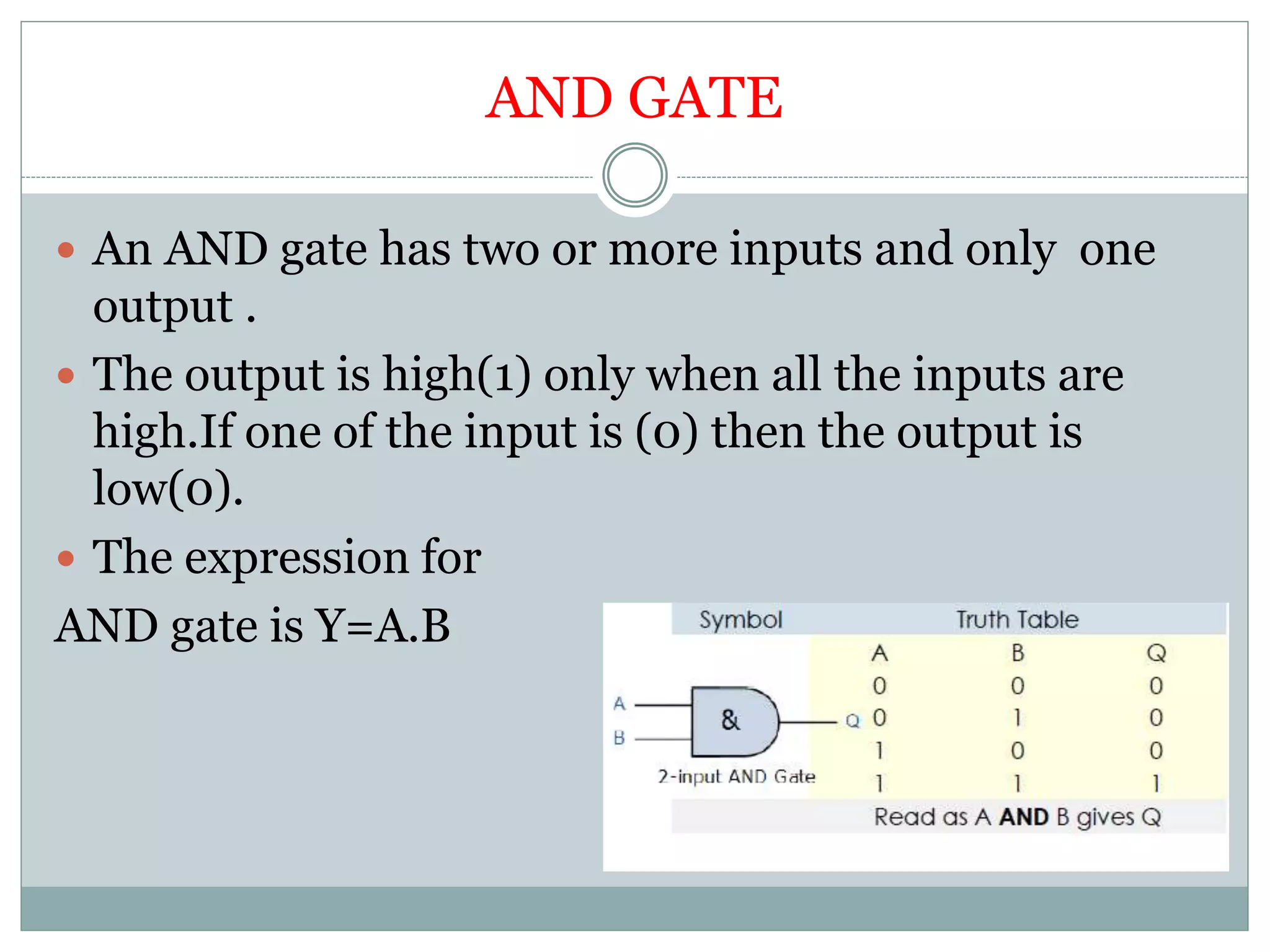
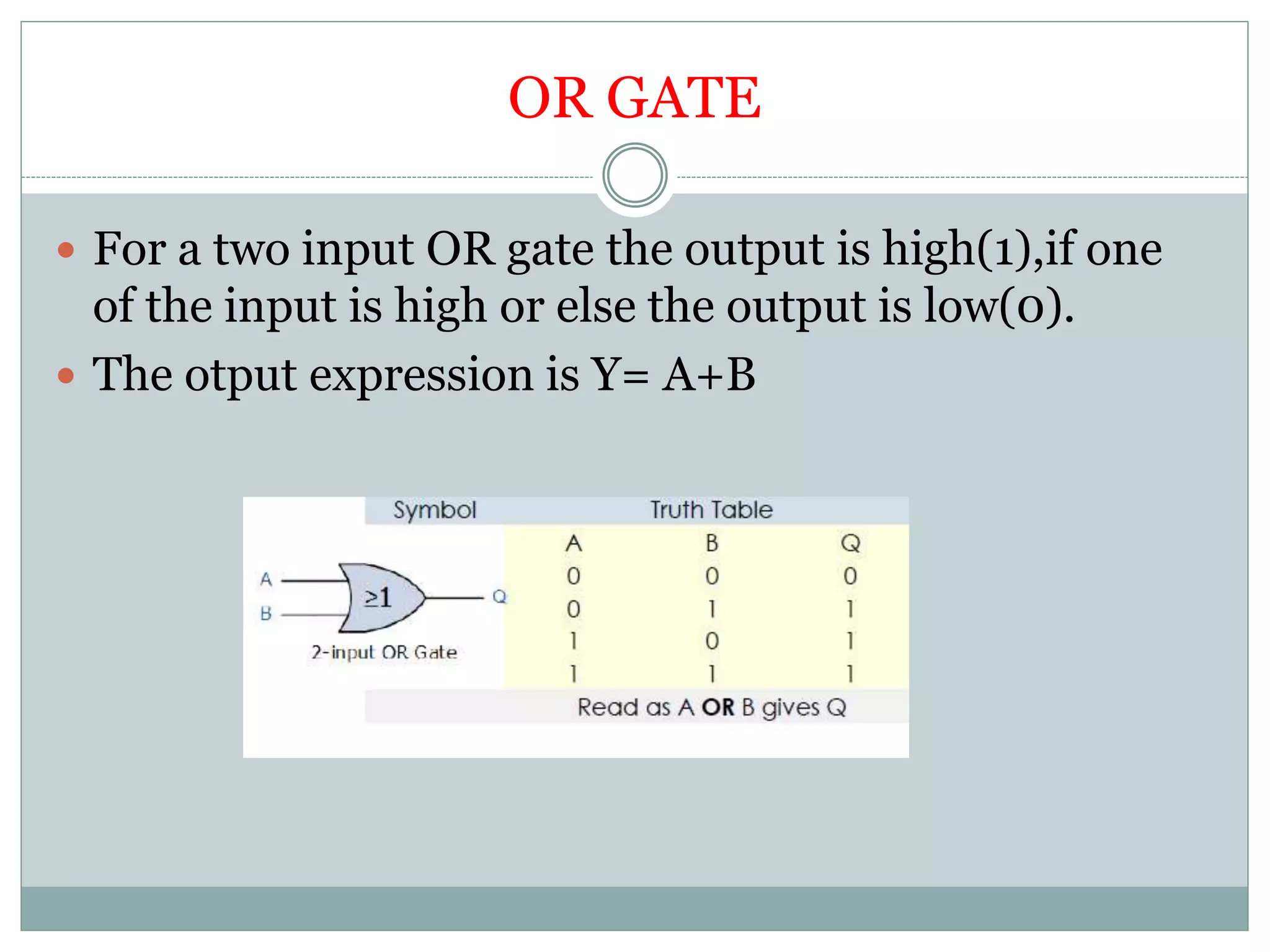
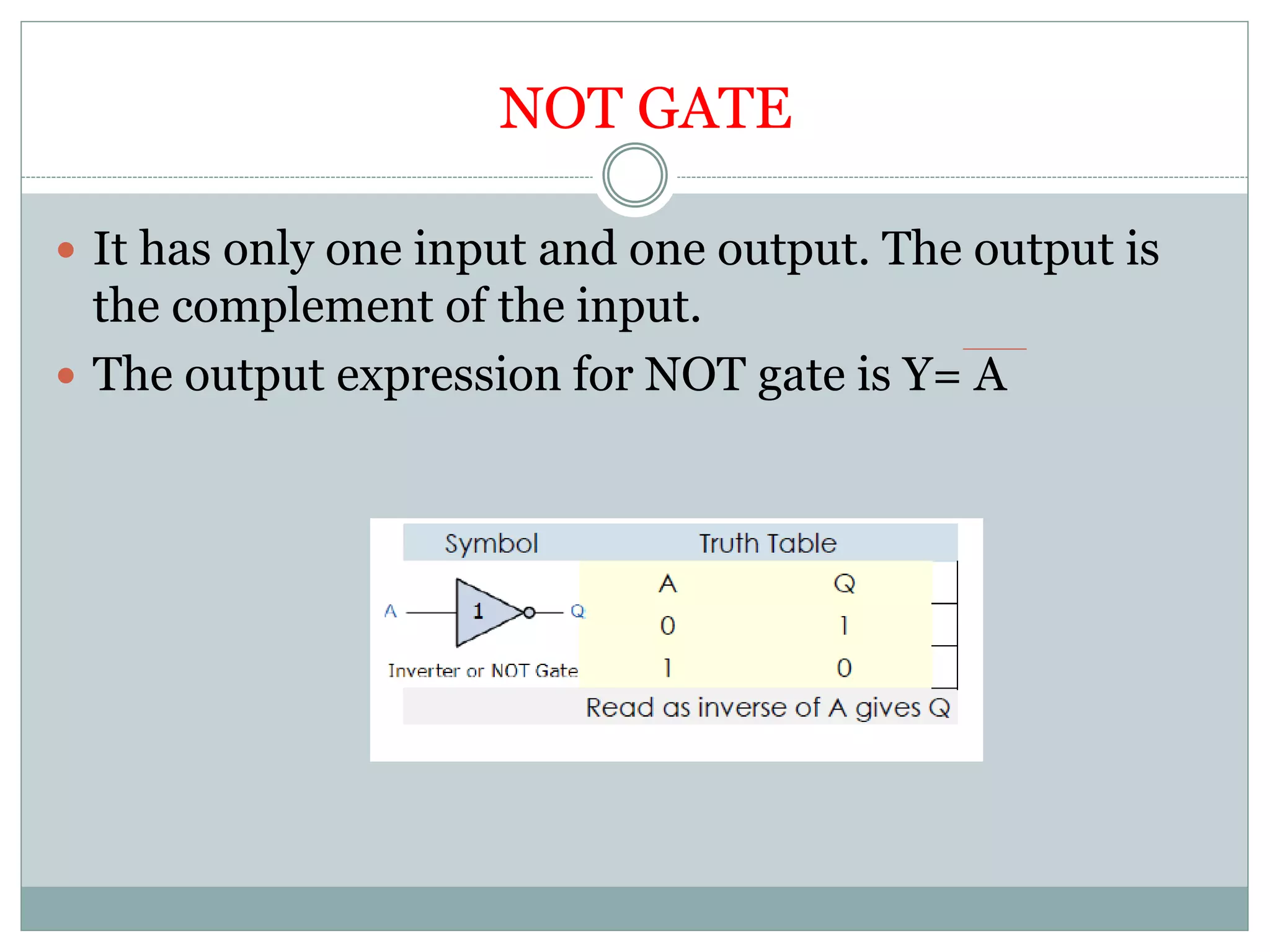
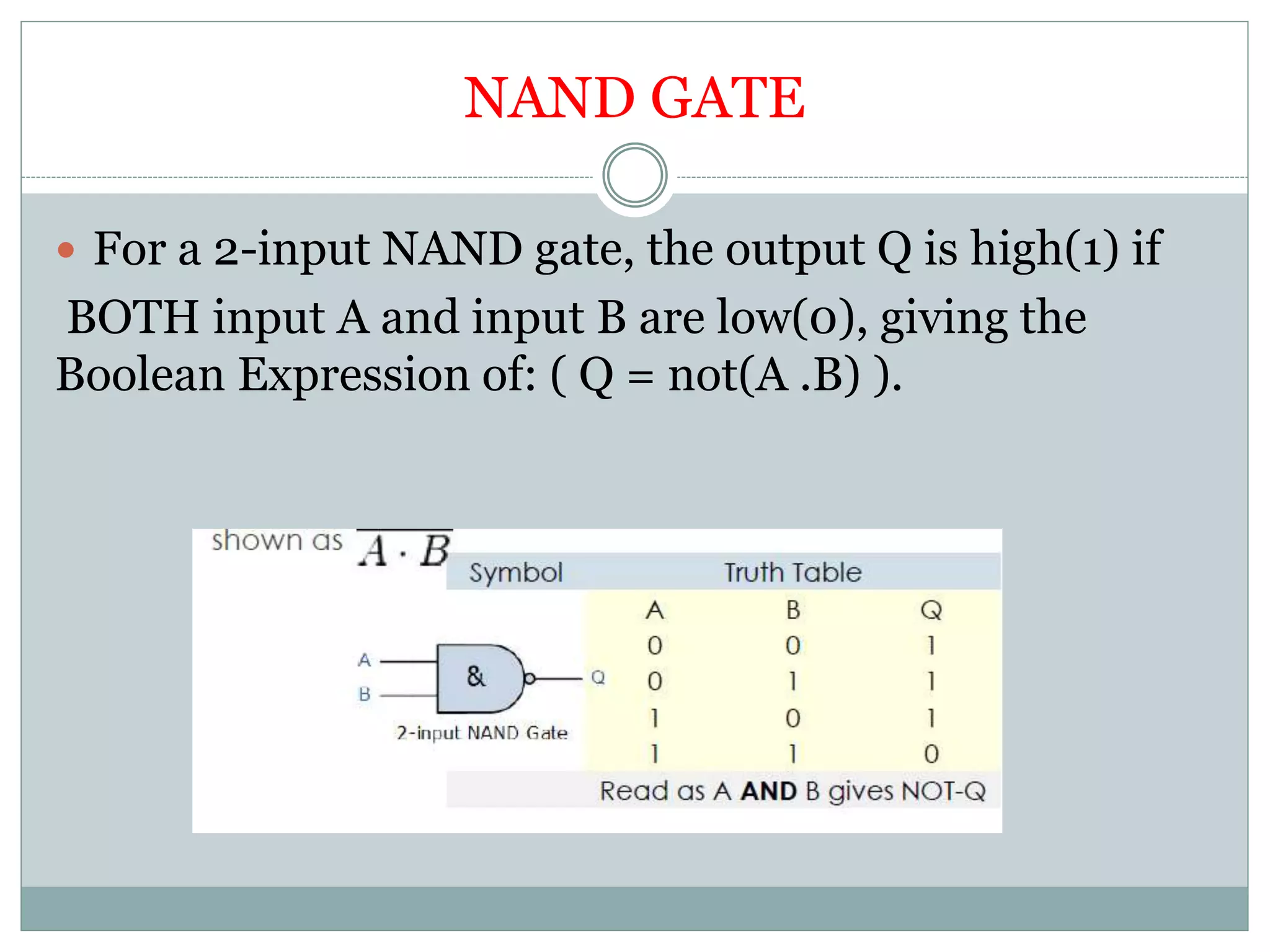
