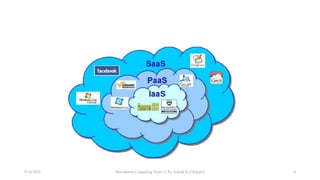
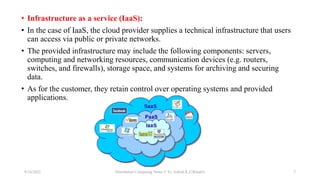
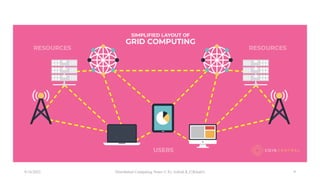
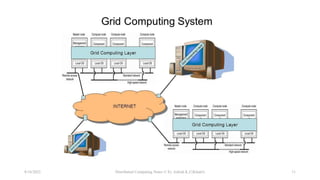
The document discusses three main types of distributed systems: cloud computing, grid computing, and cluster computing. Cloud computing uses distributed resources over the internet to provide scalable and cost-effective computing. Grid computing creates a virtual supercomputer by connecting computers to tackle computationally intensive problems. Cluster computing connects computers through a local network so they function as a single high-performance machine for mission-critical applications.