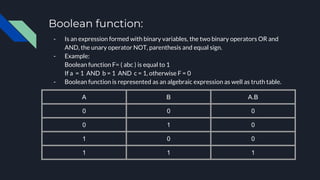
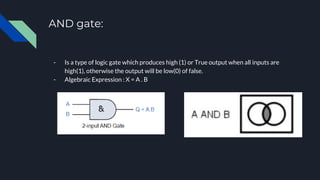
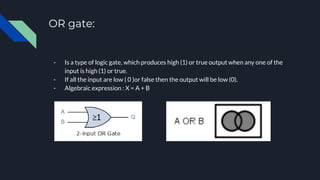
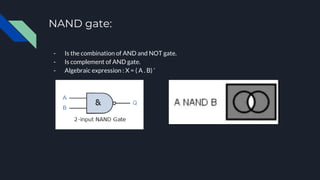
- Boolean algebra is used to analyze and design digital logic circuits and determines logical propositions as either true or false. It uses basic logic gates like AND, OR, and NOT.
- AND gates output 1 only if all inputs are 1, while OR gates output 1 if any input is 1. NOT gates invert the input. More complex gates can be made by combining basic gates, like NAND (AND with output inverted) and NOR (OR with output inverted).
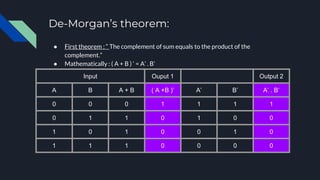
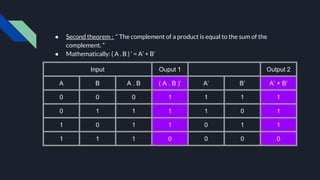
- Boolean algebra has laws like commutative, distributive, complement, identity, and associative laws that define the operations of logical variables and simplify expressions. Together, Boolean algebra and logic gates form the foundation of digital circuit and computer design.