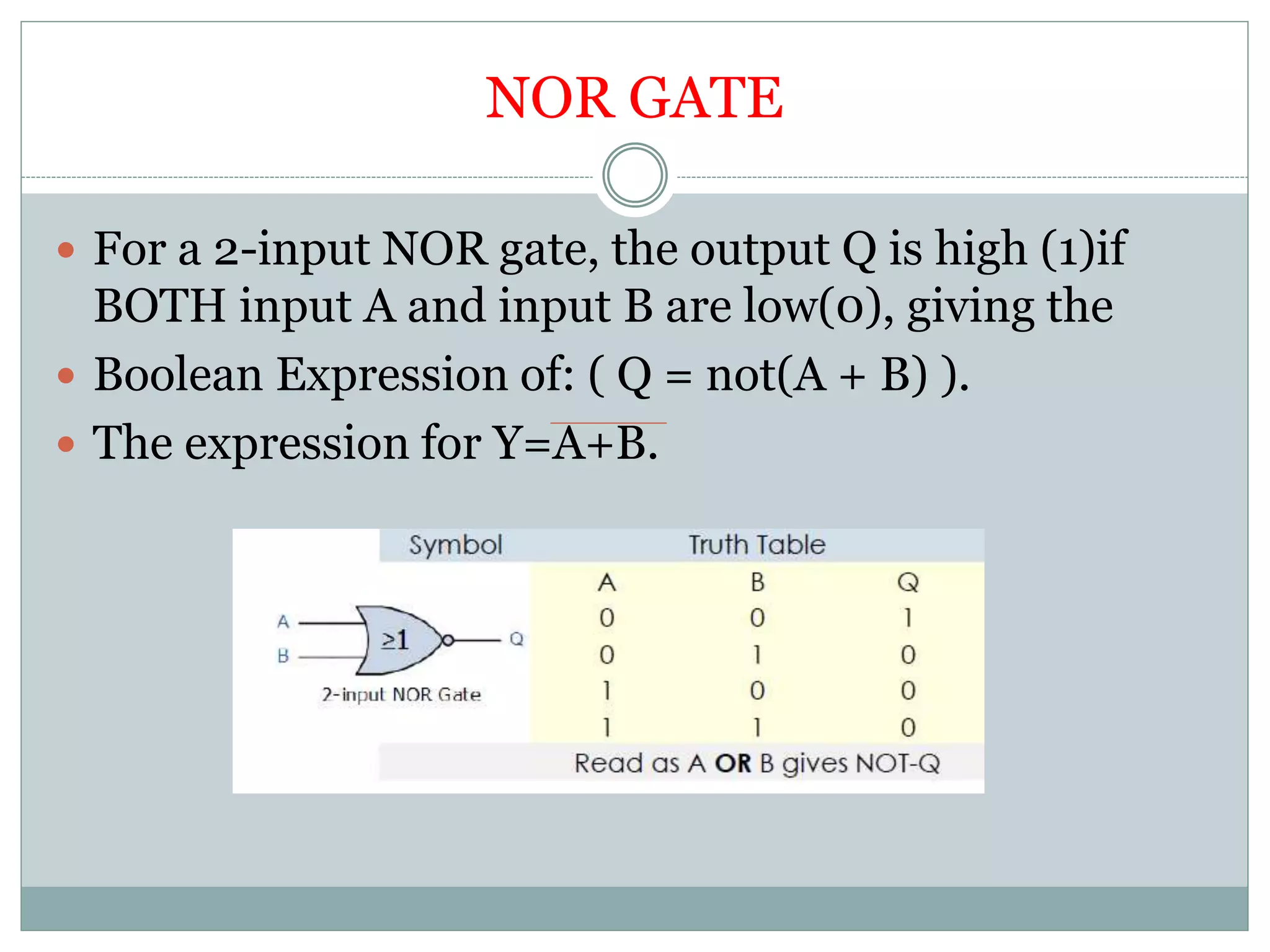
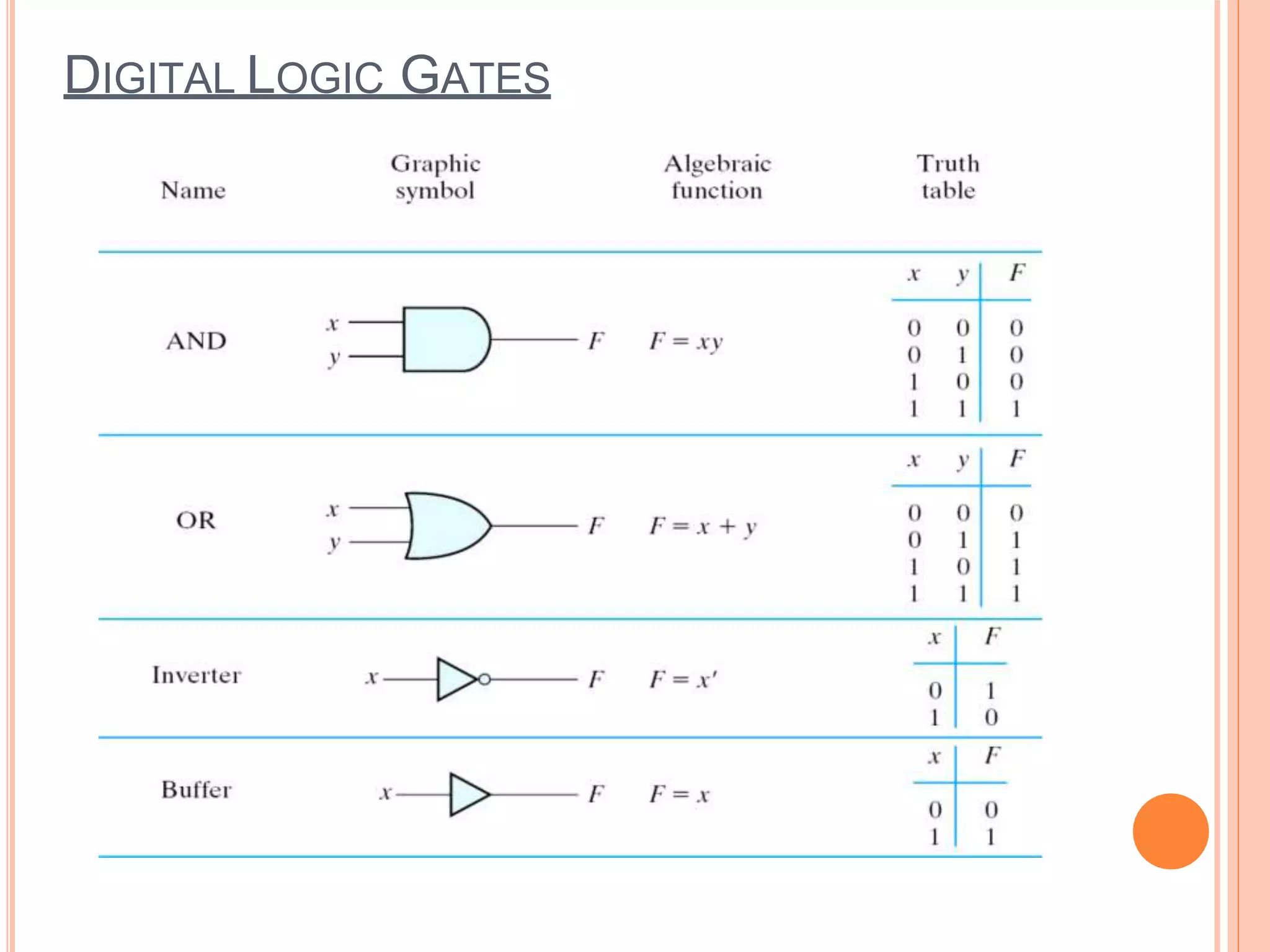
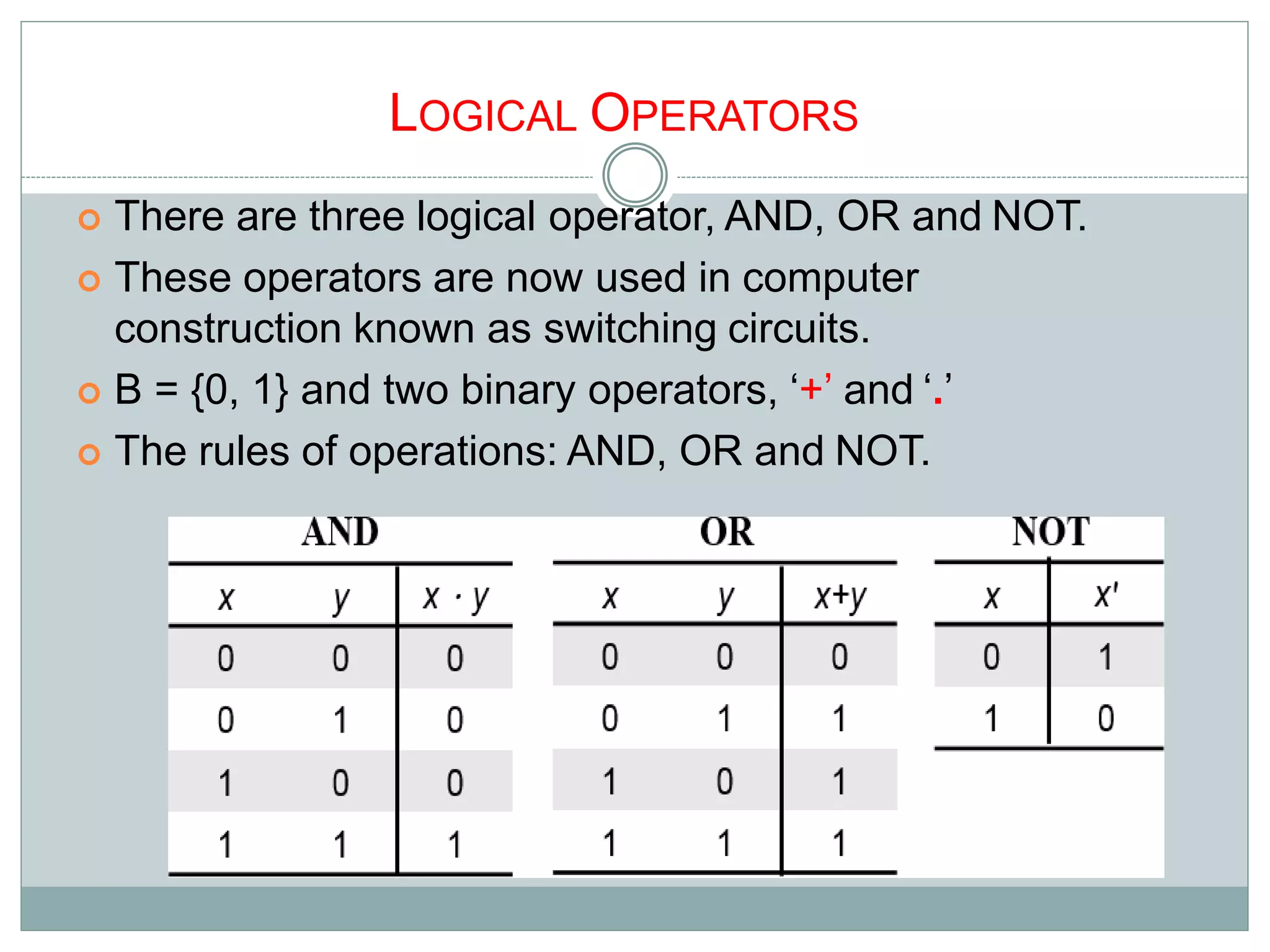
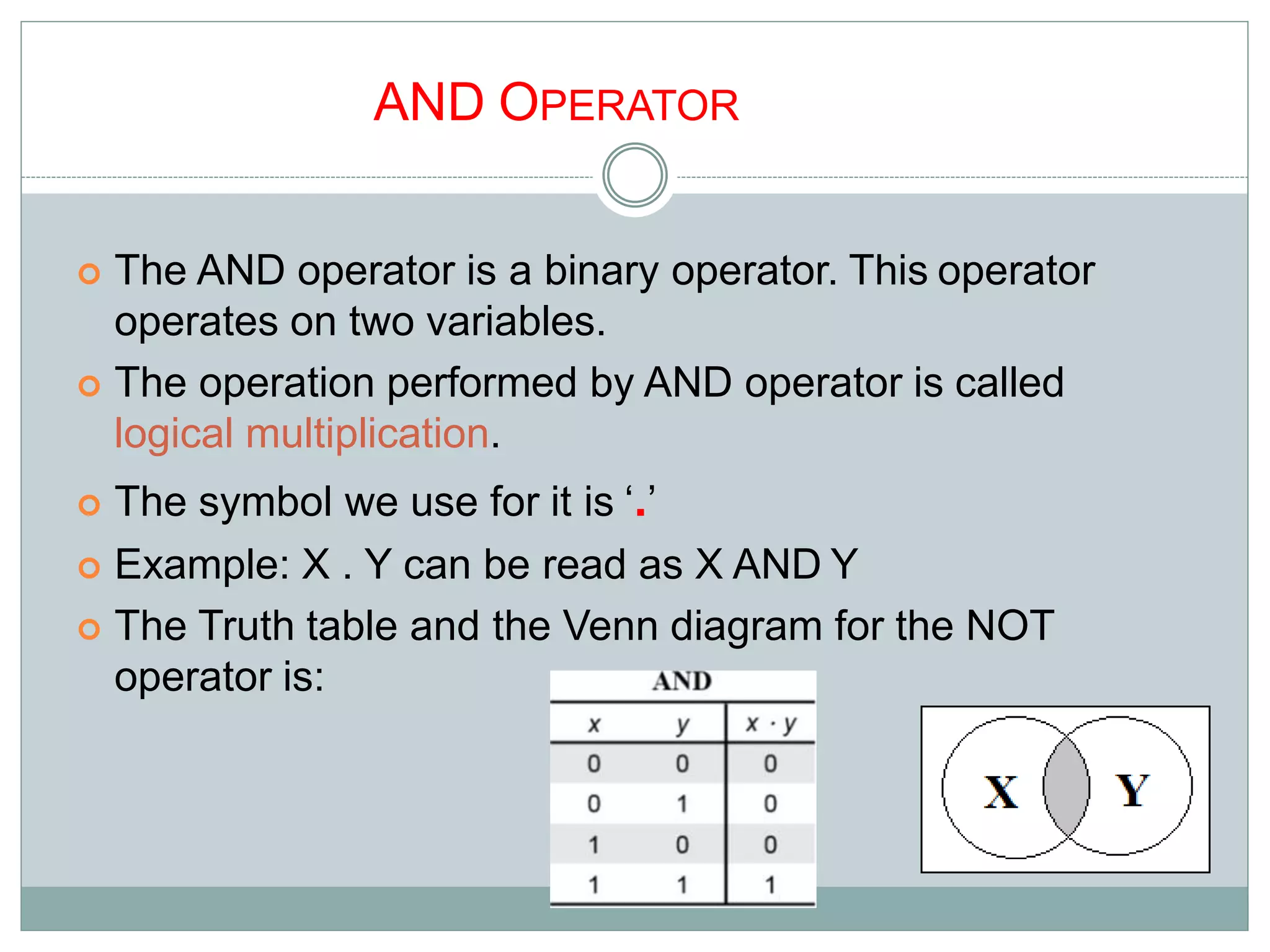
