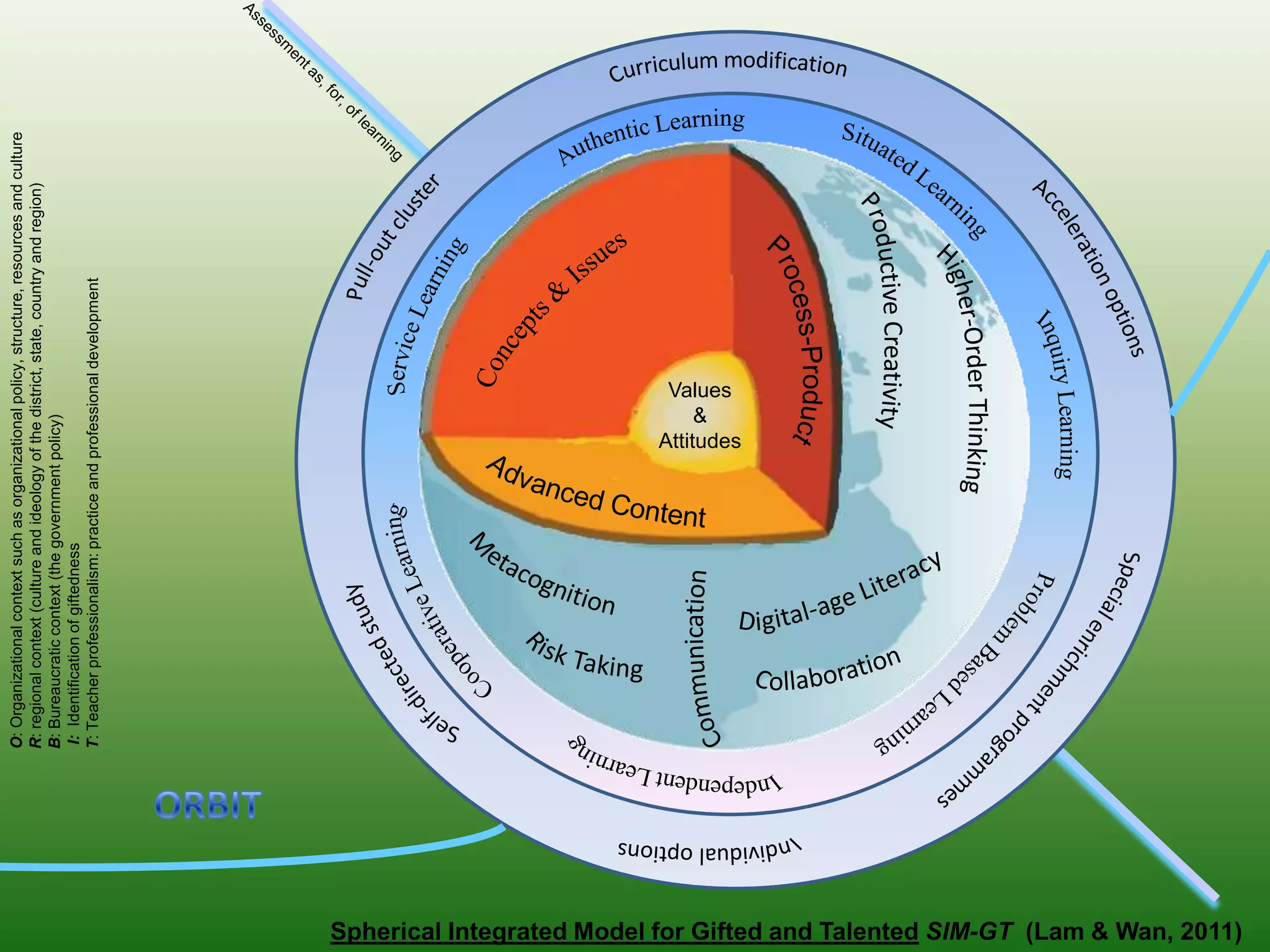
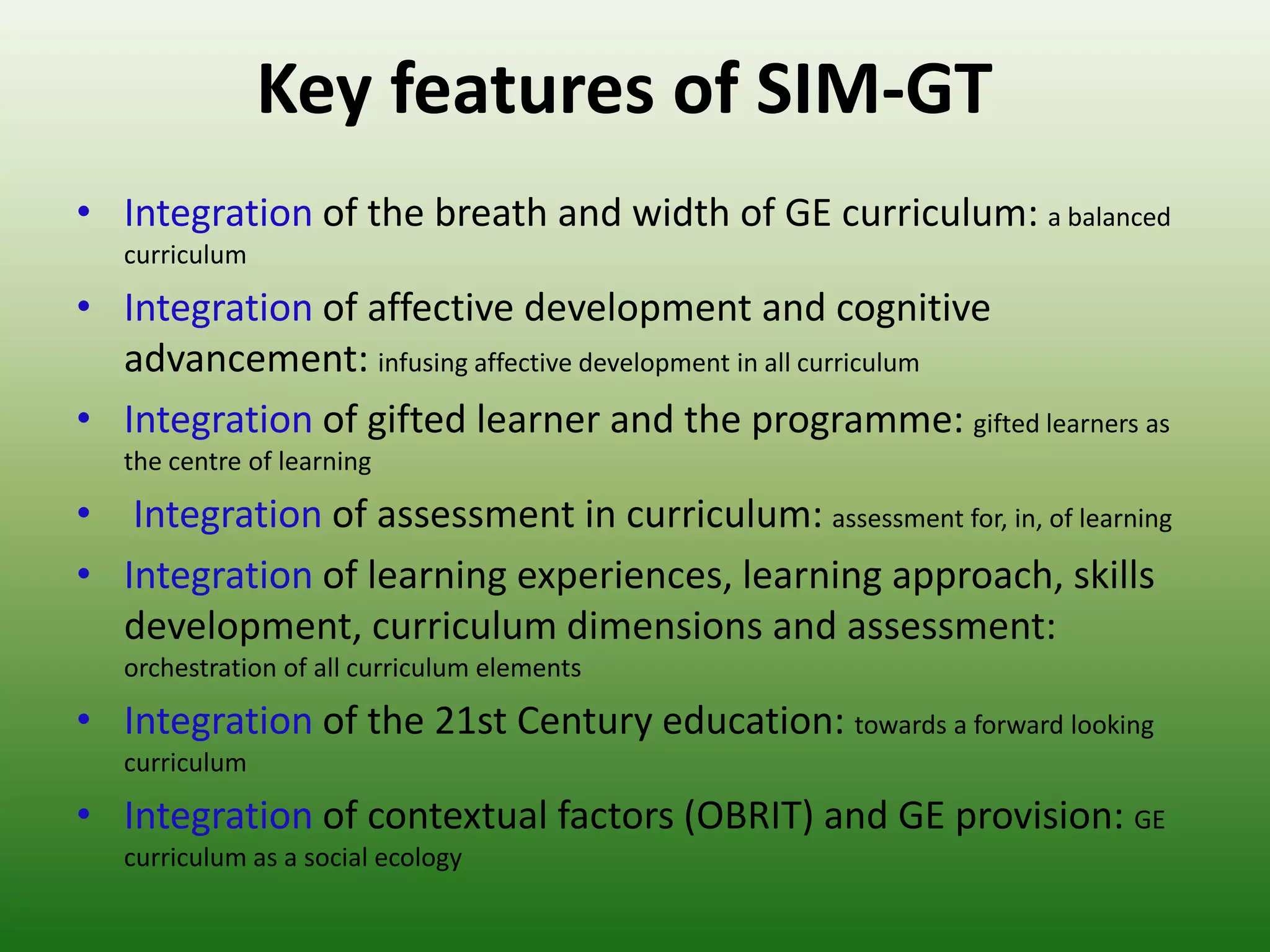
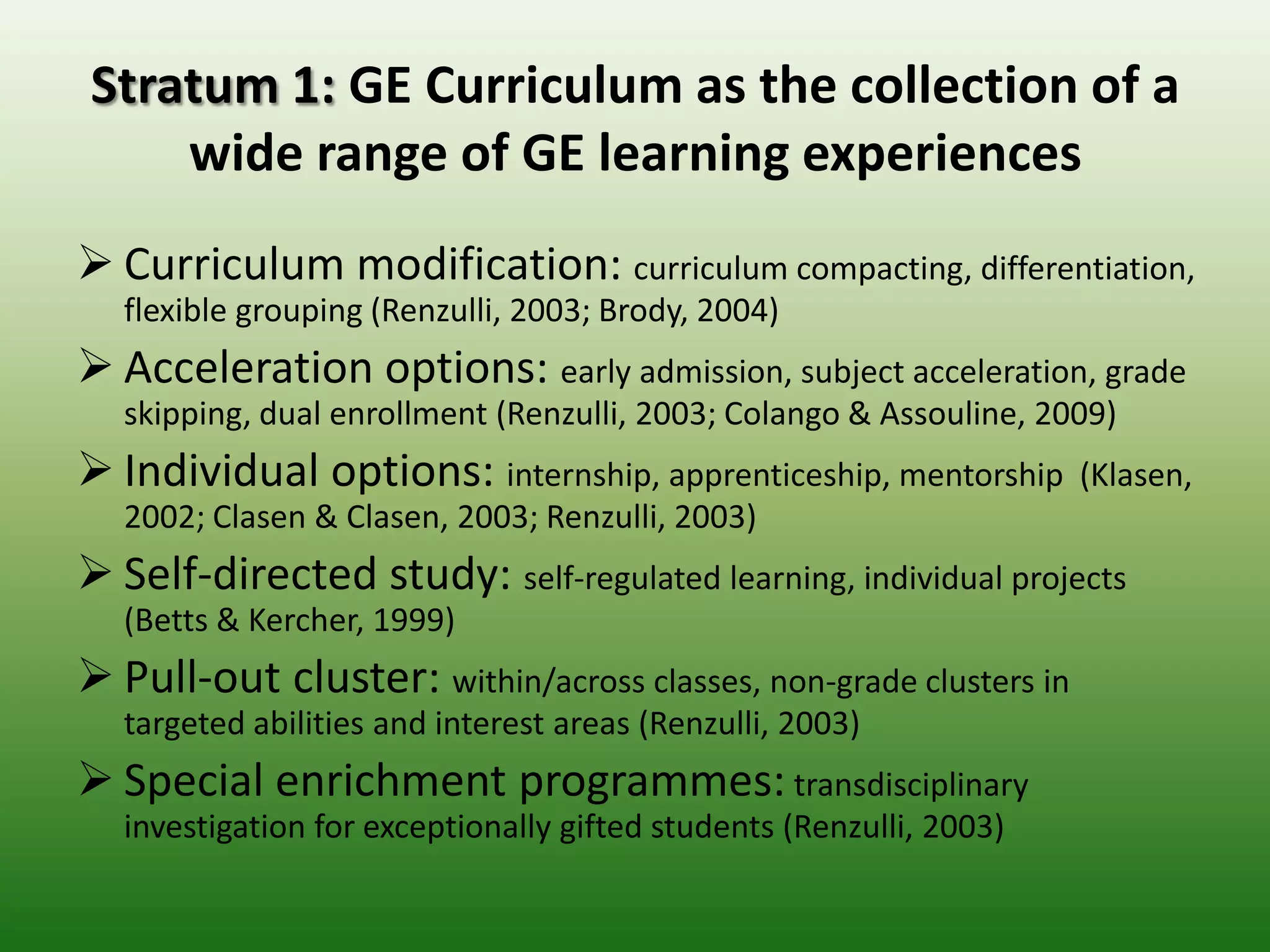
