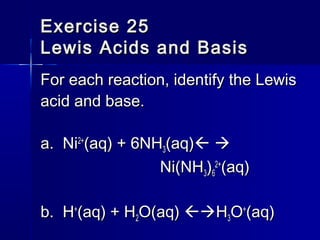This document provides an overview of acid-base theories and chemistry. It defines acids and bases according to three main theories:
1) Arrhenius theory defines acids as substances that donate H+ ions in water and bases as those that donate OH- ions.
2) Bronsted-Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors, providing a better explanation of substances like ammonia.
3) Lewis theory defines acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors, explaining both traditional acids/bases and coordination compounds.
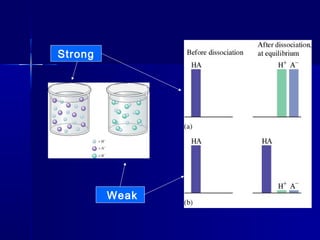
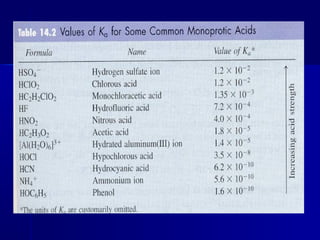
The document then discusses acid/base reactions and equilibrium expressions, relative acid/base strengths, and the differences between strong vs. weak acids and



























![a. Hydrochloric acid (HCl)a. Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
b. Acetic acid (HCb. Acetic acid (HC22HH33OO22))
c. The ammonium ion (NHc. The ammonium ion (NH44
++
))
d. The anilinium ion (Cd. The anilinium ion (C66HH55NHNH33
++
))
e. The hydrated aluminum(III) ione. The hydrated aluminum(III) ion
[Al(H[Al(H O)O) ]]3+3+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-28-320.jpg)
















![For Weak Acid Reactions:For Weak Acid Reactions:
HA + HHA + H22OO HH33OO++
+ A+ A--
KKaa == [H[H33OO++
][A][A--
]] < 1< 1
[HA][HA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-46-320.jpg)



![For Weak Base Reactions:For Weak Base Reactions:
B + HB + H22OO HBHB++
+ OH+ OH--
KKbb == [H[H33OO++
][OH][OH--
]] <1<1
[B][B]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-52-320.jpg)









![In pure water or dilute aqueousIn pure water or dilute aqueous
solutions, the concentration of watersolutions, the concentration of water
can be considered to be a constantcan be considered to be a constant
(55.4 M), so we include that with the(55.4 M), so we include that with the
equilibrium constant and write theequilibrium constant and write the
expression as:expression as:
KKeqeq[H[H22O]O]22
= K= Kww = [H= [H33OO++
][OH][OH--
]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-62-320.jpg)

![[OH[OH--
] = [H] = [H++
] : solution is neutral (in] : solution is neutral (in
pure water, each of these is 1.0 x 10pure water, each of these is 1.0 x 10-7-7
))
[OH[OH--
] > [H] > [H++
] : solution is basic] : solution is basic
[OH[OH--
] < [H] < [H++
] : solution is acidic] : solution is acidic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-64-320.jpg)


![Exercise 5, cont.Exercise 5, cont.
b. Calculate [Hb. Calculate [H++
] and [OH] and [OH--
] in a] in a
neutral solution at 60°C.neutral solution at 60°C.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-67-320.jpg)
![SolutionSolution
A: endothermicA: endothermic
B: [HB: [H++
] = [OH] = [OH--
] = 3 X 10] = 3 X 10-7-7
MM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-68-320.jpg)
![The pH ScaleThe pH Scale
Used toUsed to
designate thedesignate the
[H[H++
] in most] in most
aqueousaqueous
solutions wheresolutions where
HH++
is small.is small.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-69-320.jpg)
![pH = - log [HpH = - log [H++
]]
pOH = - log [OHpOH = - log [OH--
]]
pH + pOH = 14pH + pOH = 14
pH = 6.9 and lower (acidic)pH = 6.9 and lower (acidic)
= 7.0 (neutral)= 7.0 (neutral)
= 7.1 and greater (basic)= 7.1 and greater (basic)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-70-320.jpg)

