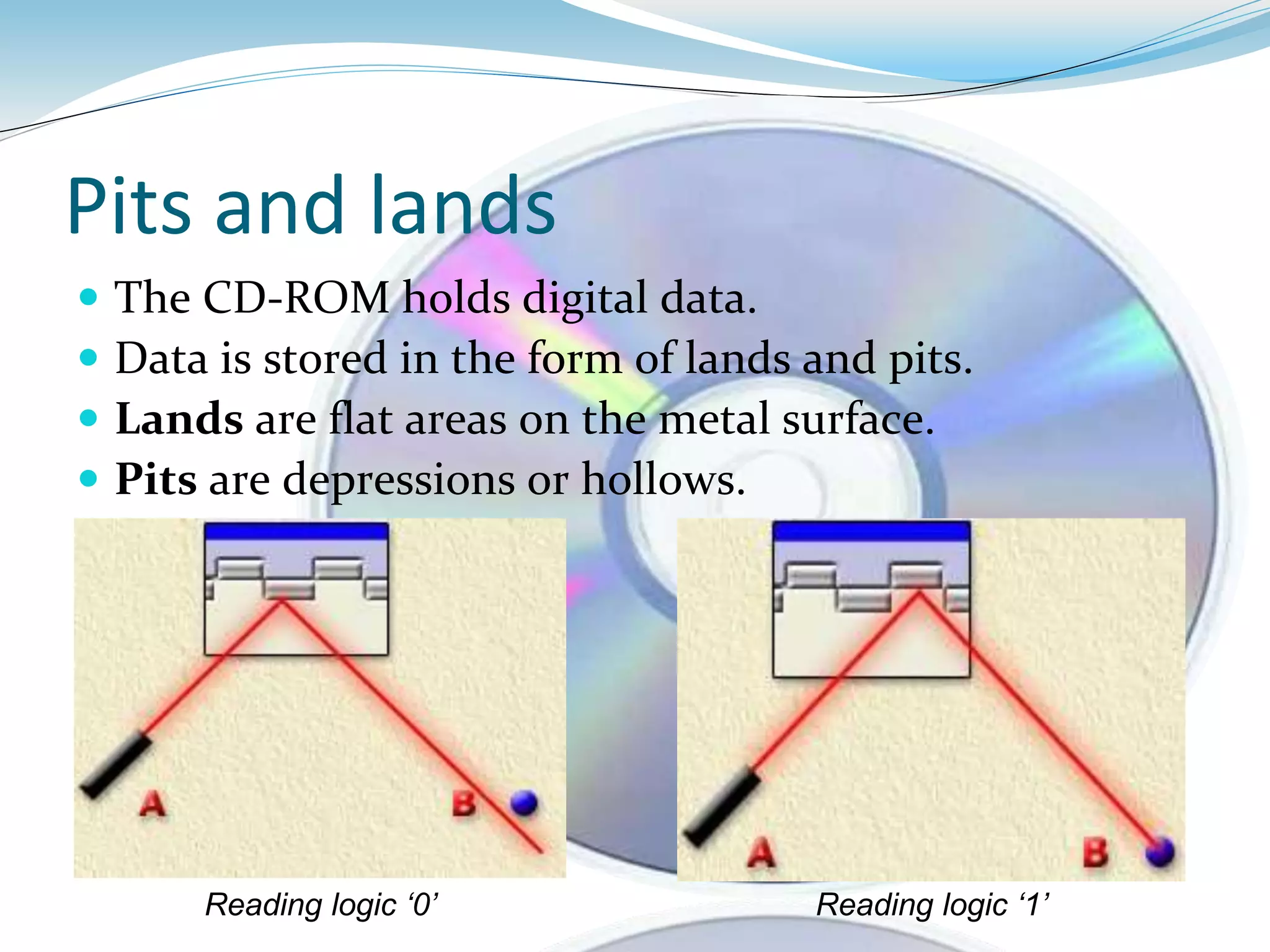
CD-ROM is an optical disc that stores digital data. It uses pits and lands on its surface to store binary data as either ones or zeros that is read by a laser. A CD-ROM drive reads this data by focusing a laser on the spinning disc. While CD-ROMs can only read data and not write it, specialized drives can burn new CDs by using laser to heat and mark the disc's surface. CD-ROMs provide a portable way to store large amounts of data that can be read on different computers.