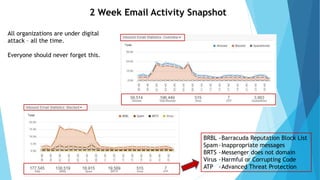
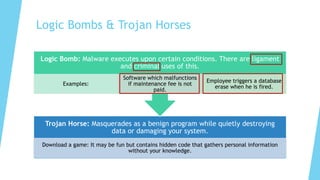
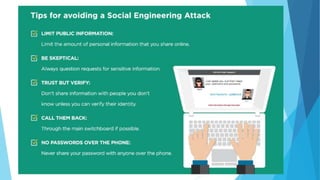
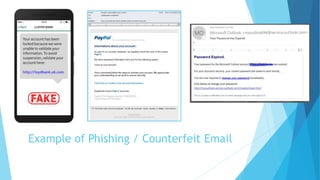
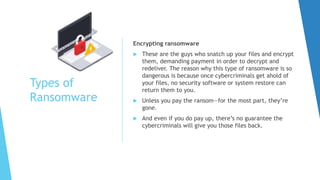
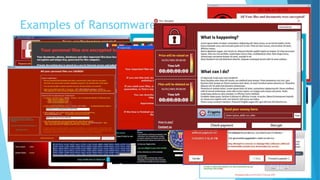
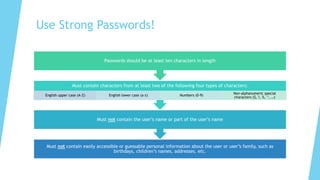
This document provides training on cybersecurity best practices for Borough of West Chester personnel. It defines cybersecurity as protecting information and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption or destruction. It outlines common cyber threats like viruses, worms, ransomware, and social engineering. It emphasizes using strong passwords, antivirus software, firewalls, and regular software updates. It also recommends avoiding malicious emails and websites, and backing up important data.