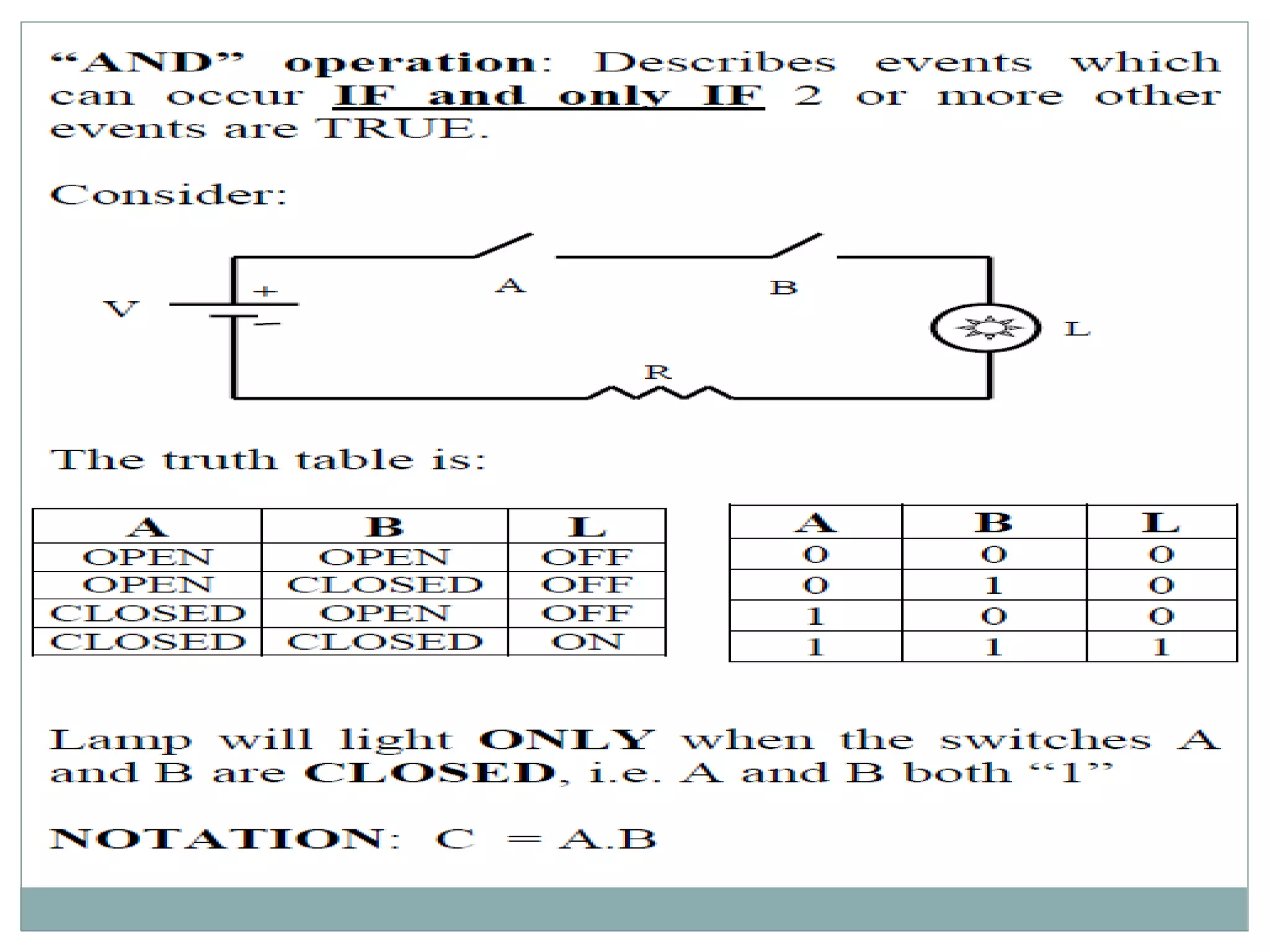
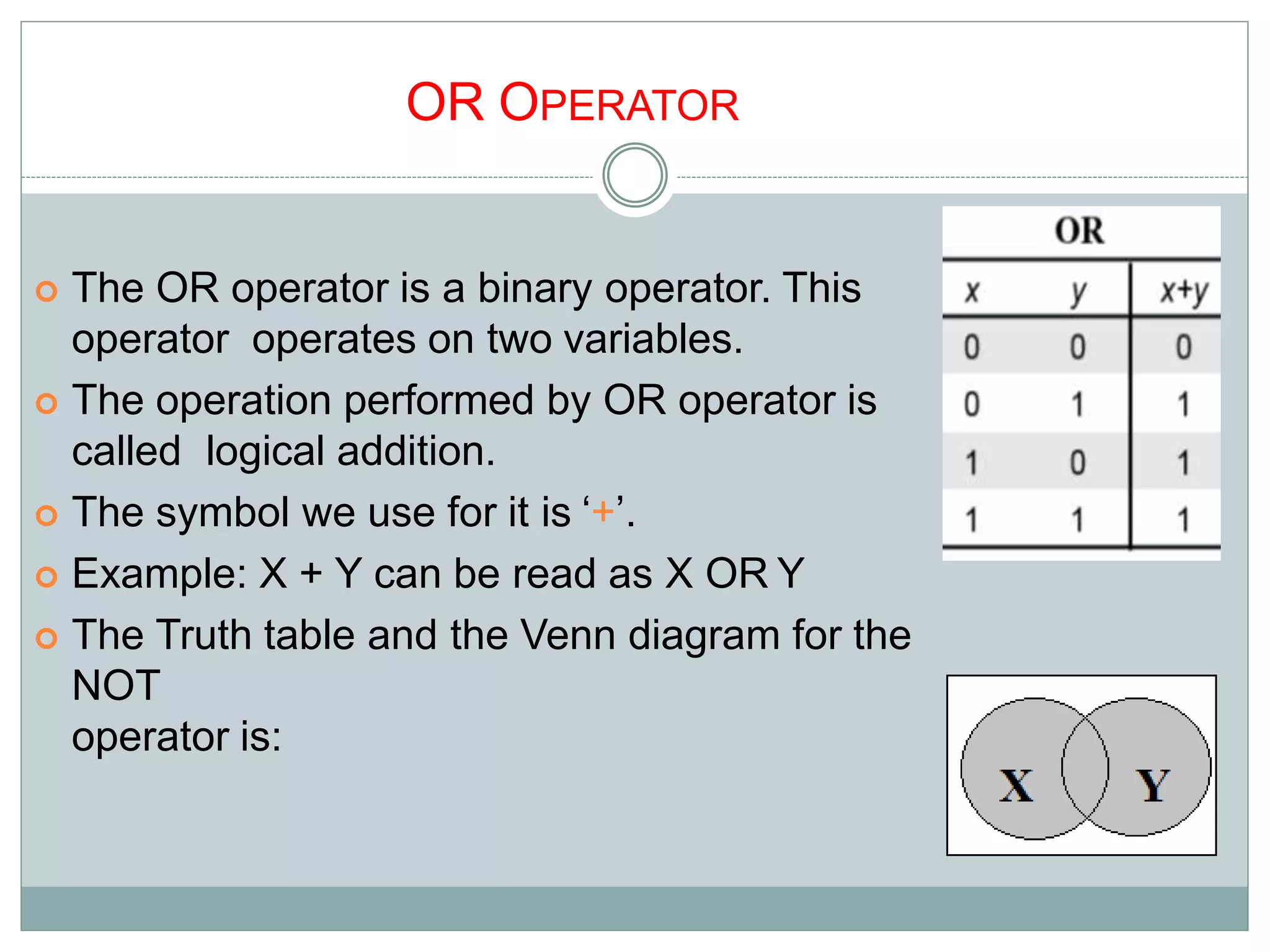
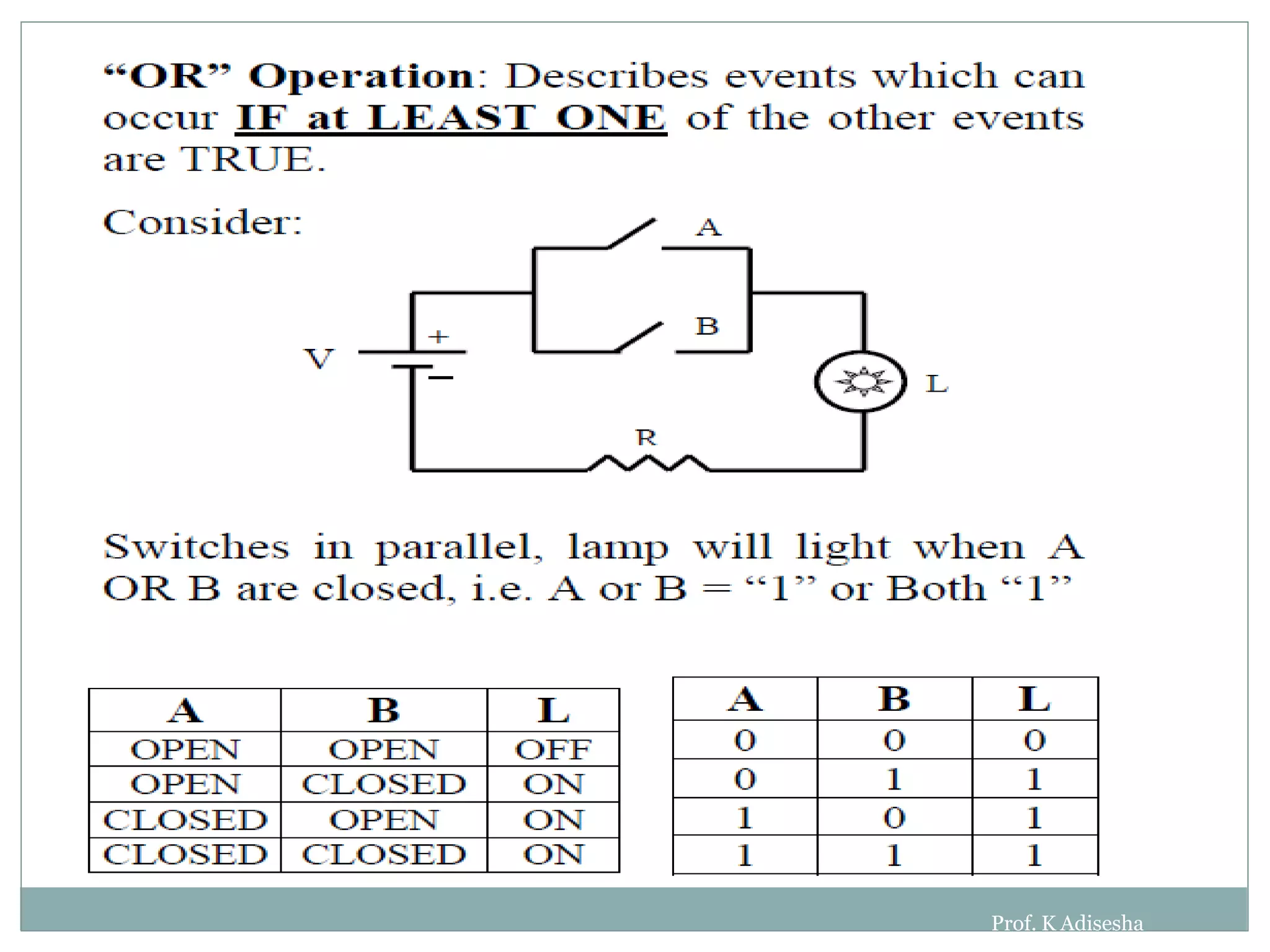
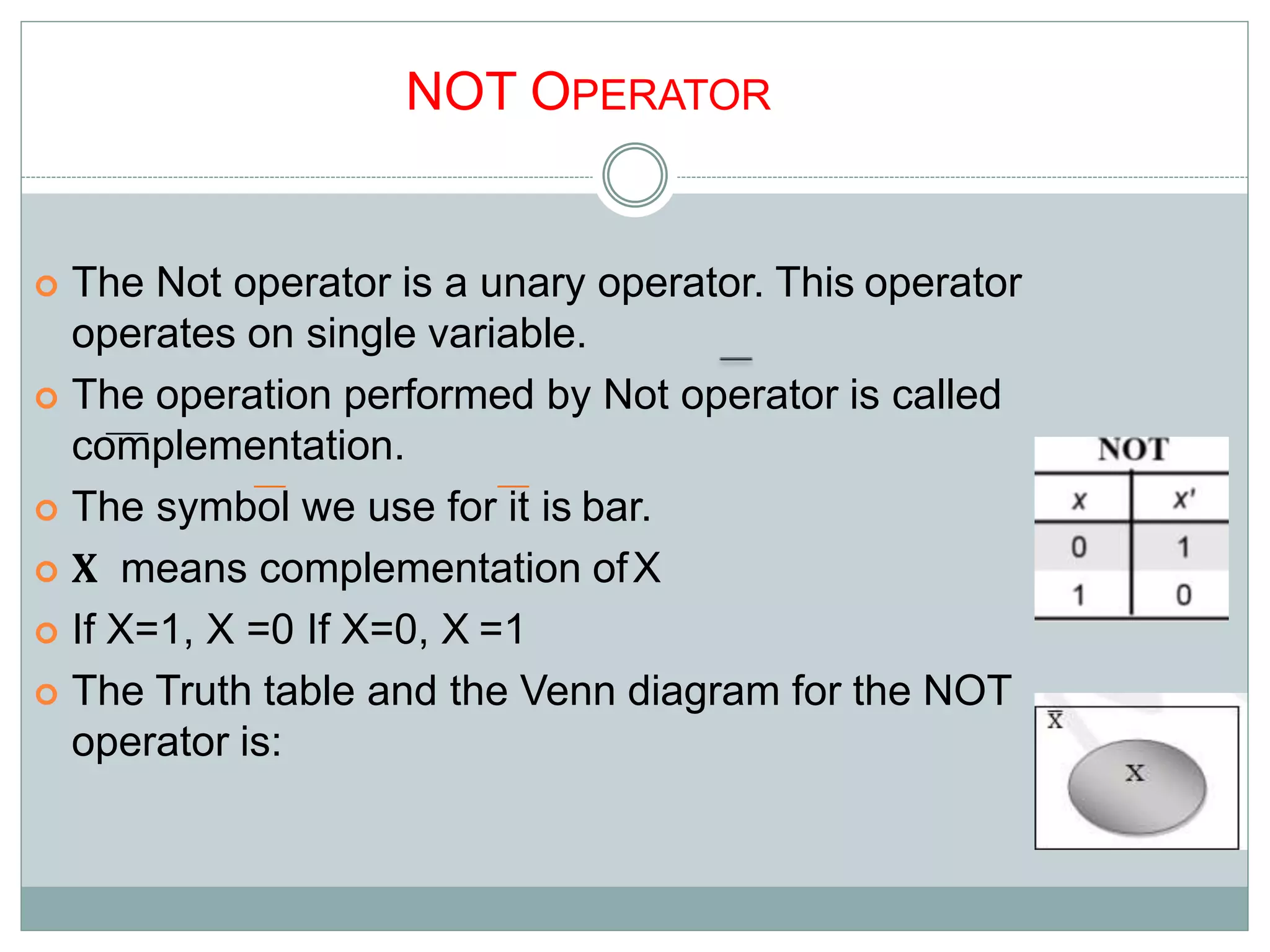
