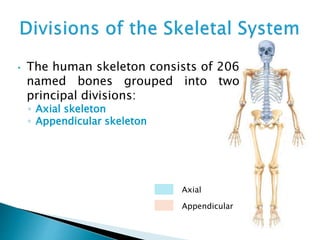
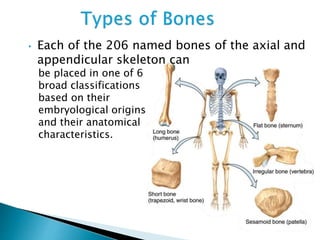
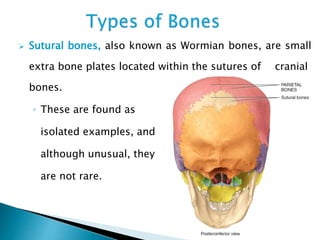
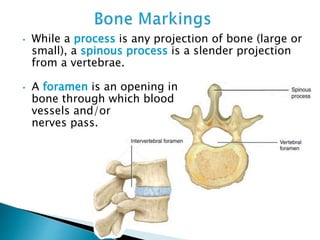
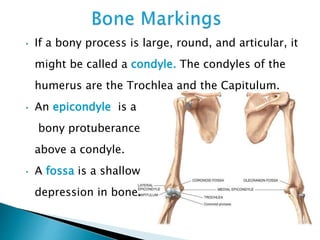
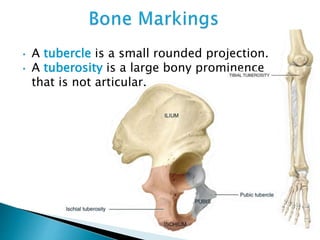
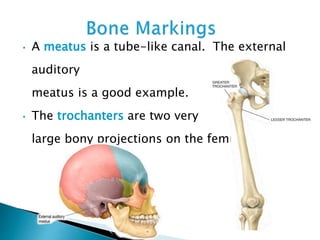
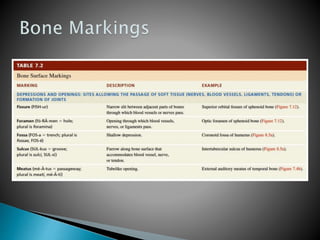
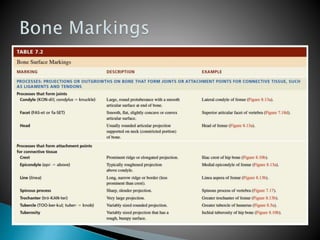
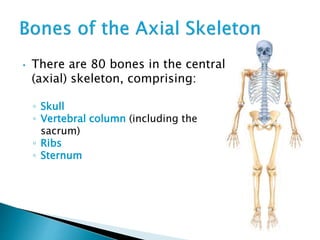
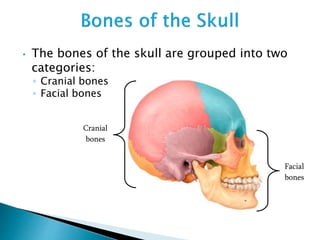
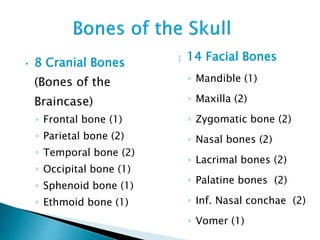
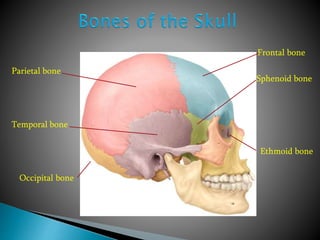
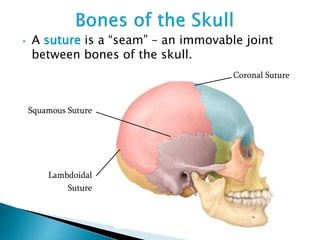
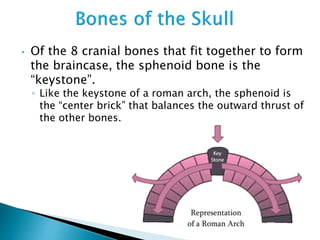
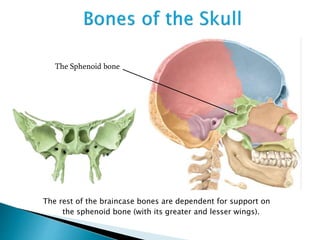
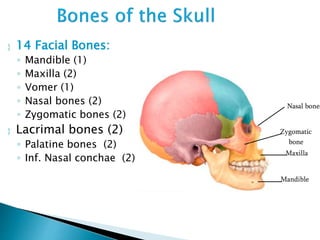
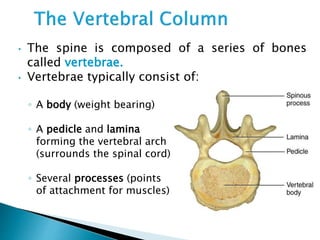