![Exercise 6Exercise 6
Calculating [HCalculating [H++
] and [OH] and [OH--
]]
Calculate [HCalculate [H++
] or [OH] or [OH--
] as required for] as required for
each of the following solutions ateach of the following solutions at
25°C, and state whether the solution25°C, and state whether the solution
is neutral, acidic, or basic.is neutral, acidic, or basic.
a. 1.0 X 10a. 1.0 X 10-5-5
MM OHOH--
b. 1.0 X 10b. 1.0 X 10-7-7
MM OHOH--
c. 10.0c. 10.0 MM HH++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-72-320.jpg)
![SolutionSolution
A: [HA: [H++
] = 1.0 X 10] = 1.0 X 10-9-9
M,M, basicbasic
B: [HB: [H++
] = 1.0 X 10] = 1.0 X 10-7-7
M,M, neutralneutral
C: [OHC: [OH--
] = 1.0 X 10] = 1.0 X 10-15-15
M,M, acidicacidic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-73-320.jpg)



![Exercise 8Exercise 8
CalculatingCalculating
pHpH
The pH of a sample of human bloodThe pH of a sample of human blood
was measured to be 7.41 at 25°C.was measured to be 7.41 at 25°C.
Calculate pOH, [HCalculate pOH, [H++
], and [OH], and [OH--
] for] for
the sample.the sample.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-77-320.jpg)
![SolutionSolution
pOH = 6.59pOH = 6.59
[H[H++
] = 3.9 X 10] = 3.9 X 10-8-8
[OH[OH--
] = 2.6 X 10] = 2.6 X 10-7-7
MM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-78-320.jpg)








![The KThe Kaa of acetic acid is 1.8 x 10of acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5-5
HCHC22HH33OO22 ↔↔ HH++
+ C+ C22HH33OO22
--
KKaa == [H[H++
][C][C22HH33OO22
--
]] = 1.8 x 10= 1.8 x 10-5-5
[HC[HC22HH33OO22]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-87-320.jpg)



![To be valid, x must be less thanTo be valid, x must be less than
5% of the number that it was to be5% of the number that it was to be
subtracted from.subtracted from.
% dissociation =% dissociation = "x""x" x 100x 100
[original][original]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-91-320.jpg)




![Since a concentration canSince a concentration can
not be negative…not be negative…
x = 3.5 x 10x = 3.5 x 10-5-5
MM
x = [Hx = [H++
] = 3.5 x 10] = 3.5 x 10-5-5
pH = -log 3.5 x 10pH = -log 3.5 x 10-5-5
= 4.46= 4.46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-96-320.jpg)






![Determination of the pH ofDetermination of the pH of
a Mixture of Weak Acidsa Mixture of Weak Acids
Only the acid with the largest KOnly the acid with the largest Kaa
value will contribute an appreciablevalue will contribute an appreciable
[H[H++
].].
Determine the pH based onDetermine the pH based on
this acid and ignore any others.this acid and ignore any others.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-103-320.jpg)


![SolutionSolution
pH = 1.35pH = 1.35
[CN[CN--
] = 1.4 X 10] = 1.4 X 10-8-8
MM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-106-320.jpg)






![Remember, however, thatRemember, however, that xx is theis the
[OH[OH--
]] and taking the negative logand taking the negative log
ofof xx will give you thewill give you the pOHpOH and notand not
the pH!the pH!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-113-320.jpg)









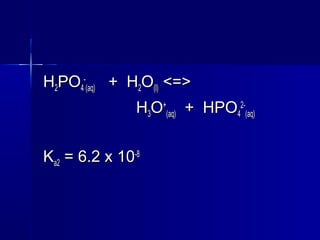



![The [HThe [H++
] obtained from this 2nd] obtained from this 2nd
and 3rd dissociation is negligibleand 3rd dissociation is negligible
compared to the [Hcompared to the [H++
] from the 1st] from the 1st
dissociation.dissociation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-127-320.jpg)


![SolutionSolution
pH = 0.72pH = 0.72
[H[H33POPO44] = 4.8] = 4.8 MM
[H[H22POPO44
--
] = 0.19] = 0.19 MM
[HPO[HPO44
2-2-
] = 6.2 X 10] = 6.2 X 10-8-8
MM
[PO[PO44
3-3-
] = 1.6 X 10] = 1.6 X 10-19-19
MM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14acidsbases-150706150729-lva1-app6892/85/acids-_bases-130-320.jpg)