Cell Notes
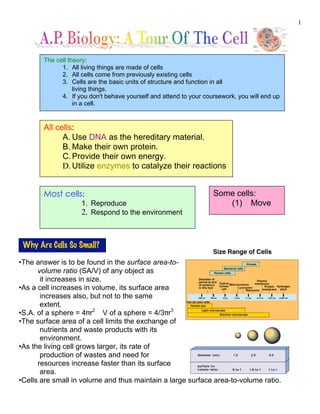
- 1. 1 •The answer is to be found in the surface area-to- volume ratio (SA/V) of any object as it increases in size. •As a cell increases in volume, its surface area increases also, but not to the same extent. •S.A. of a sphere = 4!r2 V of a sphere = 4/3!r3 •The surface area of a cell limits the exchange of nutrients and waste products with its environment. •As the living cell grows larger, its rate of production of wastes and need for resources increase faster than its surface area. •Cells are small in volume and thus maintain a large surface area-to-volume ratio. The cell theory: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. All cells come from previously existing cells 3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. 4. If you don't behave yourself and attend to your coursework, you will end up in a cell. All cells: A. Use DNA as the hereditary material. B. Make their own protein. C.Provide their own energy. D. Utilize enzymes to catalyze their reactions Most cells: 1. Reproduce 2. Respond to the environment Some cells: (1) Move Why Are Cells So Small?
- 2. 2 •In publicly funded schools, we use a compound light microscope! •A cell’s anatomy is too small for a compound light microscope, so an electron microscope is used to view organelle structure. •An electron microscope can magnify images 100X more than a CLM. •The two types of electron microscopes and their use are: If Cells Are So Small, How Do We Study Them? •Forest Hills Public Schools provides students with a Swift Model M3200 microscope. •These fine microscopes retail for $450. •The objective lens magnifications are 4X, 10X,and 40X. •The ocular lens has a constant magnification of 10X. •Total magnifications, then, are 40X, 100X, and 400X. •These microscopes have excellent resolution. That is to say that they can distinguish fine detail. •These microscopes are also parfocal, meaning that if you change from low power to medium power, the image is still in view (but might require fine focusing). 2 Types of Electron Microscopes Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) (used to study thin sections of the interior of cells) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) (used to study the surface of a specimen)
- 3. 3 Cytology – the study of cells. •During cell fractionation, cells are broken apart so that their organelles can be studied. •Cells are fractionated with a centrifuge. •A cell suspension is first centrifuged at low speed to separate suspension into two layers: •The supernatant consists of the smaller, lighter parts and organelles. •The pellet consists of the larger, heavier structures. •The two are separated and each is centrifuged for further separation. •Found in the Domains Bacteria and Archaea. Organisms in these domains are called prokaryotes. •These cells lack internal membranes that enclose compartments. (ie. they lack membrane- bound organelles.) •All prokaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, a nucleoid, and cytoplasm filled with ribosomes. •Plasma membrane - encloses the cell, regulates exchange traffic. •Nucleoid - relatively clear area, contains a circular loop of DNA. •Cytoplasm - the rest of the material within the cell - consists of cytosol and insoluble suspended particles (inclusion bodies). •Ribosomes - assembled from r-RNA and proteins. Coordinate the synthesis of the cell's proteins. •All internal reactions in prokaryotes (and eukaryotes) are catalyzed by enzymes. Cell Fractionation Cells Show Two Organizational Patterns: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells
- 4. 4 •Many (but not all) prokaryotes have a cell wall located outside the plasma membrane. In some bacteria, an outer membrane encloses the cell wall. Outside this membrane may be a layer of slime composed mostly of polysaccharide. It is simply called the capsule. •The capsule aids in protection (from viruses called bacteriophages and white blood cells), retards drying, entraps cells for bacteria to attack, or sticks them to their food source. •Some prokaryotes carry on photosynthesis. In these bacteria, the plasma membrane folds into the cytoplasm to form an internal membrane system that contains bacterial chlorophyll and other compounds needed for photosynthesis. •Other groups of prokaryotes possess membranous structures called mesosomes (also infoldings of the plasma membrane) that may function in cell division or in energy-releasing reactions. •Some prokaryotes swim by using flagella. •Structures called pili (s. pilus) project from the surface of some groups of bacteria – adherence during mating (conjugation), help adhere to animal cells. (See the electron micrograph above) •Bacteria utilize binary fission for reproduction. Flagella Pili
- 5. 5 Eukaryotic Cells •These are the cells of the Domain Eukarya -Animals, Plants, Fungi, and Protists. •Cells are larger (typically 10X) and more structurally complex than prokaryotes. •Eukaryotes have in internal cytoskeleton to maintain shape and aid in movement. •Eukaryotes possess membrane-bound organelles. (Compartmentalization) •The membranes of all organelles have a similar structure, the phospholipid bilayer. •The number of internal membranes in a eukaryotic cell is stunning and remarkable. What do they all do? What is their structure? How do they regulate materials movement? Why can't FHC A.P. Biology students get a date? •Membranes are very useful in forming compartments whose internal contents are dissimilar to the cytoplasm. •Membranes are also very helpful in regulating the flow of molecular traffic. •Much more about membranes in the next chapter! The Nucleus •Cells store information in the sequence of bases (A,T,C, and G) in DNA. •Most of the DNA in eukaryotes resides in the nucleus. •The nucleus is nearly always the largest subcellular structure. •A nucleus is surrounded by two membranes, the nuclear envelope. •This membrane is stable during all parts of the cell cycle except mitosis. •During mitosis it fragments into vesicles, then re-forms. •The nucleus is permeated by pores. RNA and water-soluble molecules pass through these pores. •DNA combines with proteins to form a fibrous complex called chromatin (long, thin, entangled threads that cannot be clearly seen by our microscopes.) •Surrounding the chromatin are water and dissolved substances composing the nucleoplasm.