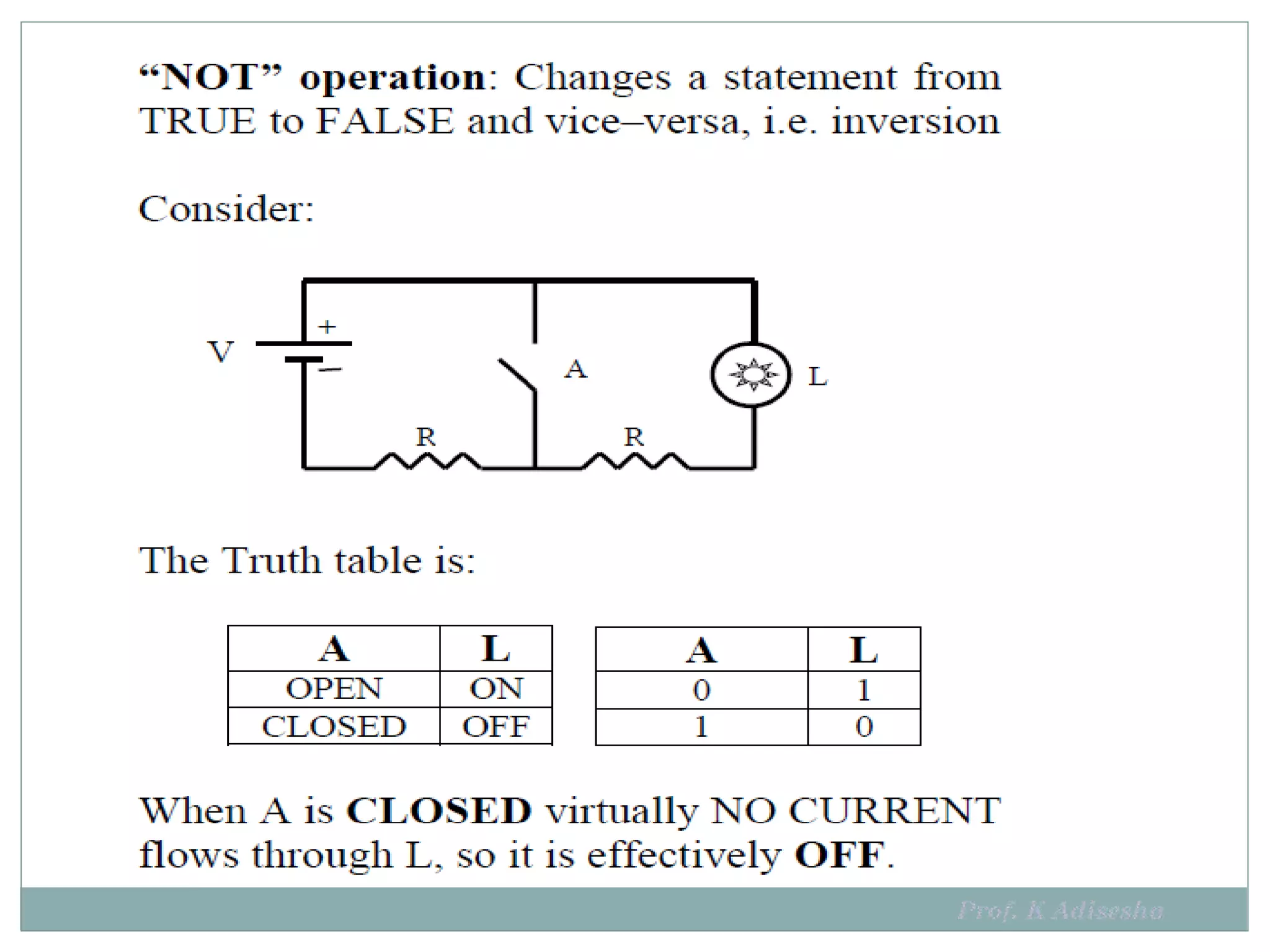
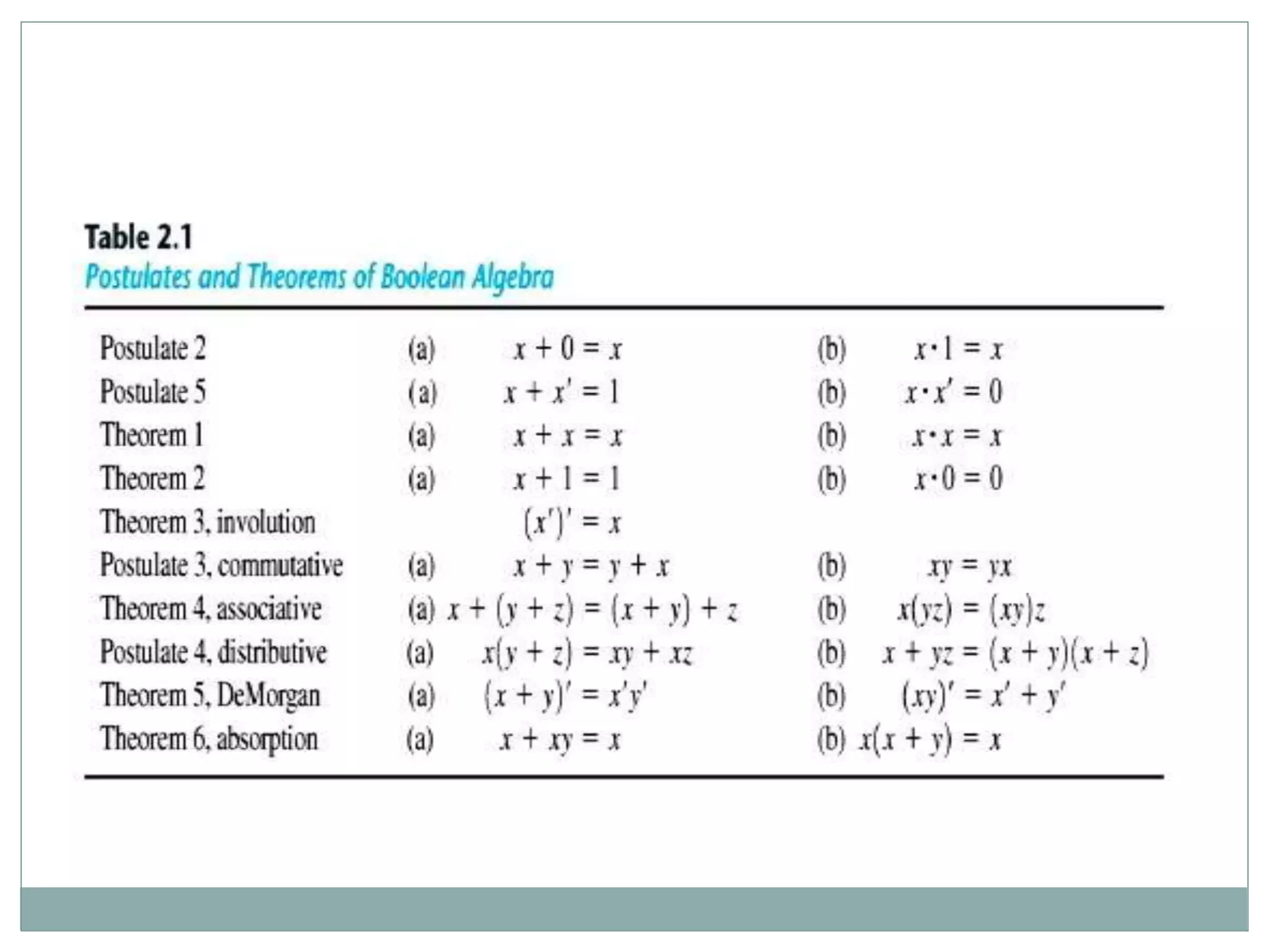
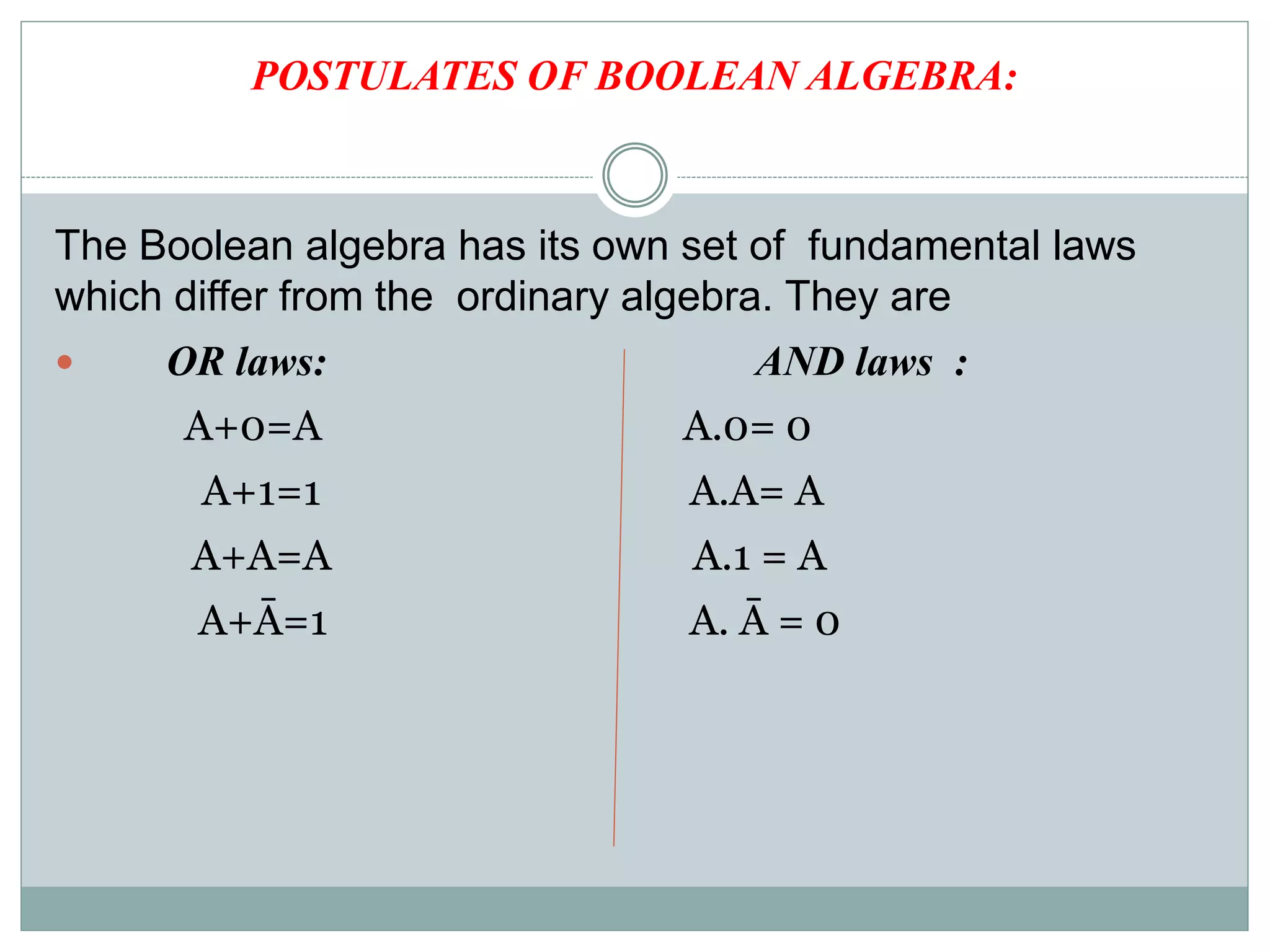
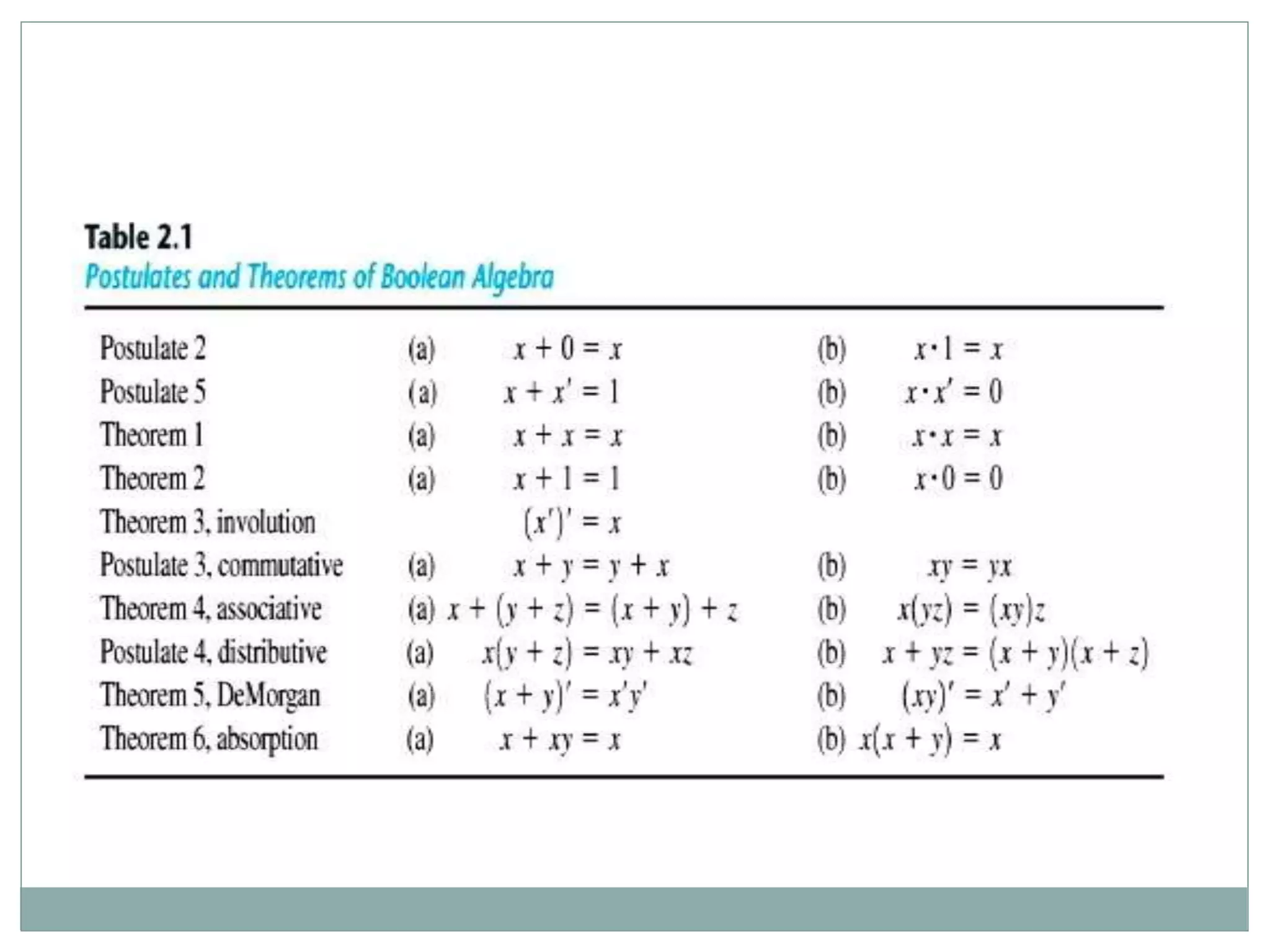