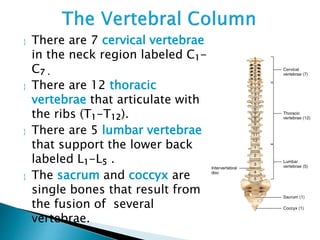
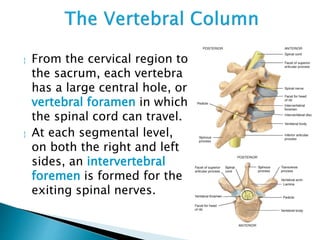
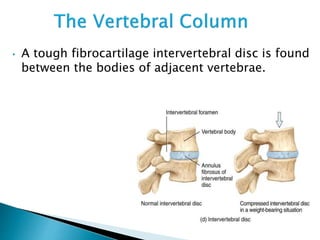
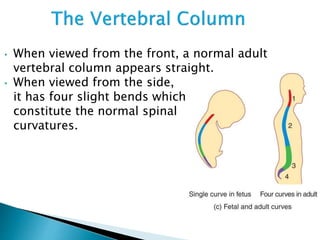
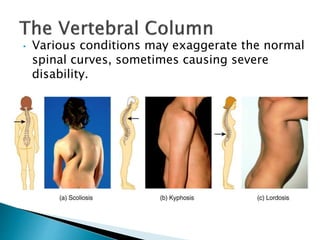
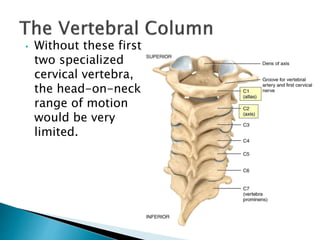
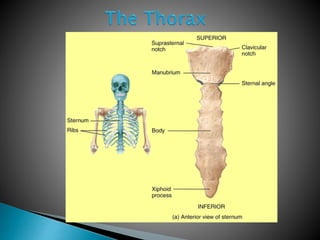
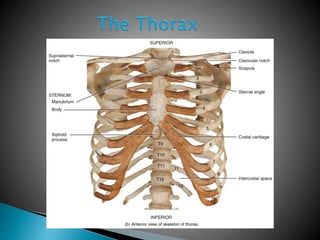
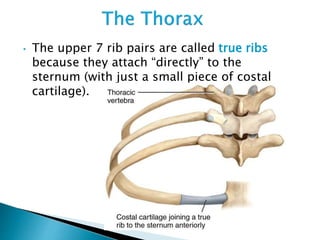
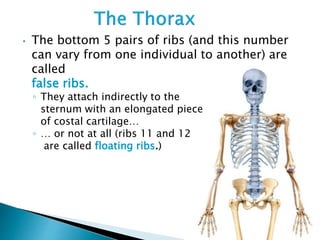
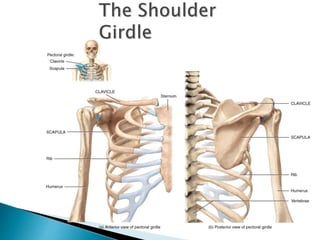
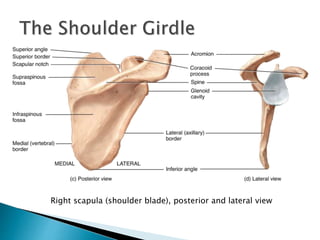
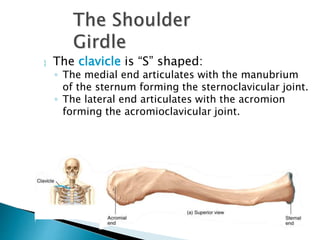
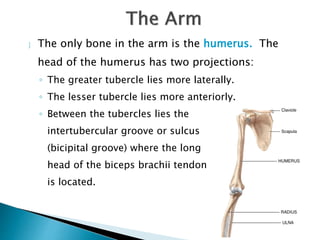
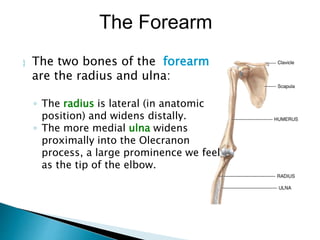
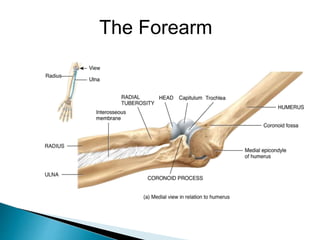
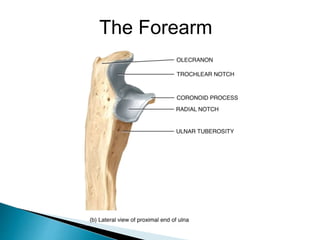
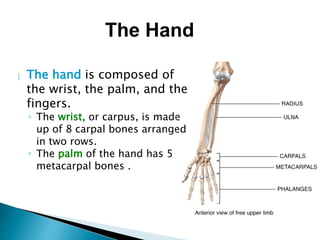
