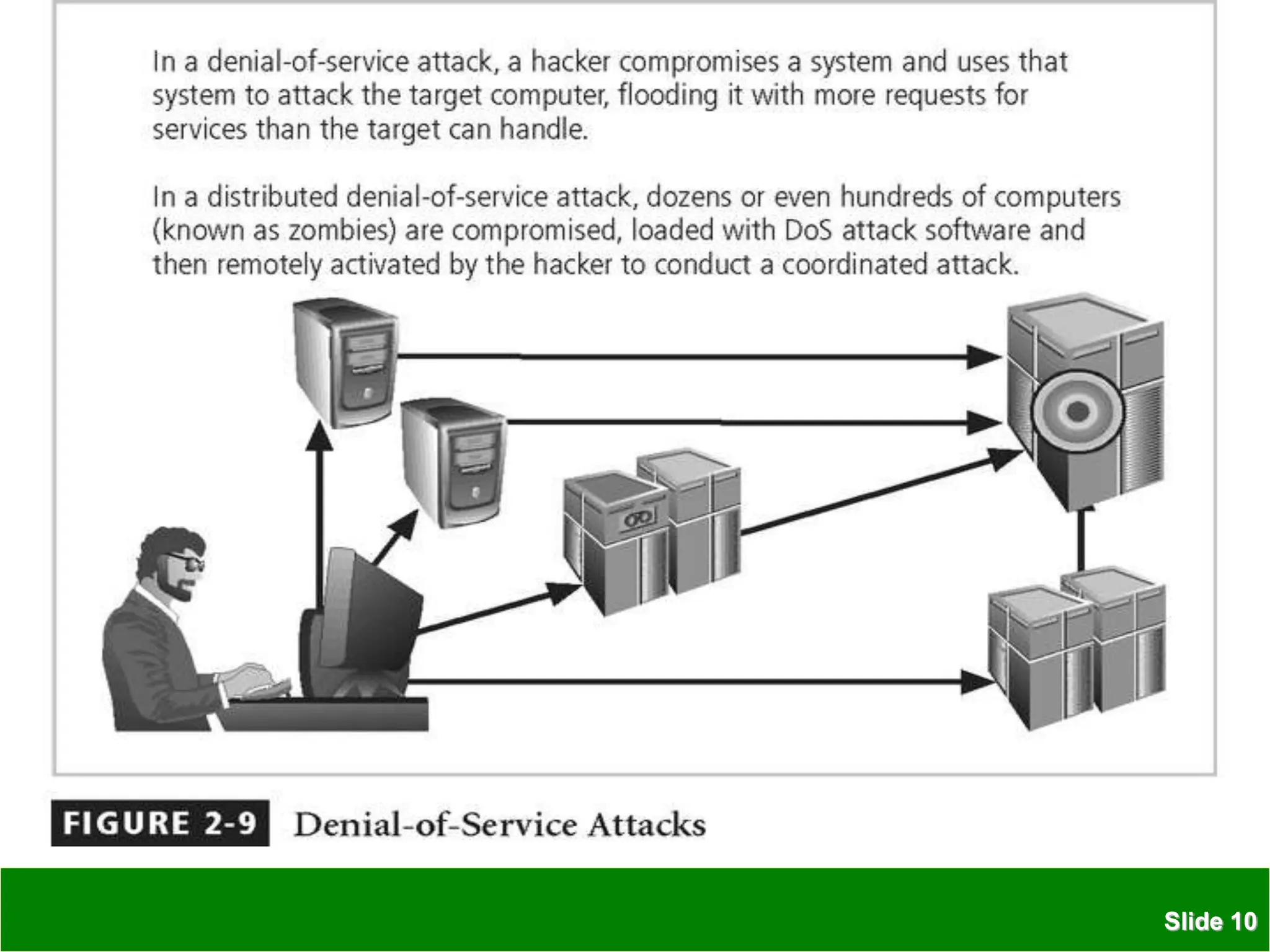
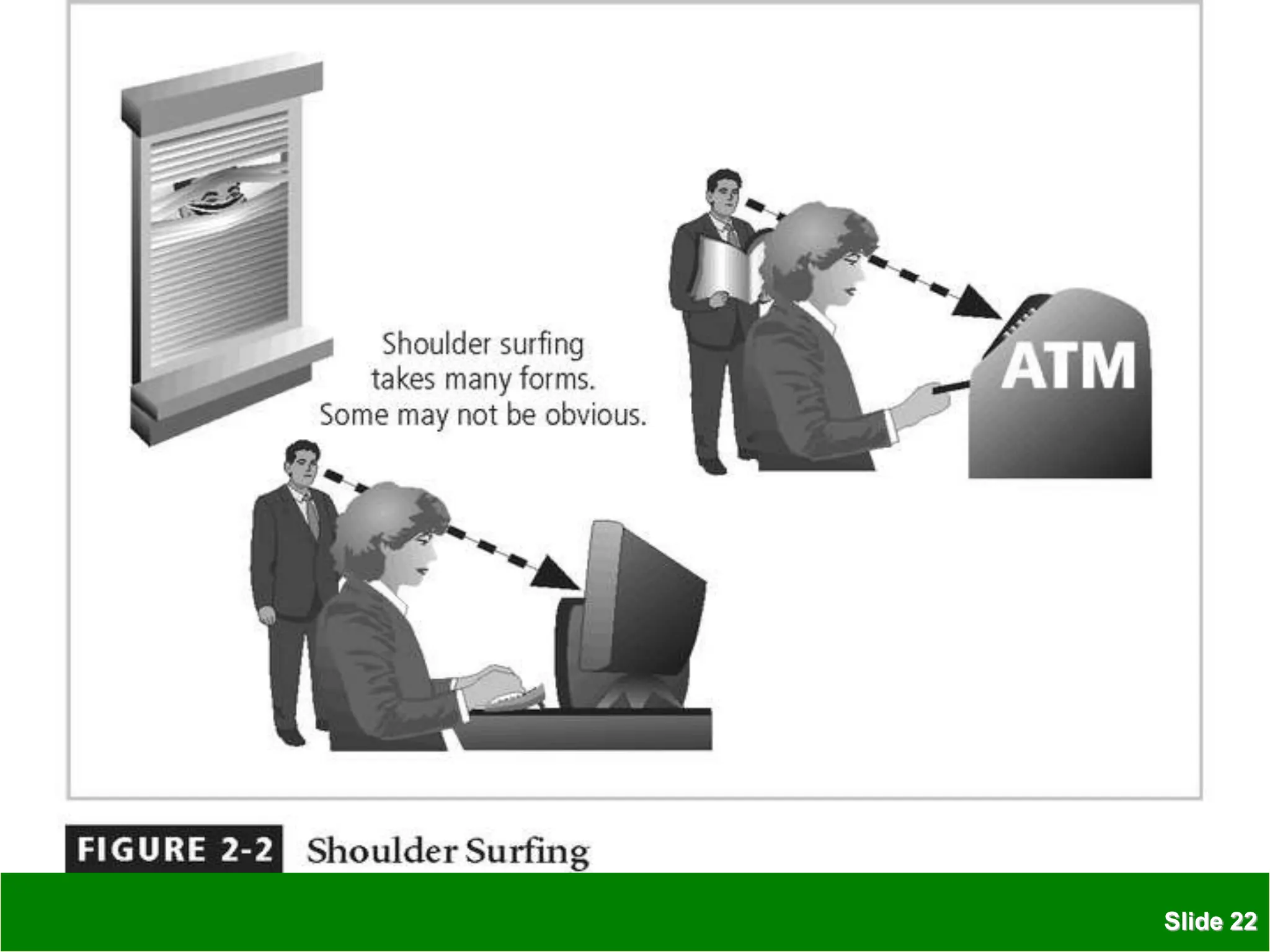
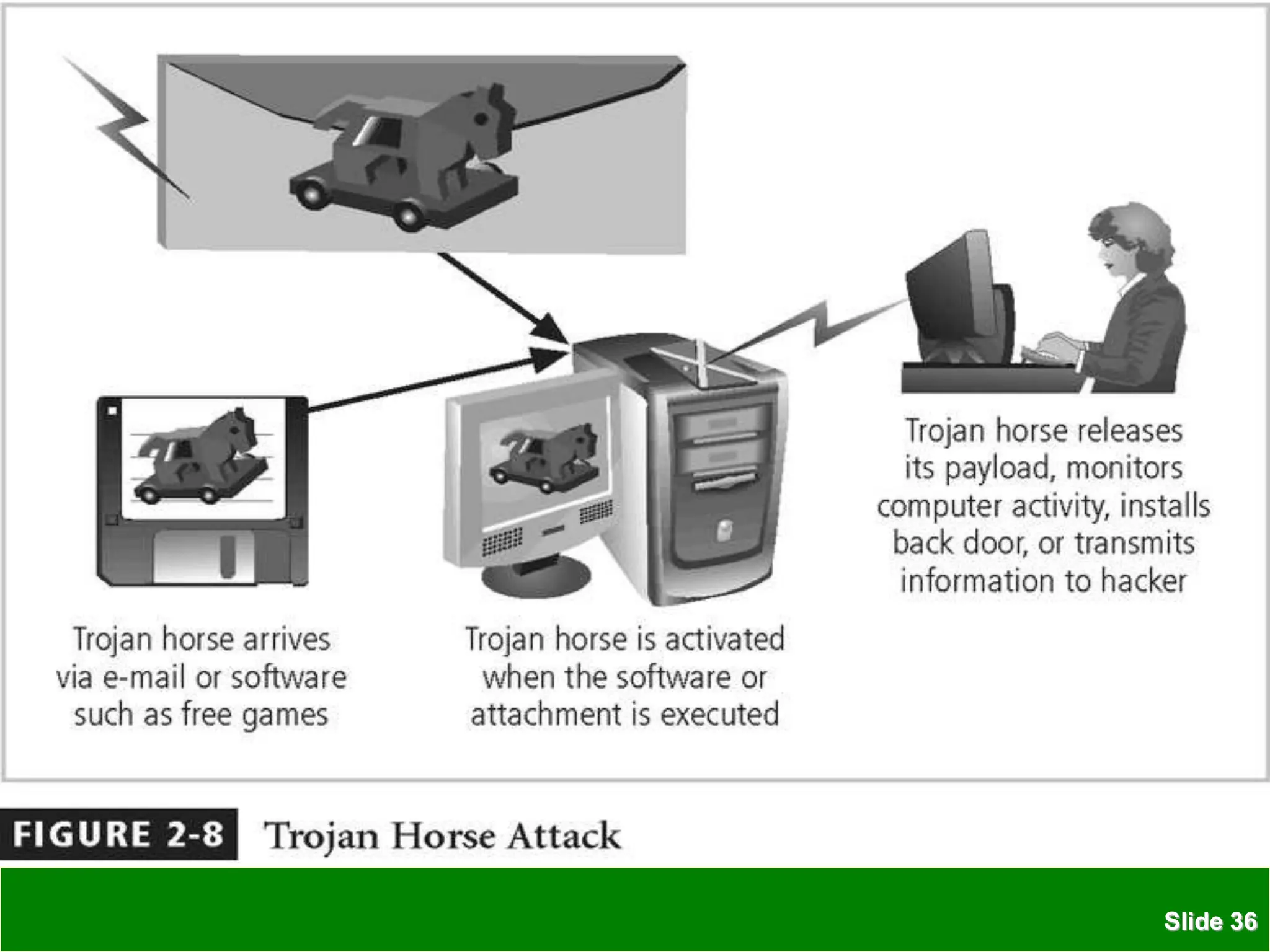
The document discusses various security threats to information technology systems and assets. It covers common types of threats such as hacking, malware, and social engineering attacks. It also discusses vulnerabilities in hardware, software, networks, physical sites, and personnel. The document outlines features of IT security including confidentiality, integrity and availability. It provides examples of protective measures organizations can take including strong access control, keeping software updated, network protection, employee training, and backups.