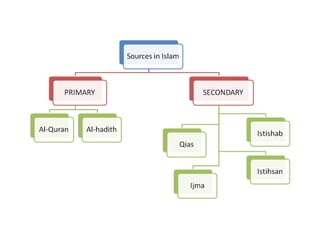
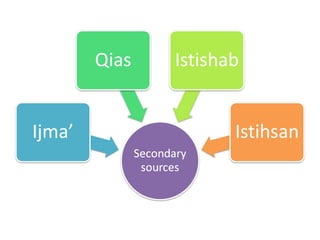
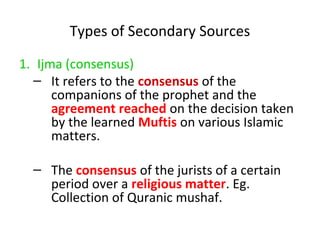
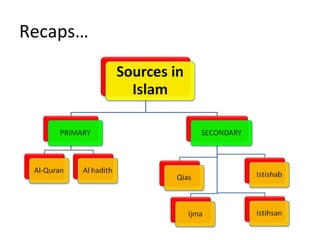
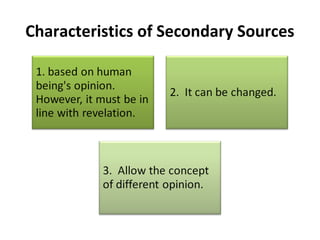
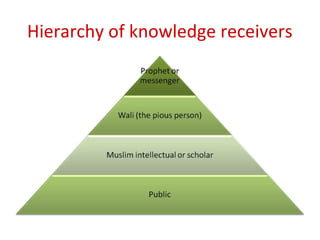
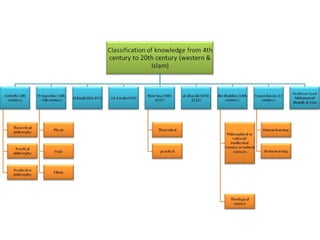
This document discusses sources of knowledge in Islam and how knowledge is classified from an Islamic perspective. It outlines that primary sources in Islam are the Quran and Hadith, which are directly revealed by God. Secondary sources include consensus of scholars, analogy, and reasoning based on public interest. Knowledge can be acquired through revelation, senses, mind, and ideas. The hierarchy of knowledge receivers starts with prophets, then pious people, scholars, and finally the public. Knowledge is typically divided into revealed knowledge from the Quran and Hadith, and acquired knowledge from observation and reasoning. It can also be categorized as individual or social obligations.