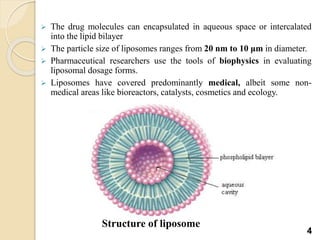
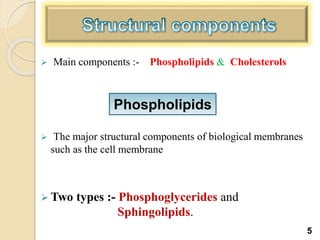
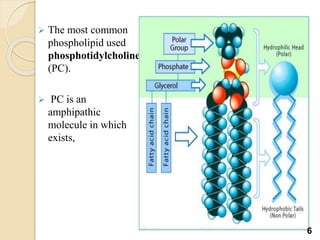
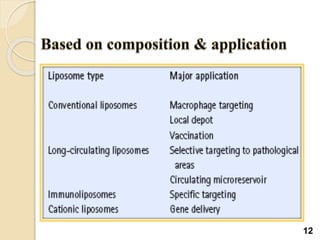
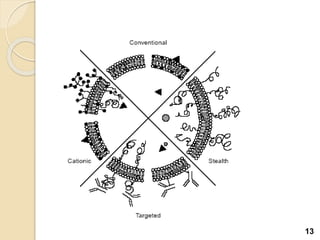
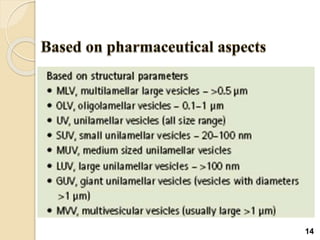
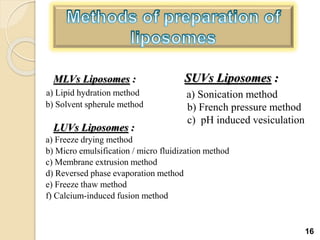
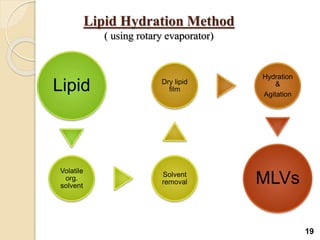
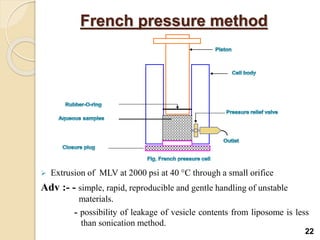
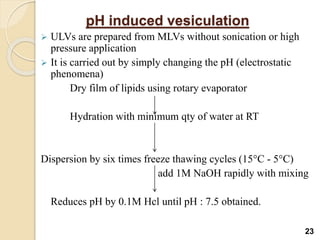
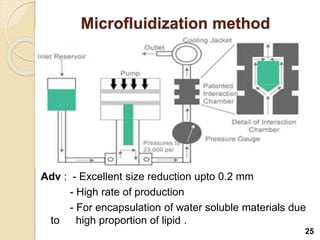
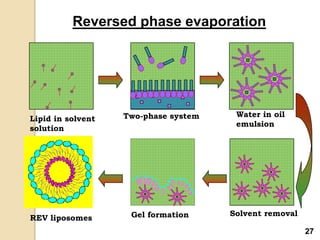
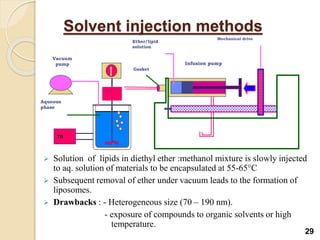
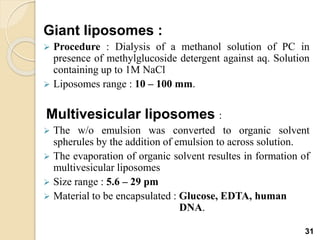
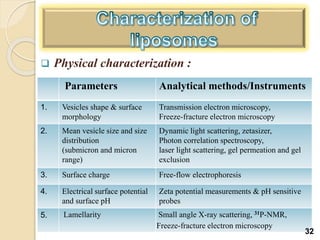
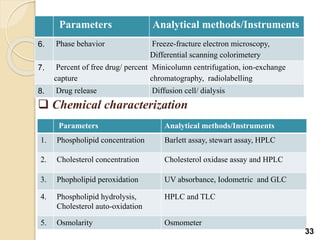
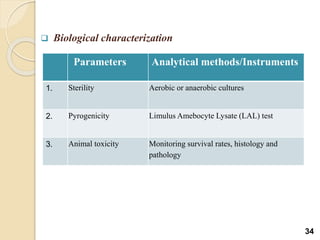
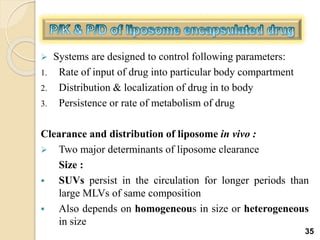
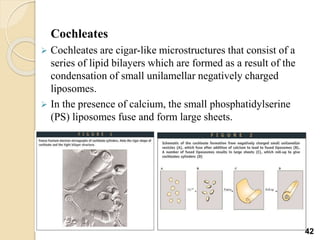
Liposomes are spherical vesicles made of phospholipid bilayers that can encapsulate hydrophilic or hydrophobic drugs. They offer several advantages for drug delivery such as protection of encapsulated drugs, controlled release, targeted delivery, and improved pharmacokinetics. There are various methods for preparing liposomes of different sizes and compositions, with the most common being lipid hydration, sonication, and extrusion. Liposomes must be characterized based on their size, lamellarity, drug encapsulation efficiency, and stability to ensure quality for pharmaceutical applications such as drug delivery.