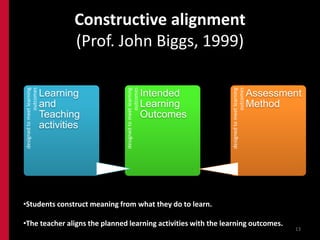
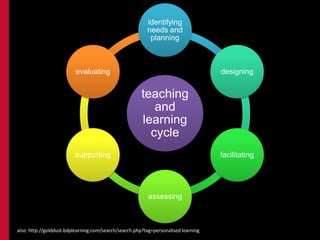
This document provides an overview of the ReTeach program, which focuses on teaching and learning in higher education. It includes Chinese proverbs about learning, principles of good teaching, theories of teaching, and frameworks for constructive alignment between learning outcomes, teaching methods, and assessment. The goal of ReTeach is to involve students and teachers in the learning process through active and social learning experiences, clear expectations, feedback, and reflection on teaching practices. References are provided for further reading on quality learning and teaching in higher education.