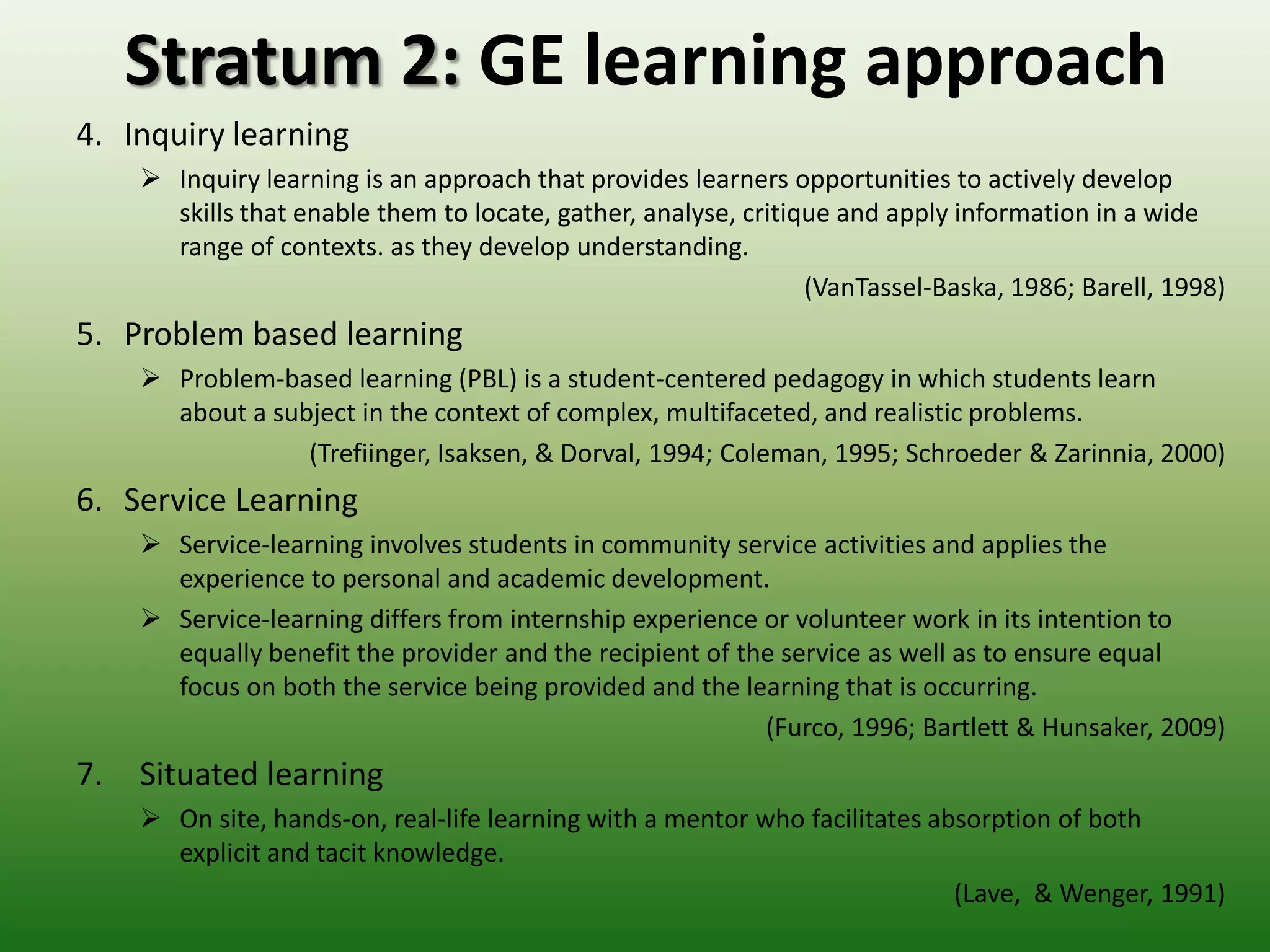
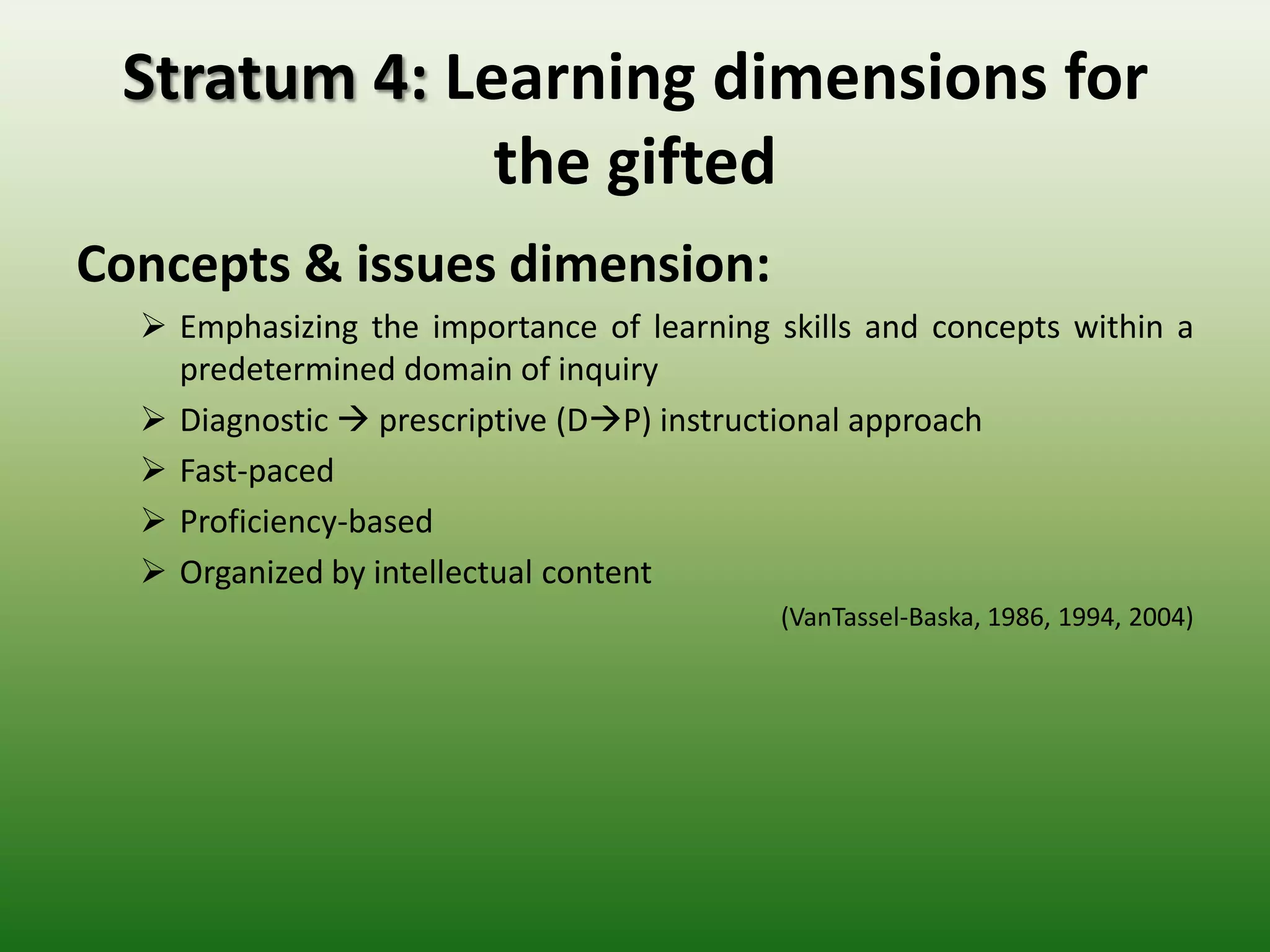