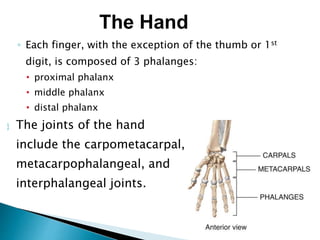
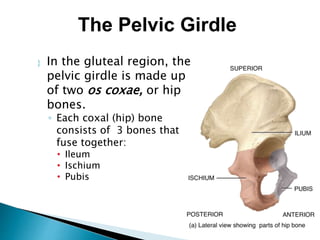
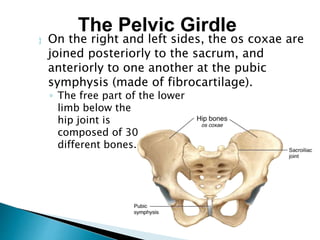
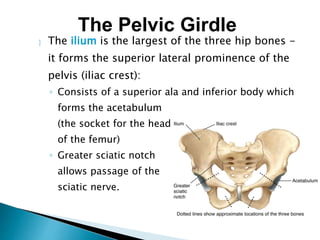
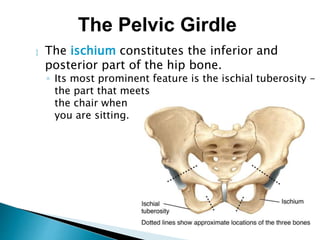
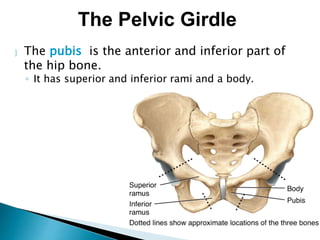
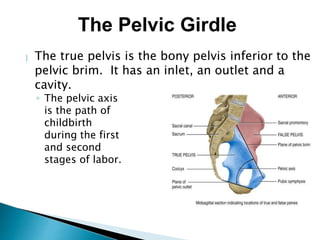
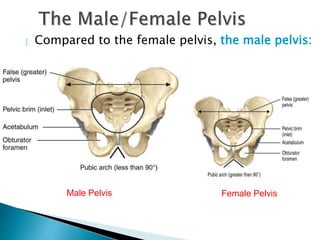
There are 206 bones in the human body grouped into the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes 80 bones that make up the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum. It forms the central core and foundation of the body. The appendicular skeleton includes 126 bones arranged in the upper and lower limbs, including their attaching girdles, forming the shoulders, arms, legs and allowing for movement.