- 6. 6 . Nuclear lamina - a meshwork of proteins just inside the nuclear envelope that help maintain the shape of the nucleus •Some nuclear envelope pores are continuous with the E.R. •When the nucleus is ready to divide (mitosis), the chromatin replicates and then condenses and coils tightly to form easily visible structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome contains 2 chromatids, both containing a single long molecule of DNA. Nucleoli •Dense, roughly spherical bodies located in the nucleus. •Contain 10-20% of a cell's RNA. •Ribosomal subunits are assembled in the nucleolus from r-RNA and protein. •Ribosome assembly is completed in the cytoplasm •Nucleoli disappear during mitosis. •Appear and disappear as RNA concentrations change. •There may be more (or less) than 1 nucleolus per cell.
- 7. 7 Ribosomes •Ribosomes are synthesized in the nucleolus. •Proteins are made upon the ribosomes after the ribosomes have migrated from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. •Ribosomes are found in 3 sites in eukaryotic cells: 1. bound to the outer surface of the Rough E.R. 2. unbound in the cytoplasm 3. within the mitochondria and chloroplasts (these ribosomes are different in structure!) •Ribosomes are also found in prokaryotic cells (because they are NOT membrane- bound) •Ribosomes in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes consist of a pair of subunits: •Blue = large subunit Yellow = small subunit in the diagram below •Chemically, ribosomes consist of ribosomal RNA and protein. •The function of the ribosome is to temporarily bind two other types of RNA (t-RNA and m-RNA) during translation (the construction of protein.) Large Subunit Small Subunit Ribosomes are the sites where the cell assembles proteins according to genetic instructions. A bacterial cell may have a few thousand ribosomes, although a human cell has a few million. Cells that have high rates of protein synthesis have a particularly great number of ribosomes. Cells active in protein synthesis also have prominent nucleoli, which make the ribosomes. Ribosomes function in two cytoplasmic areas. Free ribosomes are spread throughout the cytosol, while bound ribosomes are attached to the outside of a membranous network, endoplasmic reticulum. Most of the proteins that are made by free ribosomes will function inside the cytosol. The proteins produced by bound ribosomes usually exported from the cell. Each ribosome is built from two subunits, each having its own mix of ribosomal RNA and proteins. Ribosomes are built with RNA from the nucleolus and are made in the nucleolus itself. These subunits join together to form a functional ribosome only when they attach to a messenger RNA molecule. The ribosomes present in eukaryotic cells are slightly larger than those found in prokaryotic cells. Ribosomes function in protein synthesis. As they move along messenger RNA, amino acids are joined in an order originally dictated by DNA. Several ribosomes can be moving along the same messenger RNA at once and the entire complex is called a polysome.
- 8. 8 Energy-Processing (ATP-Generating) Organelles Mitochondria •Function - convert the potential chemical energy of fuel molecules into a form that cells can use, namely ATP (or adenosine triphosphate). •This process is termed cellular respiration. •Small - about the size of bacteria. •Consist of two membranes, an outer and an inner membrane. Both are phospholipid bilayers. •The outer membrane is merely protective. •The inner membrane has many irregular folds, called cristae. •It is within the cristae that ATP is generated. The cristae house the protein molecules (cytochromes) that participate in chemiosmosis. •Inside the cristae is a region called the mitochondrial matrix. Here we find enzymes, ribosomes, and a circular loop of DNA. •Mitochondria bear a striking resemblance to bacteria. Remember this. •Cells that require the most energy have the most mitochondria. Chloroplasts •Site of photosynthesis, contains the green protein pigment chlorophyll. •Like the mitochondrion, the chloroplast possesses 2 membranes. •There is more variety in the arrangement of these membranes than there is in mitochondria.
- 9. 9 •Within the inner membrane is a third membrane, the thylakoid, which is arranged as interconnected foldings AND stacks. •The structures that resemble stacks of coins are called grana. •The fluid surrounding the thylakoid is called stroma. •The chloroplast stroma contains ribosomes and DNA. •ATP generation occurs in chloroplasts via chemiosmosis. This ATP is then used (along with NADPH) to drive the light independent reactions of photosynthesis (the Calvin cycle). Other Plastids •Contain carotenoid pigments. Red, orange, or yellow. •Give color to petals and fruits to aid in pollination and seed dispersal. •No one, however, knows why carrots are orange. Chromoplasts
- 10. 10 •Leucoplasts are storage sites in plant cells for starch and fats. •It is interesting to note that: •All plastid types are related to one another. •All plastid types develop from small protoplastids. •Leucoplasts are sometimes called amyloplasts. Both Chloroplasts and Mitochondria are capable of self-replication. They are both the size of whole prokaryotes. They both contain DNA and have ribosomes that are similar to prokaryotic ribosomes. Leucoplasts Dr. Lynn Margulis, a Distinguished Professor of Biology at The University of Massachusetts at Amherst and a member of the National Academy of Sciences, played a crucial role in introducing the radical theory that eukaryotic cells (cells with nuclei: protists, fungi, plants and animals) evolved through a symbiotic relationship between different kinds of prokaryotic cells (cells without nuclei: bacteria and cyanobacteria). This "Endosymbiosis Theory" is has become widely accepted by biologists. Another widely accepted theory, the "infolding theory," suggests that the complex internal endomembrane system of eukaryotic cells--such as the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi body, evolved as infoldings of the cell membrane that allowed for the separate packaging of cellular processes. Endosymbiosis I have Lynn's autograph.