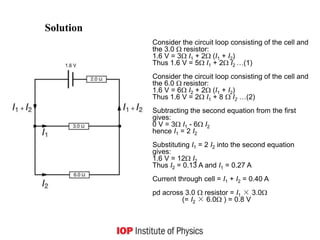
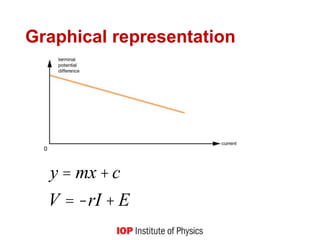
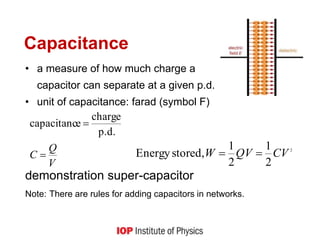
This document outlines the key concepts and learning outcomes for a circuit theory course, including:
1) Explaining DC circuits using concepts such as EMF, internal resistance, and potential dividers.
2) Analyzing DC circuits using Kirchhoff's laws to solve problems involving resistors, capacitors, and energy stored.
3) Describing resistance at a microscopic level and defining related concepts like resistivity and conductance.




![Resistors in series
V = V1+ V2 [conservation of energy]
IR = IR1 + IR2
R = R1 + R2 R is always larger than any of R1, R2 etc
Resistors in parallel
I = I1 + I2 [conservation of charge]
V/R = V/R1 + V/R2
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 R is always smaller than any of R1, R2 etc
Resistor networks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc-circuit-theory-230630061839-e6cb2f36/85/DC-circuit-theory-ppt-5-320.jpg)






![Conductivity
Metal wires conduct extremely well.
Conductance G = I / V , unit siemens (symbol S)
• depends on the number of carriers available
• ratio I / V is 'effect per unit of cause‘
Note:
• conductance is the reciprocal of resistance
• conductivity, [unit S m-1] is the reciprocal of resistivity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc-circuit-theory-230630061839-e6cb2f36/85/DC-circuit-theory-ppt-13-320.jpg)

![Kirchhoff’s 1st law
The total current
entering a circuit
junction equals the
total current
leaving it.
[conservation of charge]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc-circuit-theory-230630061839-e6cb2f36/85/DC-circuit-theory-ppt-16-320.jpg)
![Kirchhoff’s 2nd law
The sum of the emfs round a loop in any circuit
= the sum of the p.d.s round the loop.
[conservation of energy]
E1 + E2 + E3 + … = I1R1 + I2R2 + I3R3 + …
where I1, I2, I3 … represent currents through the resistances R1, R2,
R3 …
Physlets (simulations): ‘Second semester’< ‘DC Circuits’
• ‘Kirchhoff's Loop Rule’
• ‘Applying Kirchhoff's Rules’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc-circuit-theory-230630061839-e6cb2f36/85/DC-circuit-theory-ppt-17-320.jpg)