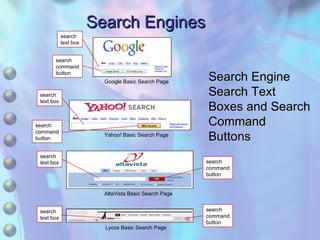
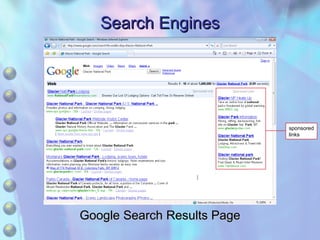
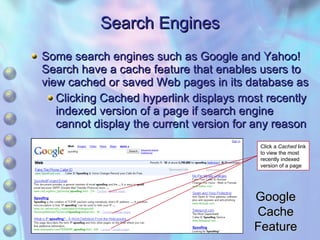
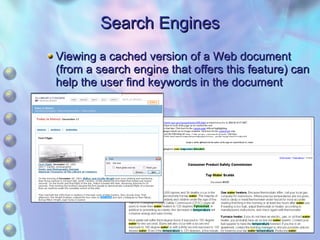
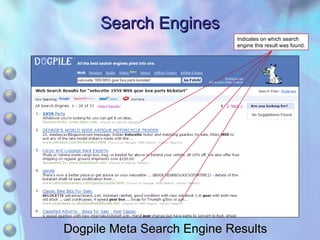
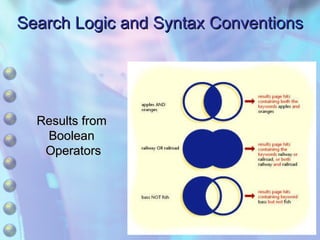
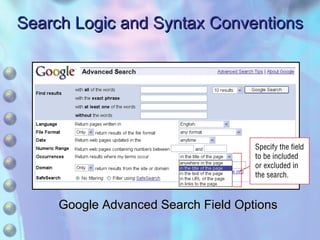
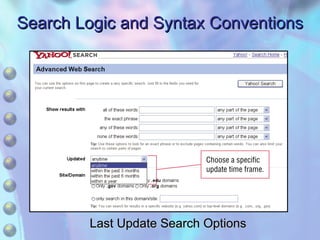
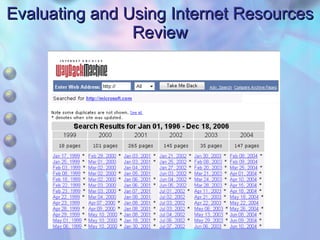
This chapter discusses accessing information resources on the web, including the difference between the surface web and deep web. It covers various search tools like search engines, subject directories, and meta search engines. Boolean logic and search syntax are explained to refine queries. Advanced search features and evaluating results are also summarized. Methods to define search questions and formulate strategies are provided to efficiently find relevant information online.