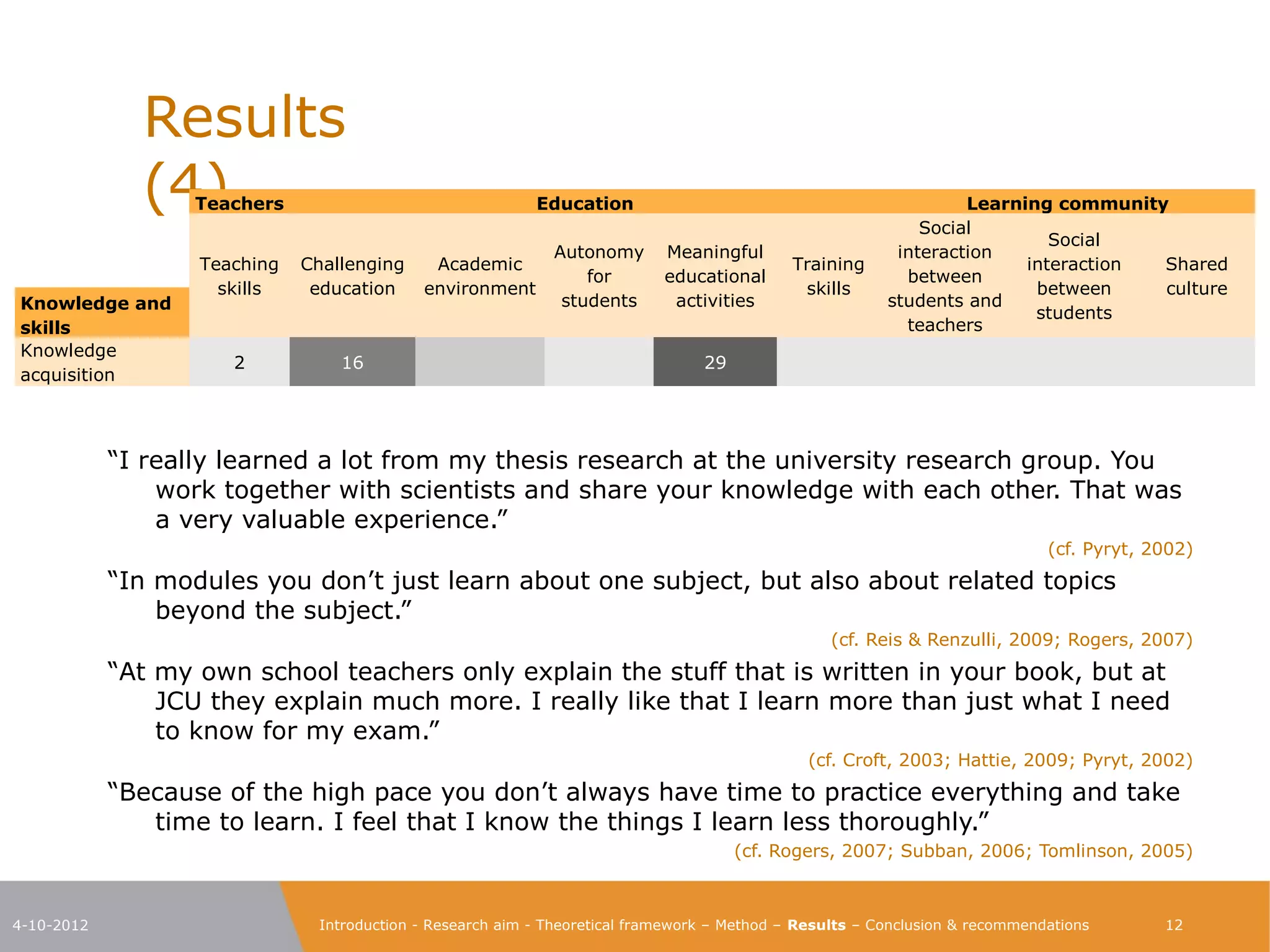
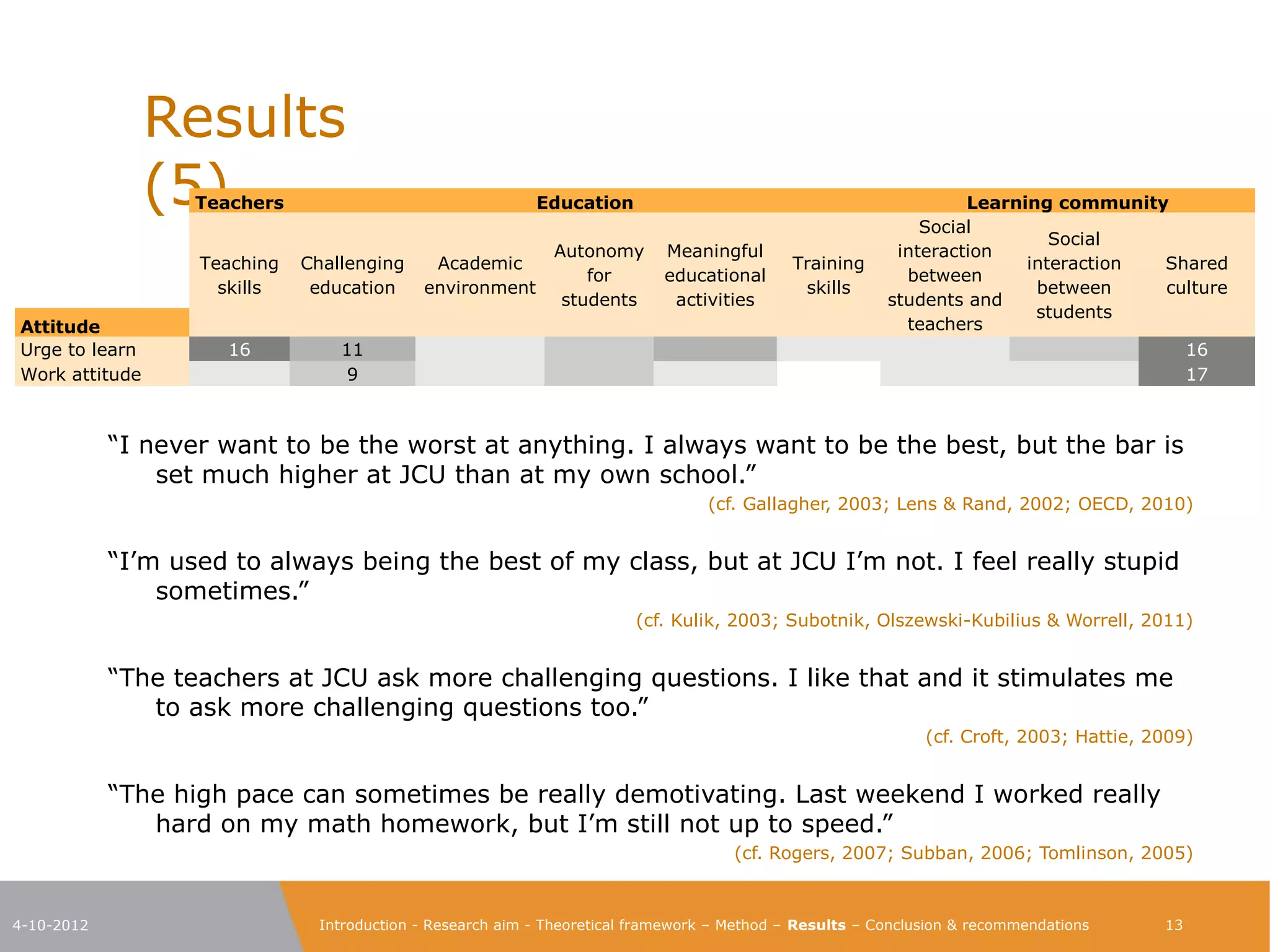
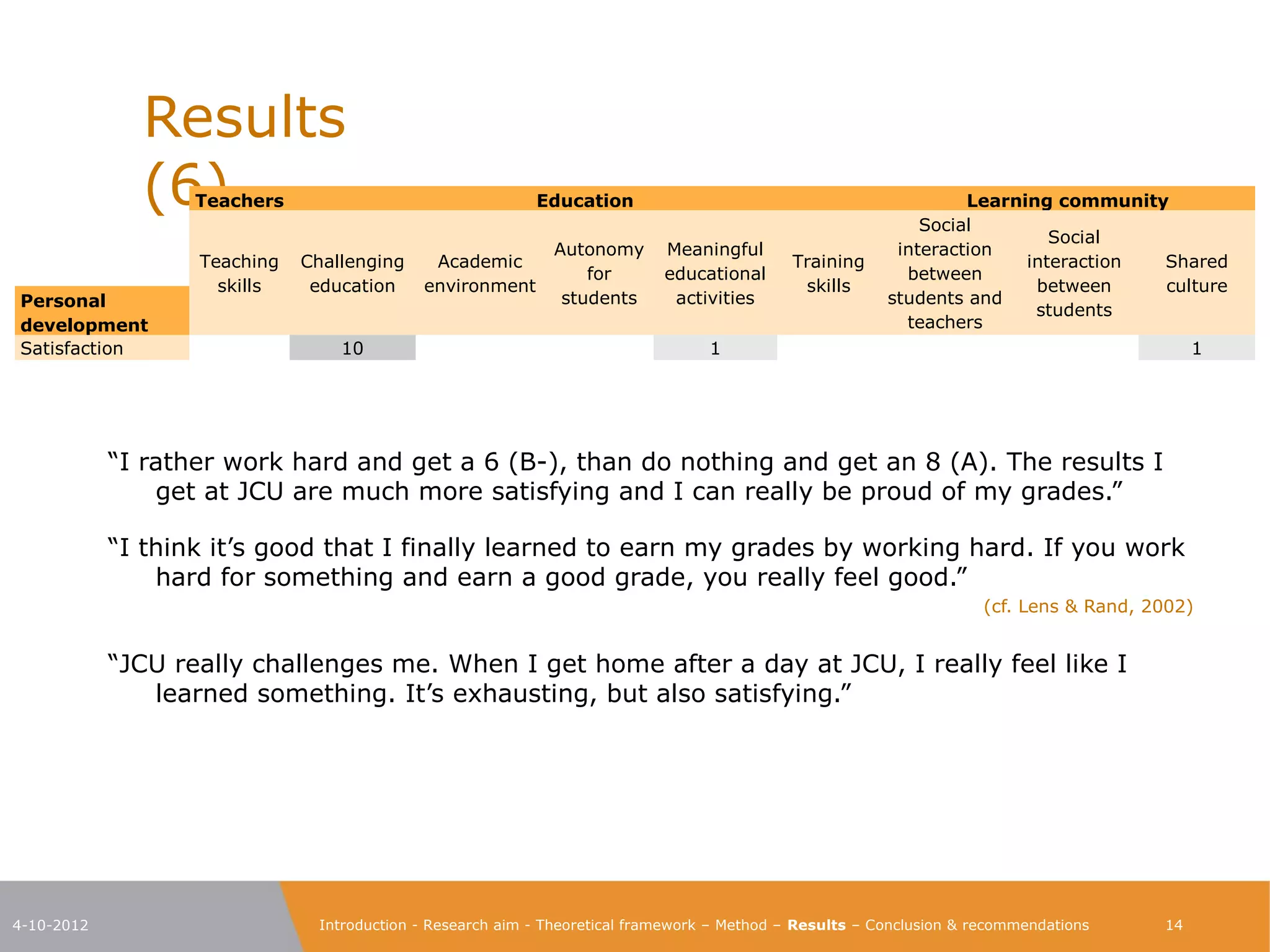
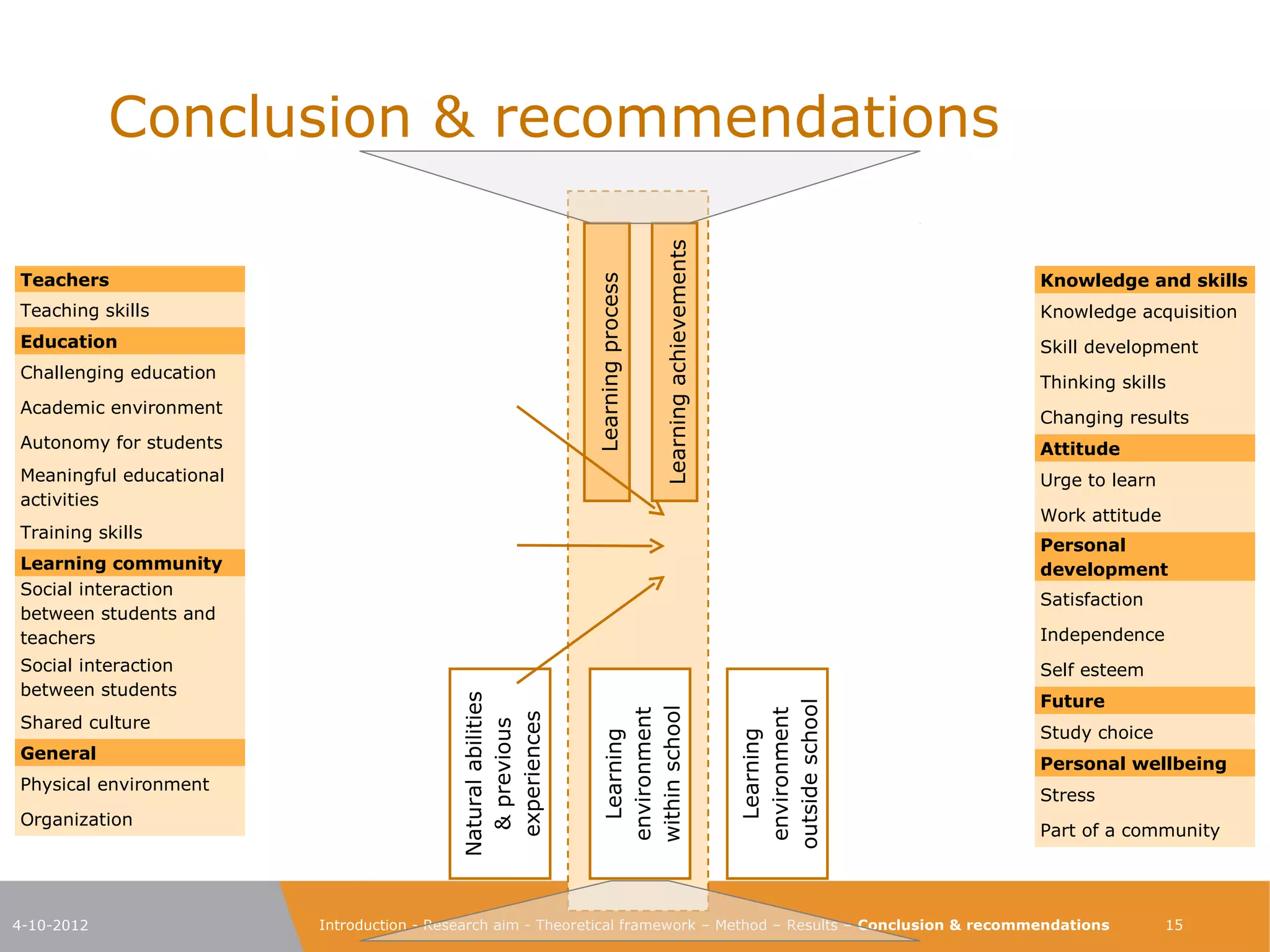
The document explores the characteristics of a challenging learning environment at Junior College Utrecht (JCU) and its impact on the learning processes and achievements of talented pre-university students. It details the research aim, methodology, and findings, emphasizing the necessity for tailored education that stimulates these students' capabilities. The results indicate that attributes such as a supportive learning community, interaction with knowledgeable teachers, and challenging academic tasks significantly enhance students' knowledge, skills, and personal development.