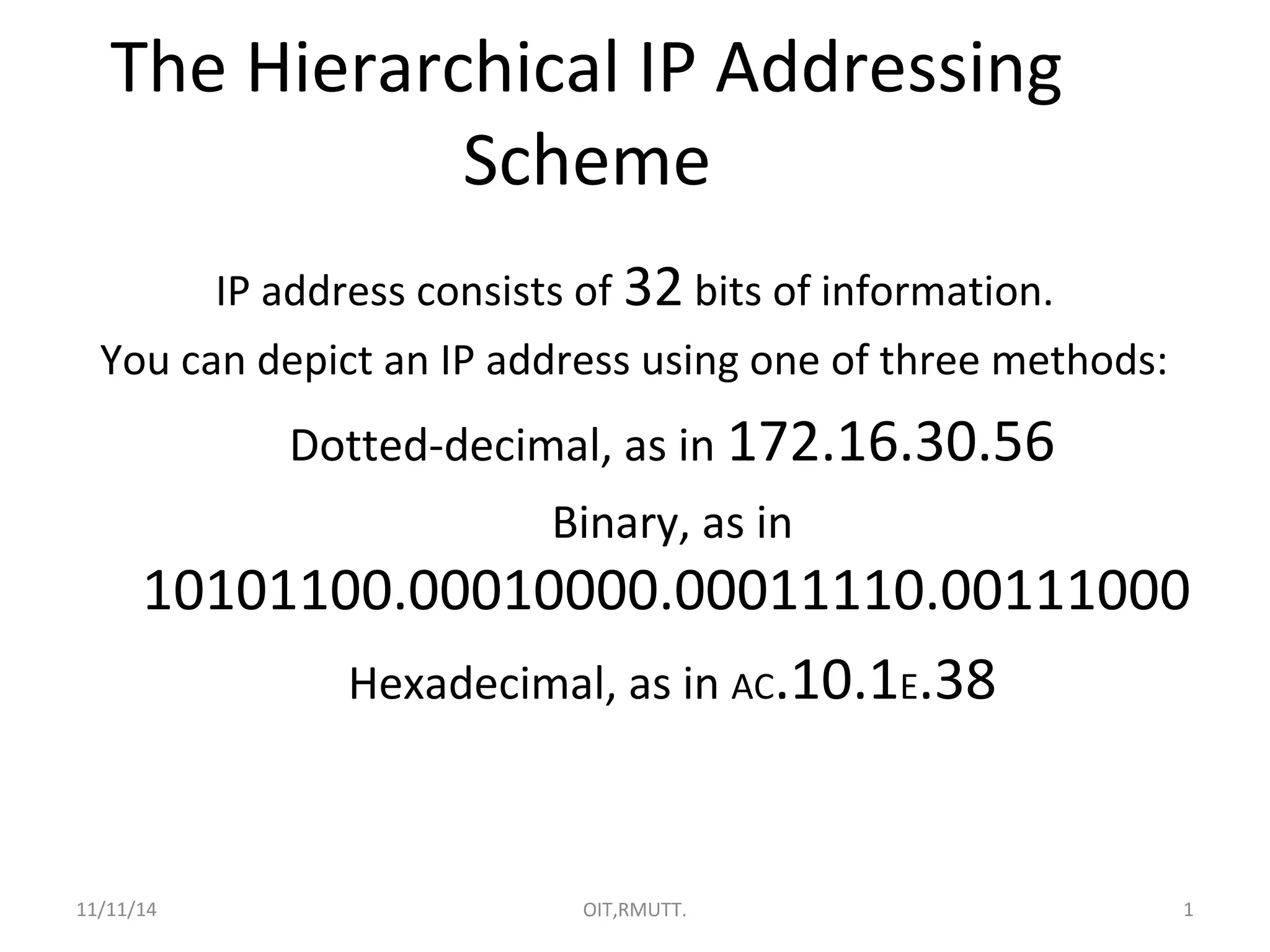
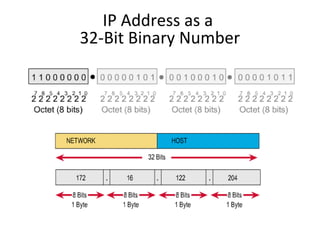
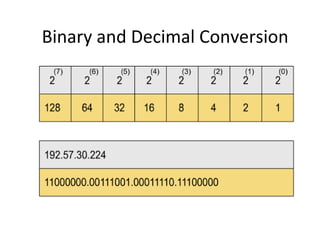
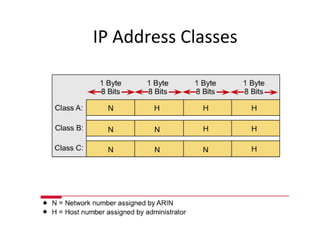
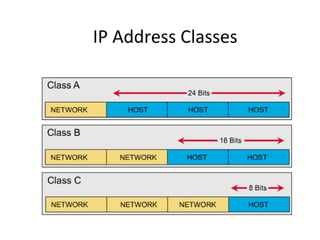
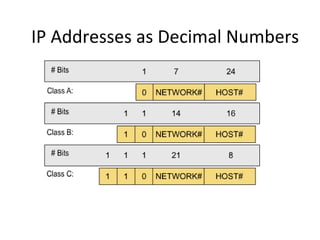
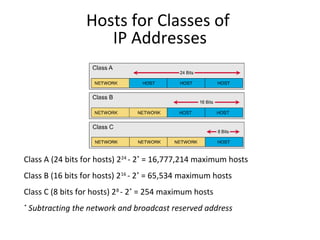
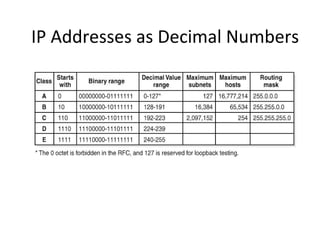
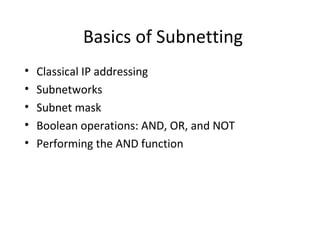
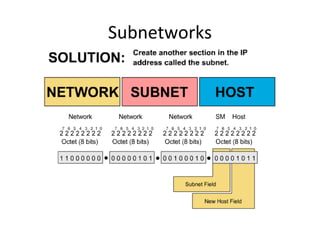
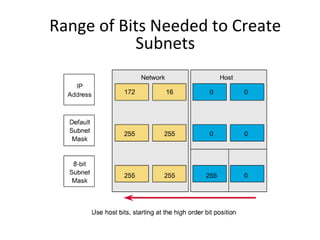
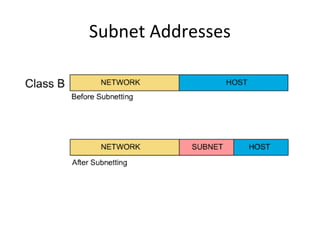
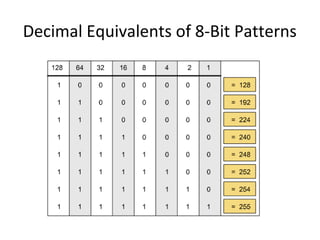
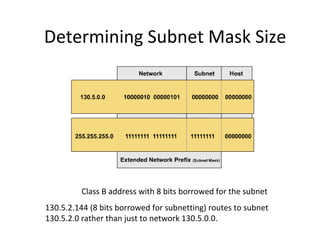
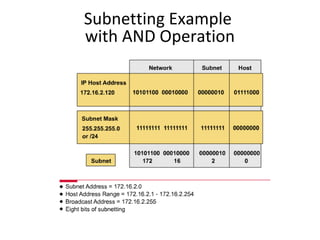
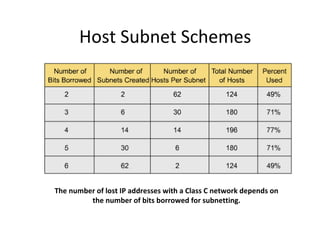
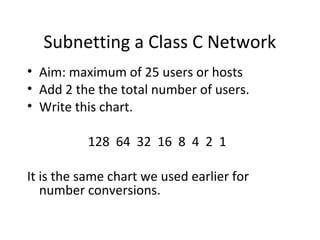
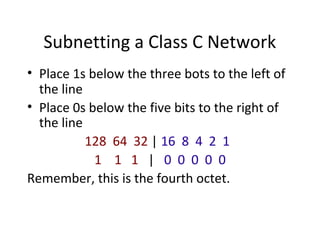
The document discusses IP addressing and subnetting. It explains that an IP address consists of 32 bits and can be represented in dotted-decimal, binary, or hexadecimal notation. The 32-bit address is divided into four octets. Subnetting allows a network administrator to create multiple logical subnets within a single IP network by borrowing bits from the host field of the address and designating them as the subnet field. The document provides an example of how to determine the subnet mask size, create subnets, and calculate subnet, host, and broadcast addresses when subnetting a network.