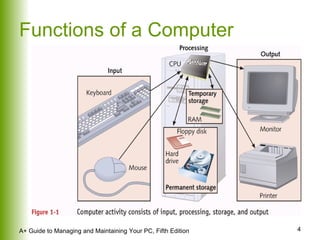
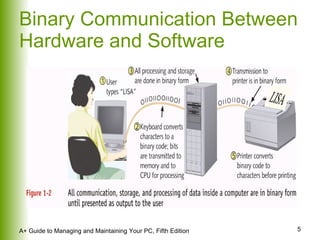
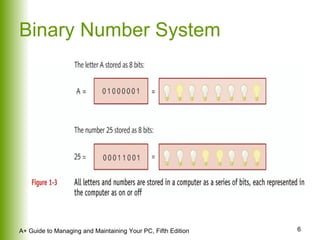
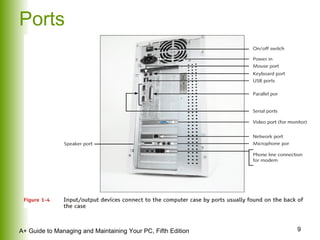
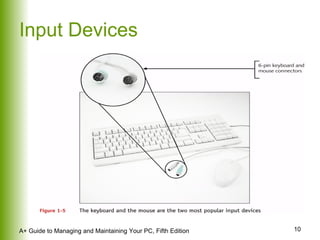
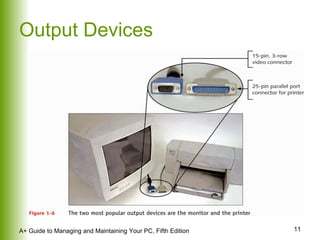
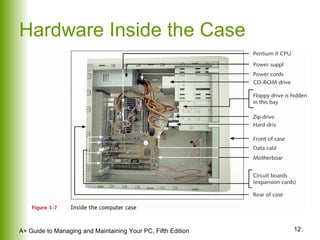
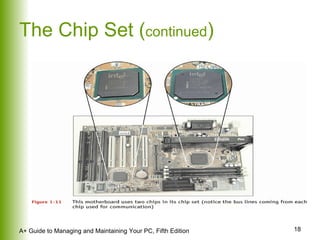
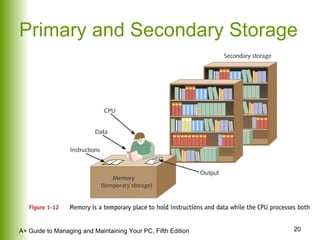
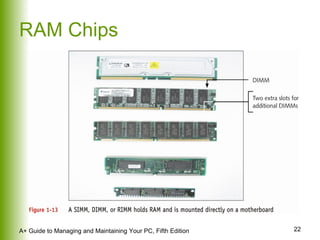
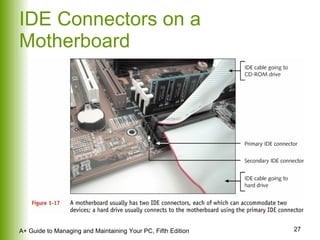
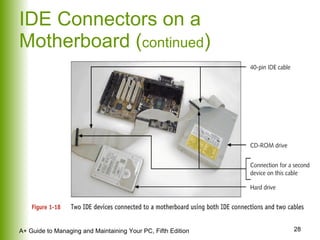
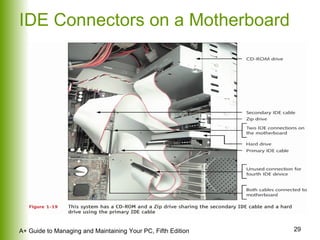
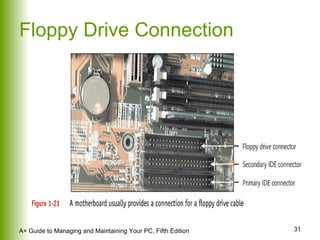
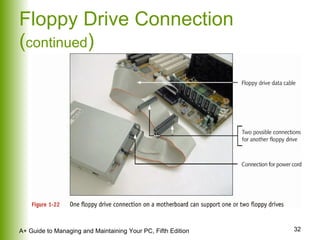
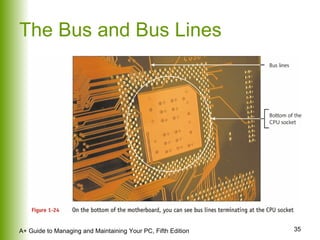
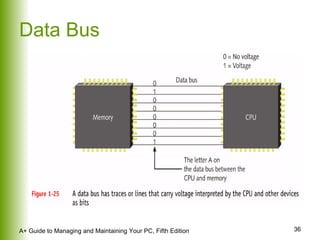
This document provides an overview of the main hardware components of a computer system. It discusses both internal components like the CPU, motherboard, RAM, storage devices, and expansion slots. It also covers external input/output devices that connect to the computer. The key points are that hardware requires software instructions to function, and that the CPU and chipset on the motherboard work together to allow communication between different hardware components using buses and slots. Memory and storage devices are also distinguished.