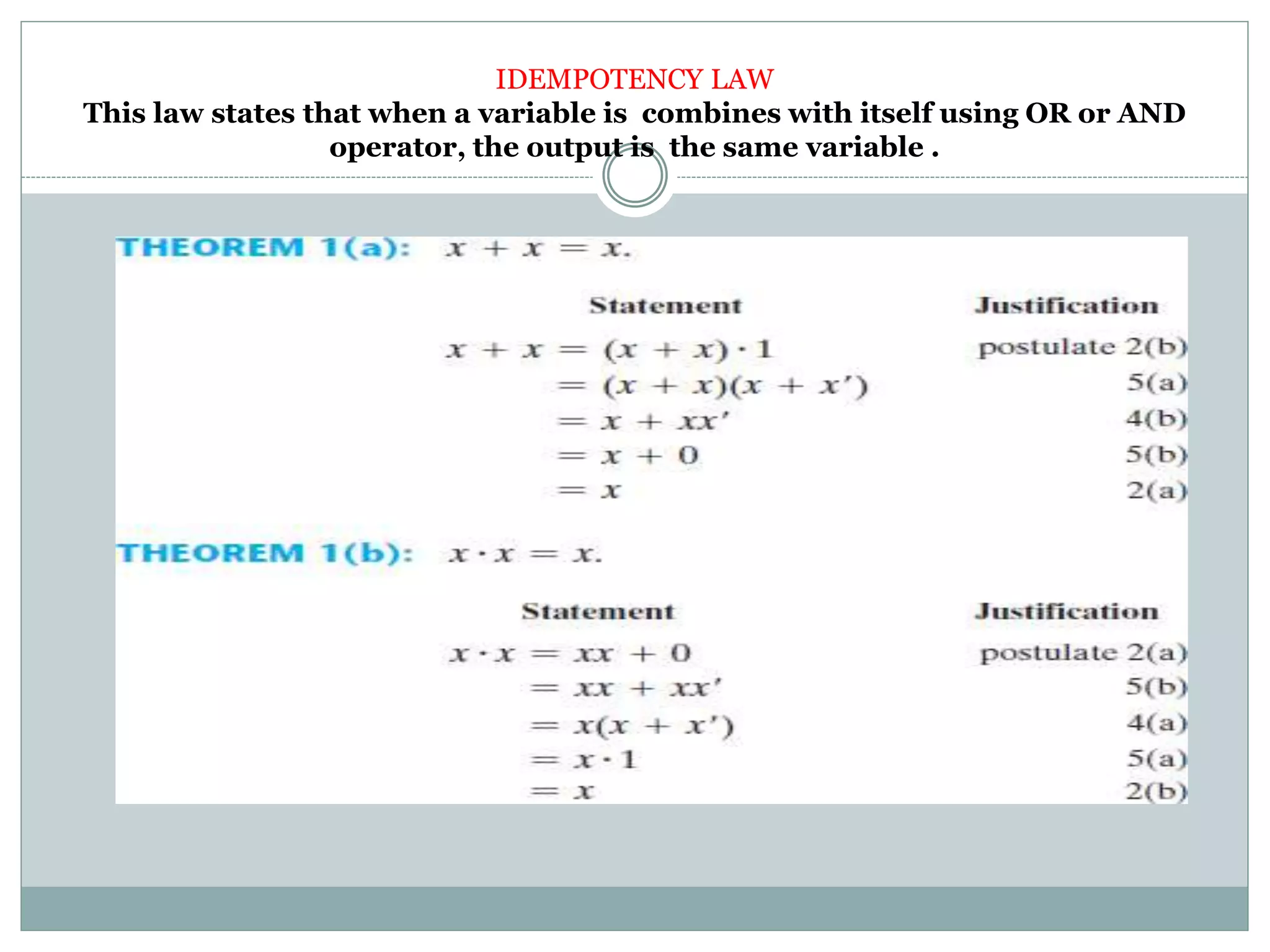
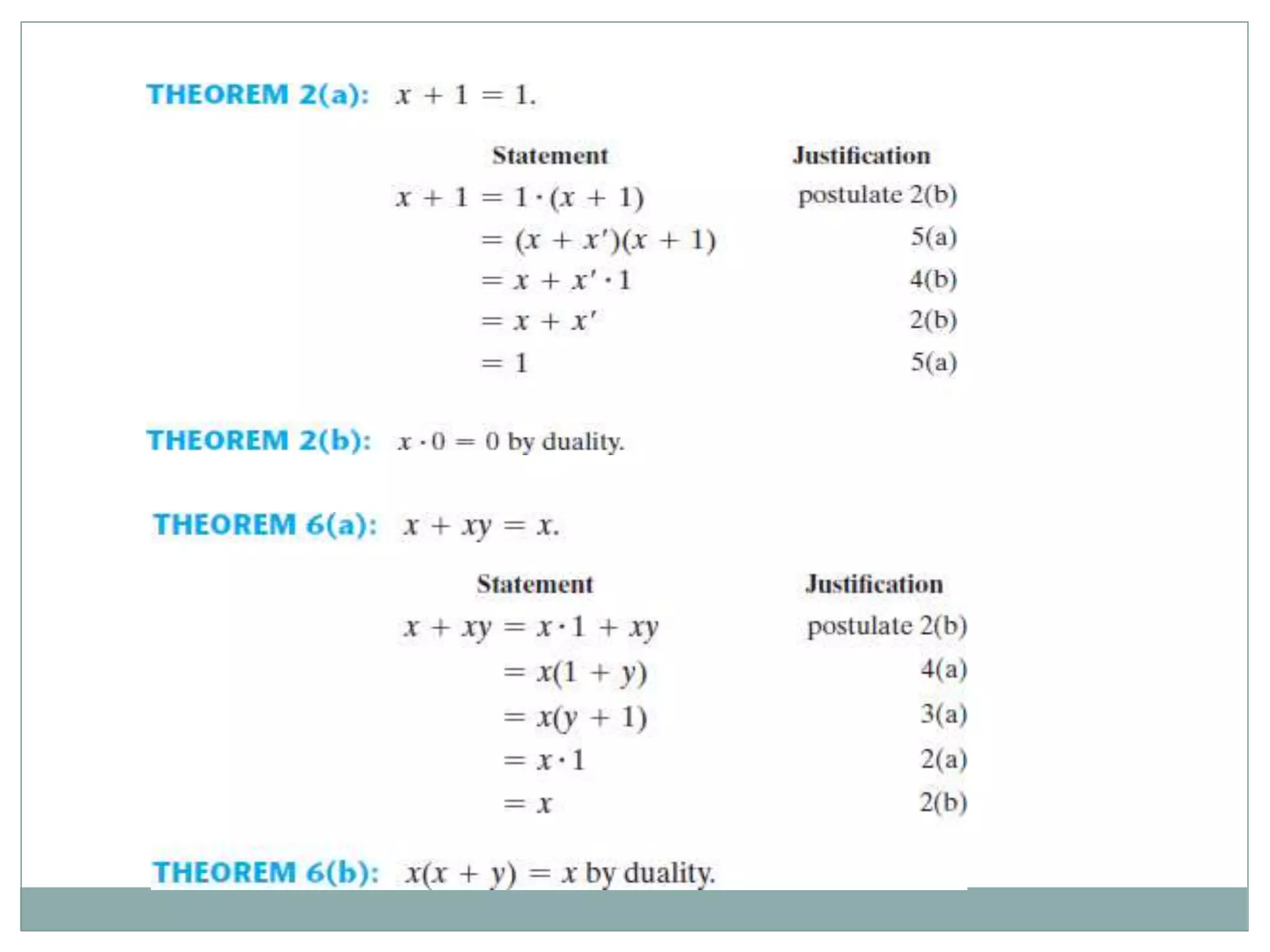
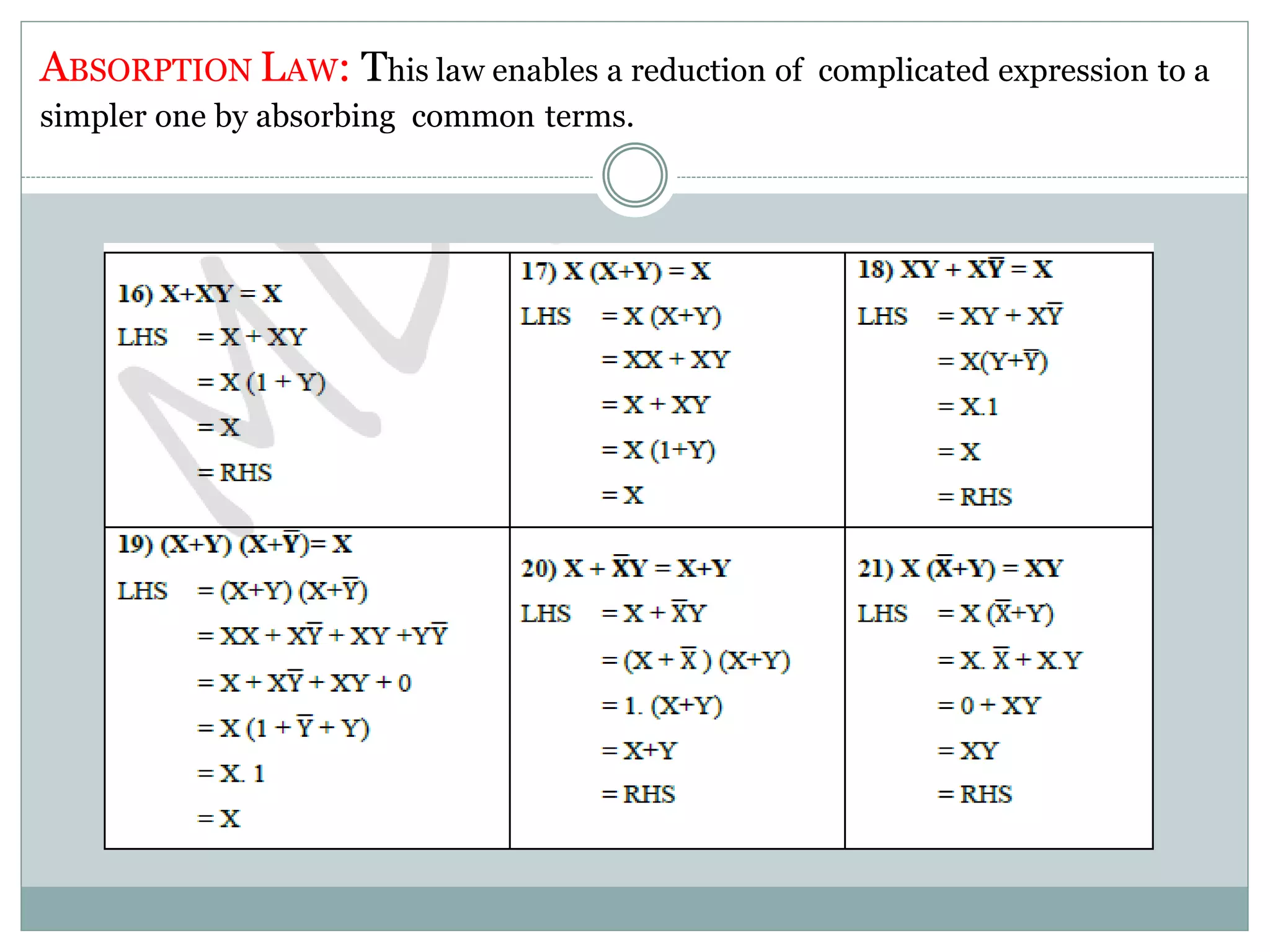
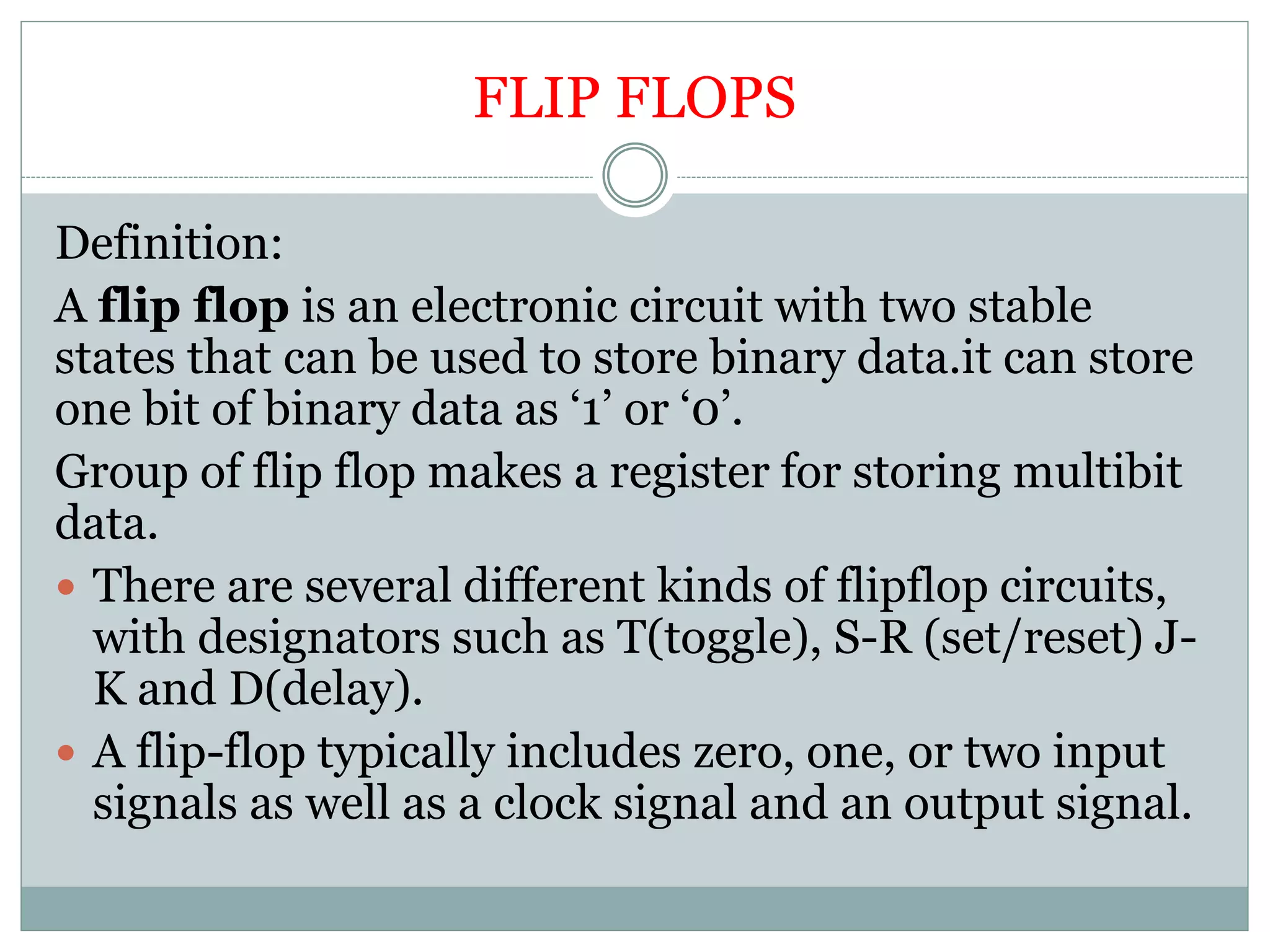
The document discusses different digital logic components including logic gates, flip flops, registers, and counters. It describes the basic types of logic gates such as AND, OR, NOT, NAND, and NOR gates. It also discusses different types of flip flops including T, S-R, J-K, and D flip flops which are used to store binary data. Registers are formed using groups of flip flops to store multi-bit data. Counters are also discussed as another component of digital logic systems.