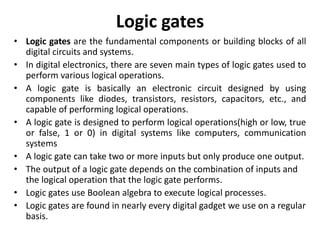
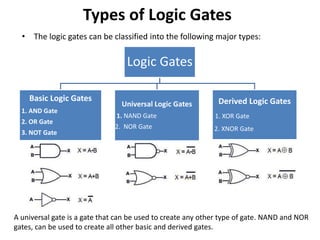
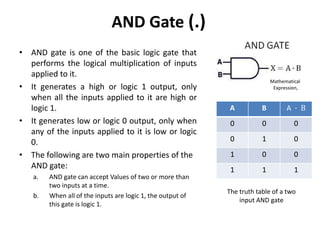
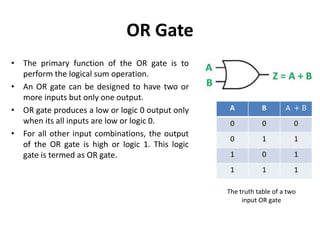
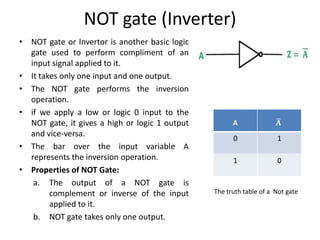
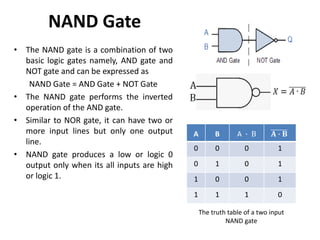
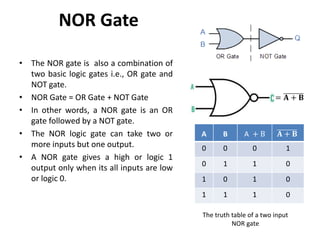
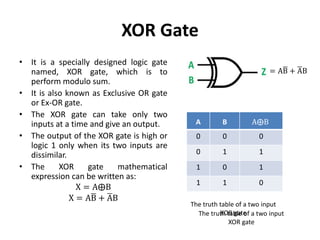
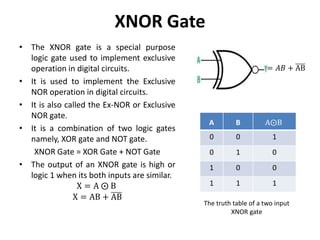
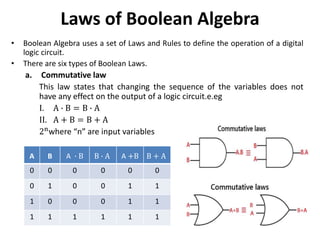
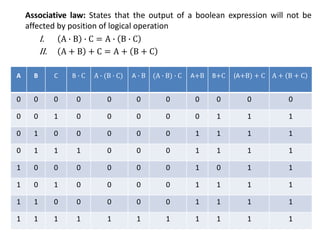
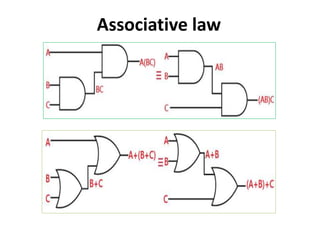
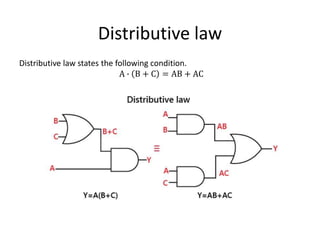
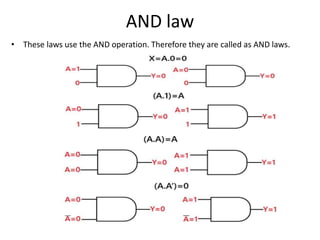
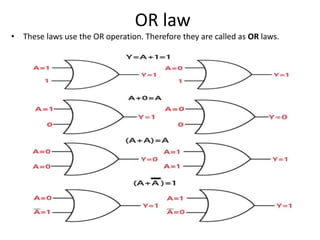
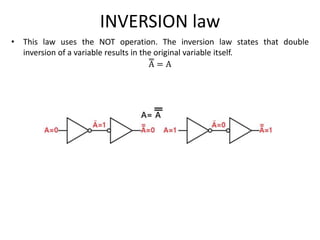
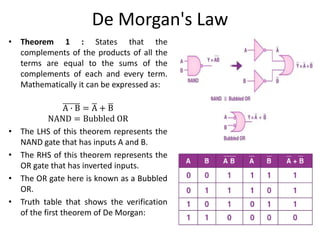
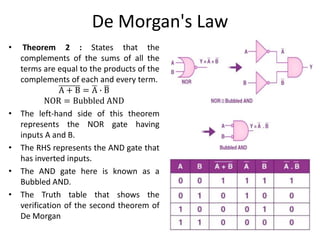
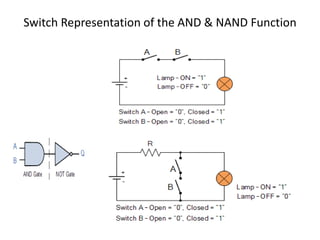
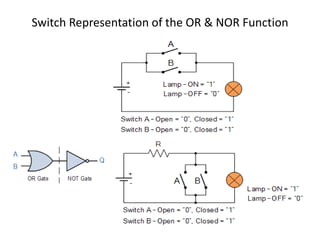
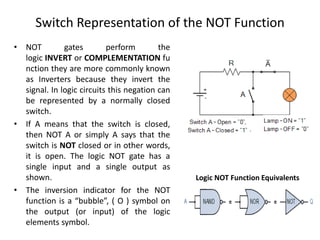
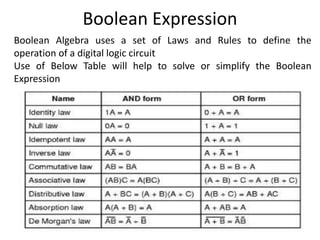
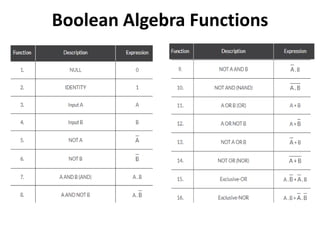
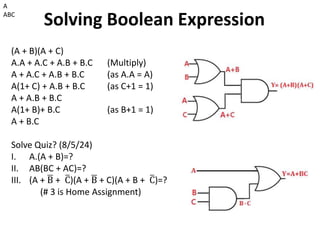
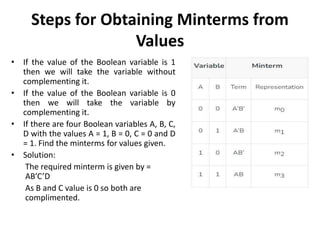
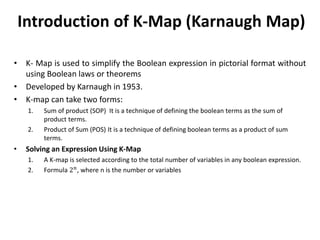
The document explains digital logic design focusing on logic gates, their functions, and boolean algebra. It outlines types of logic gates such as AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR, detailing their operations and truth tables. Additionally, it covers the basics of boolean algebra, its laws, and the use of Karnaugh maps (K-maps) for simplifying boolean expressions.