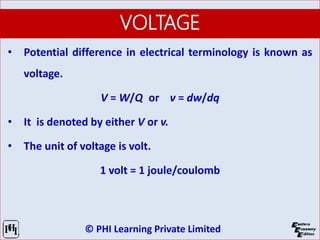
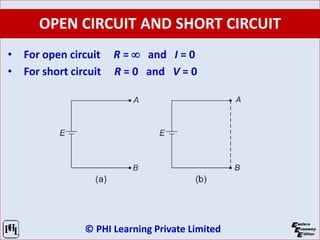
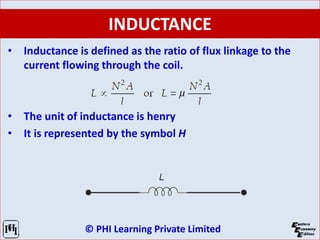
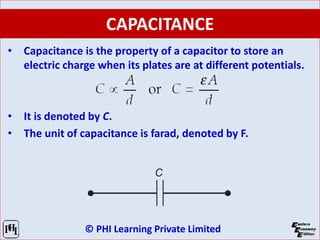
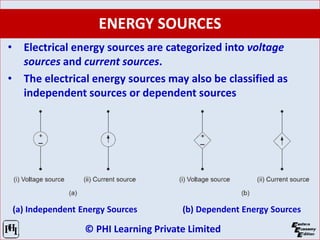
The document is a comprehensive guide on network analysis and synthesis, covering various electrical engineering topics including circuit elements, Kirchhoff’s laws, methods for analyzing circuits, and network theorems. It details key concepts such as voltage, current, resistance, inductance, capacitance, and energy sources, along with how these elements interact in both series and parallel configurations. Additionally, it provides information on different types of circuit components and laws governing electrical circuits.