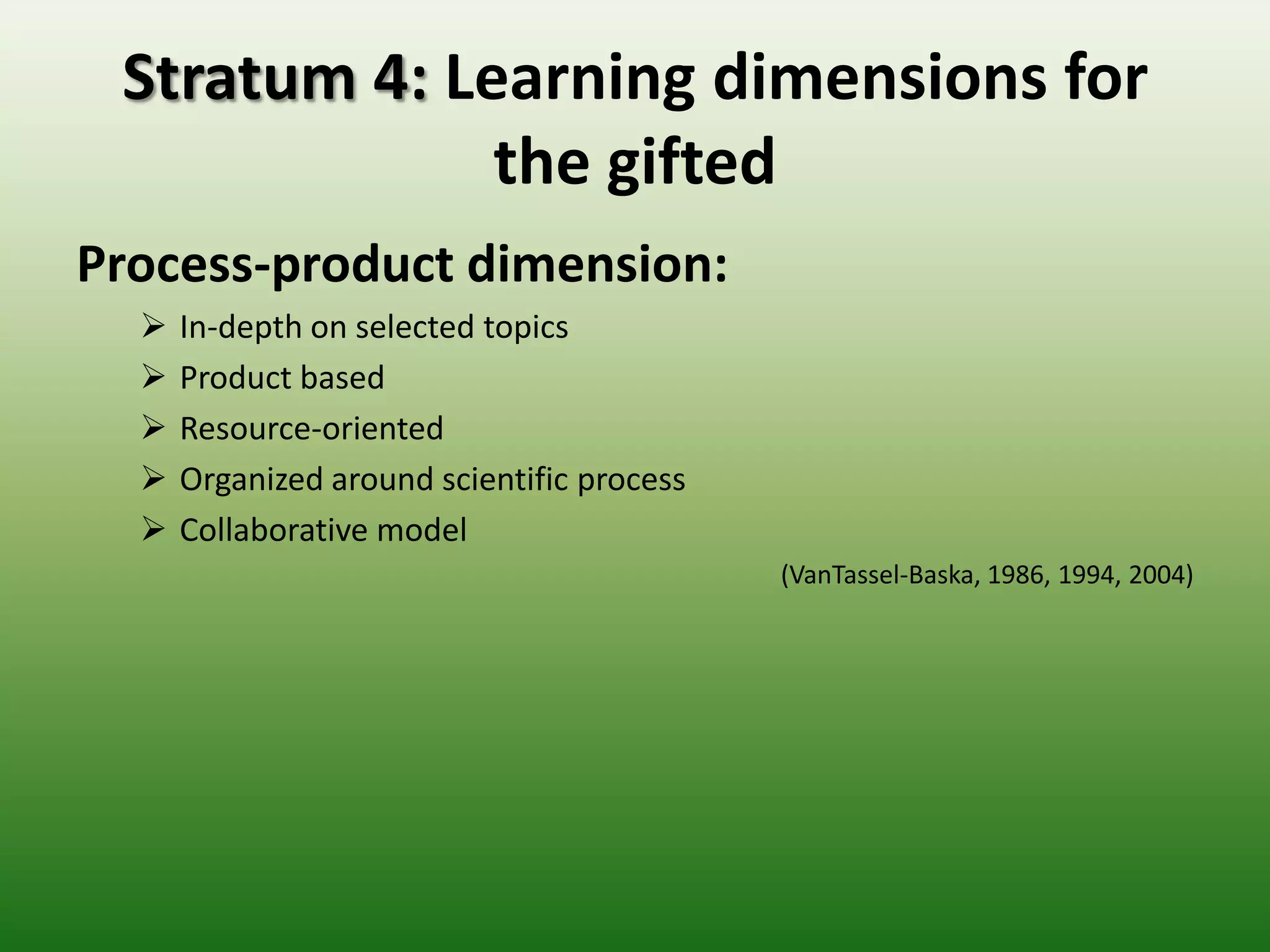
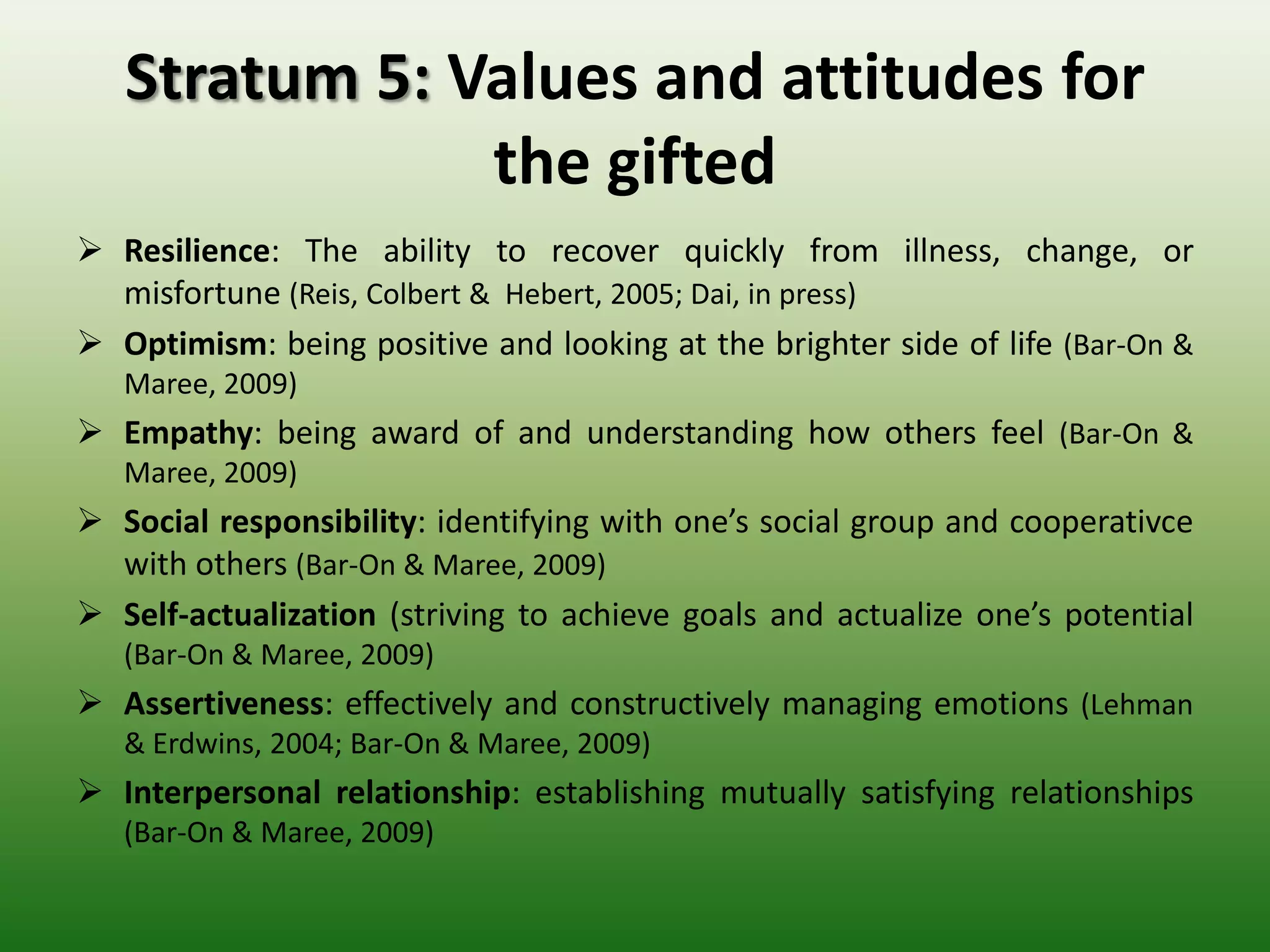
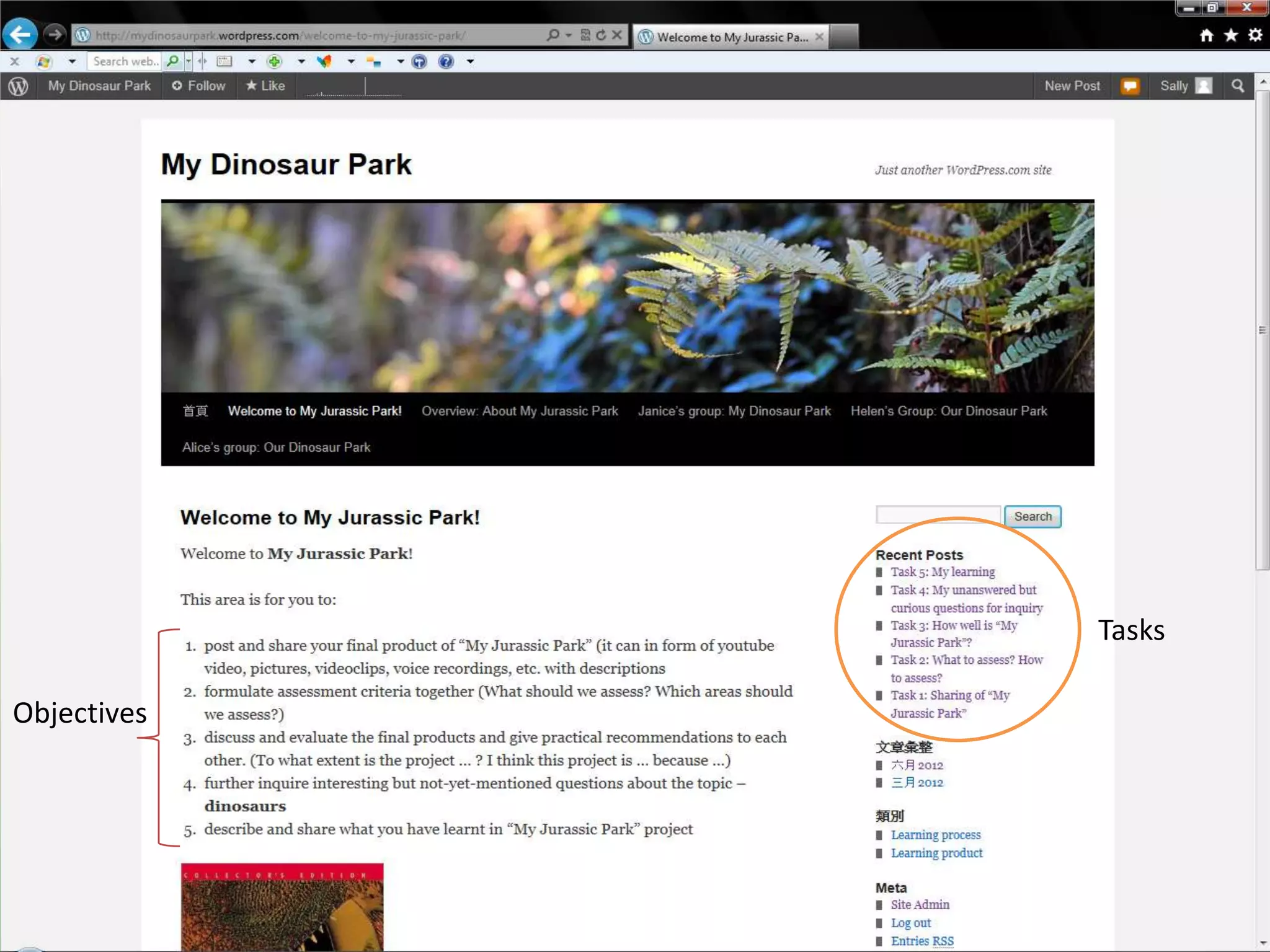
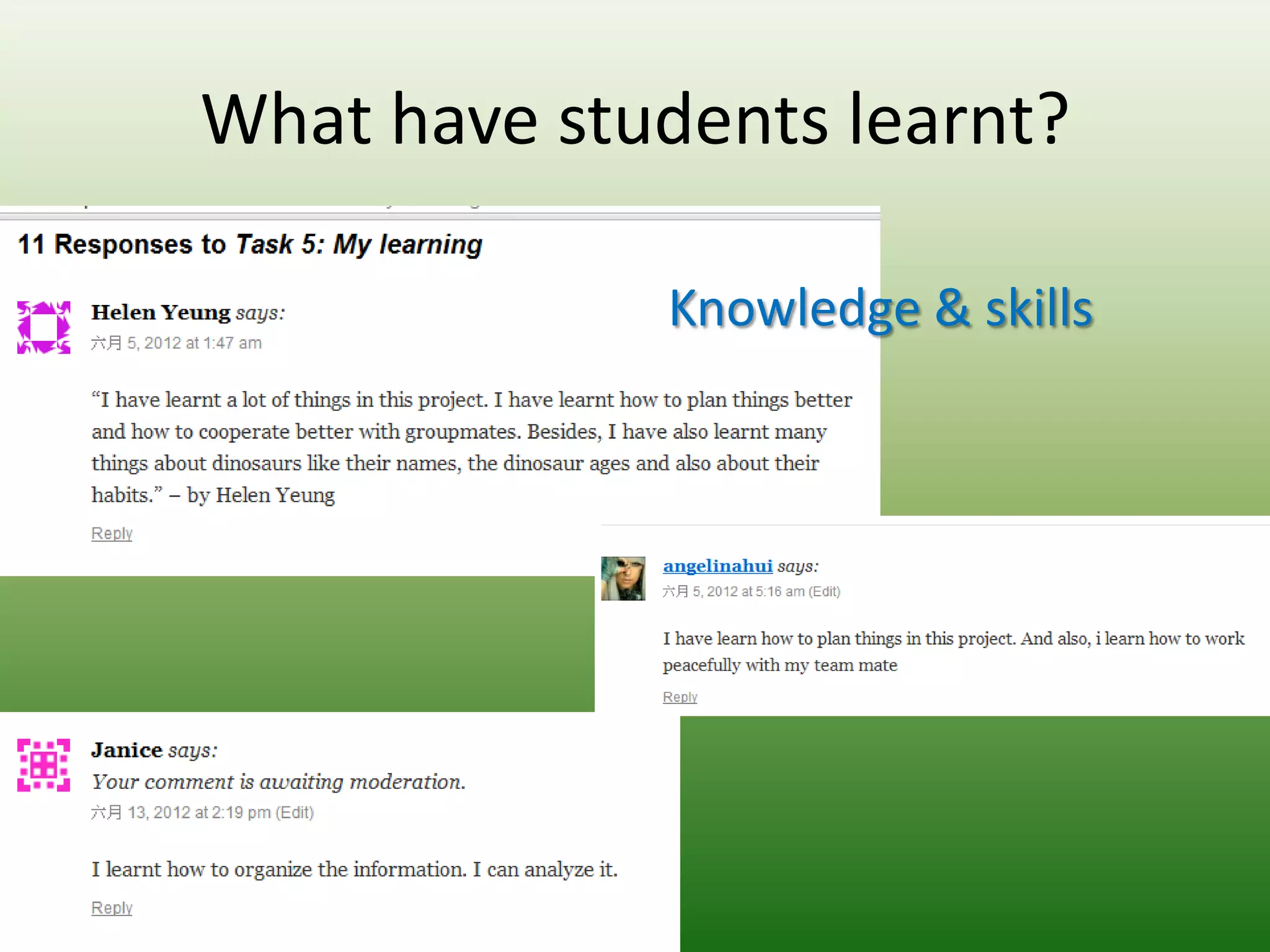
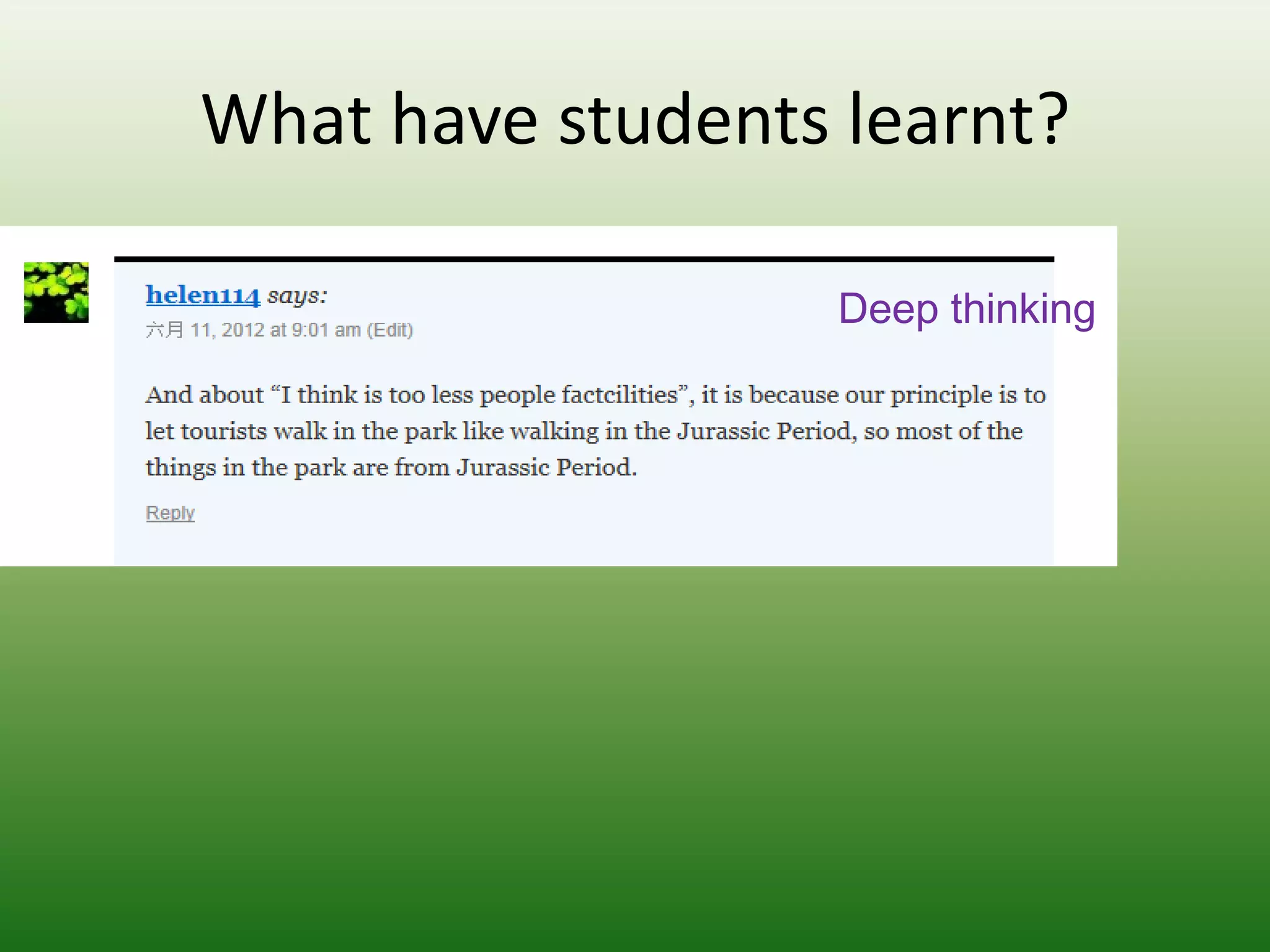
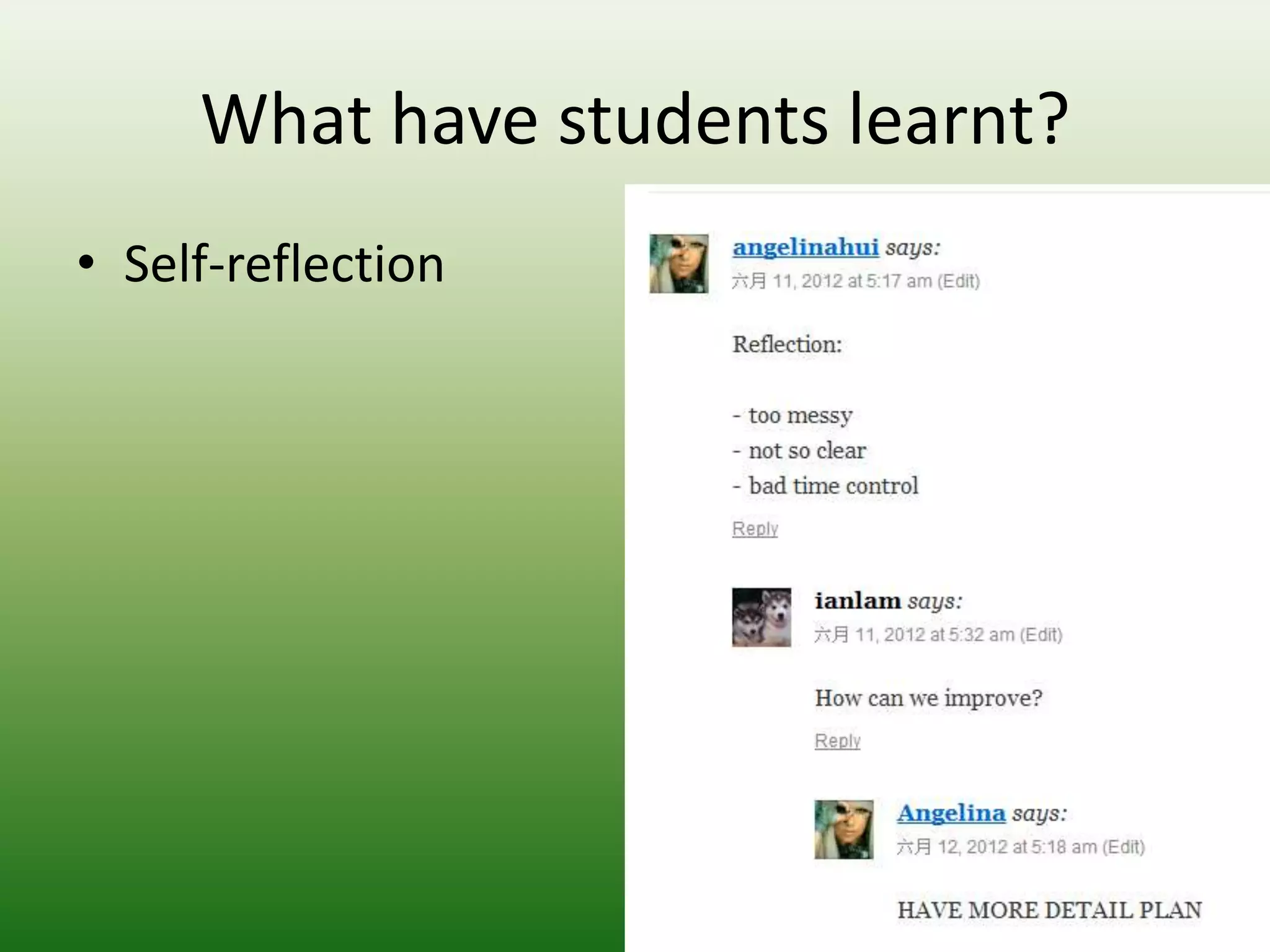
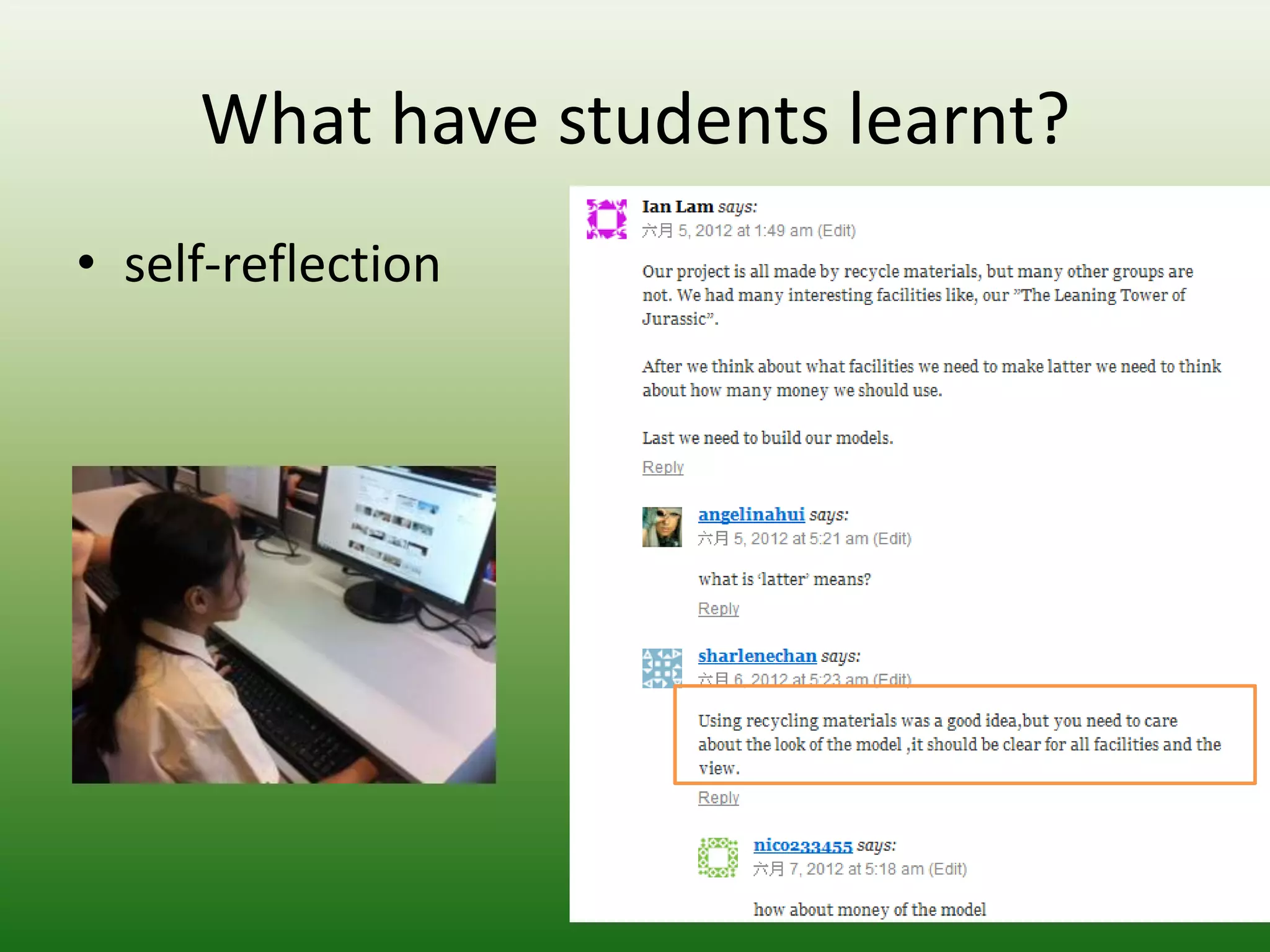
Students reported learning new knowledge about dinosaurs, improving their English language skills, learning how to use computers and the internet efficiently for learning, exchanging ideas online, and reflecting on their own learning through participating in the "My Dinosaur Park" project. They felt it was a valuable learning experience.