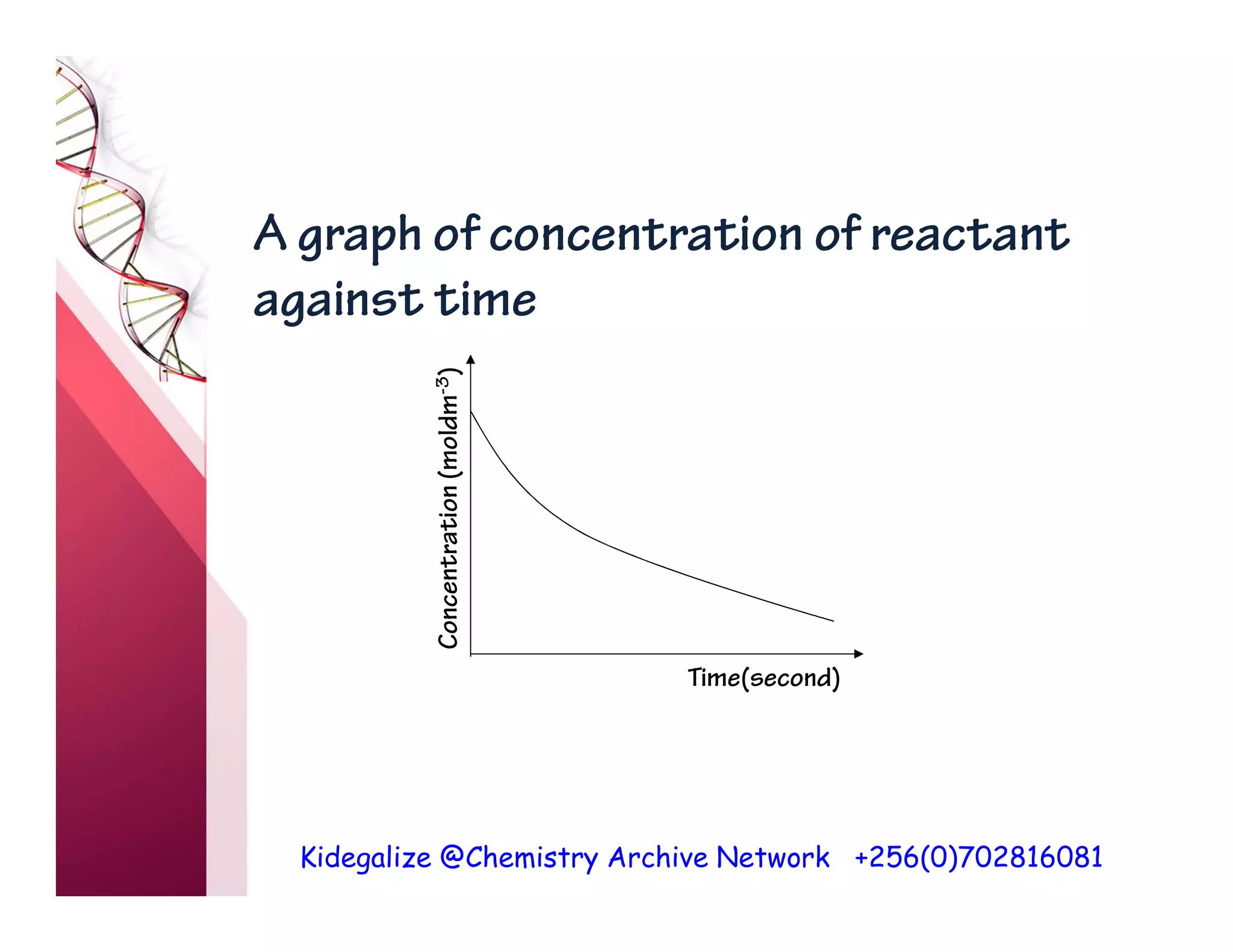
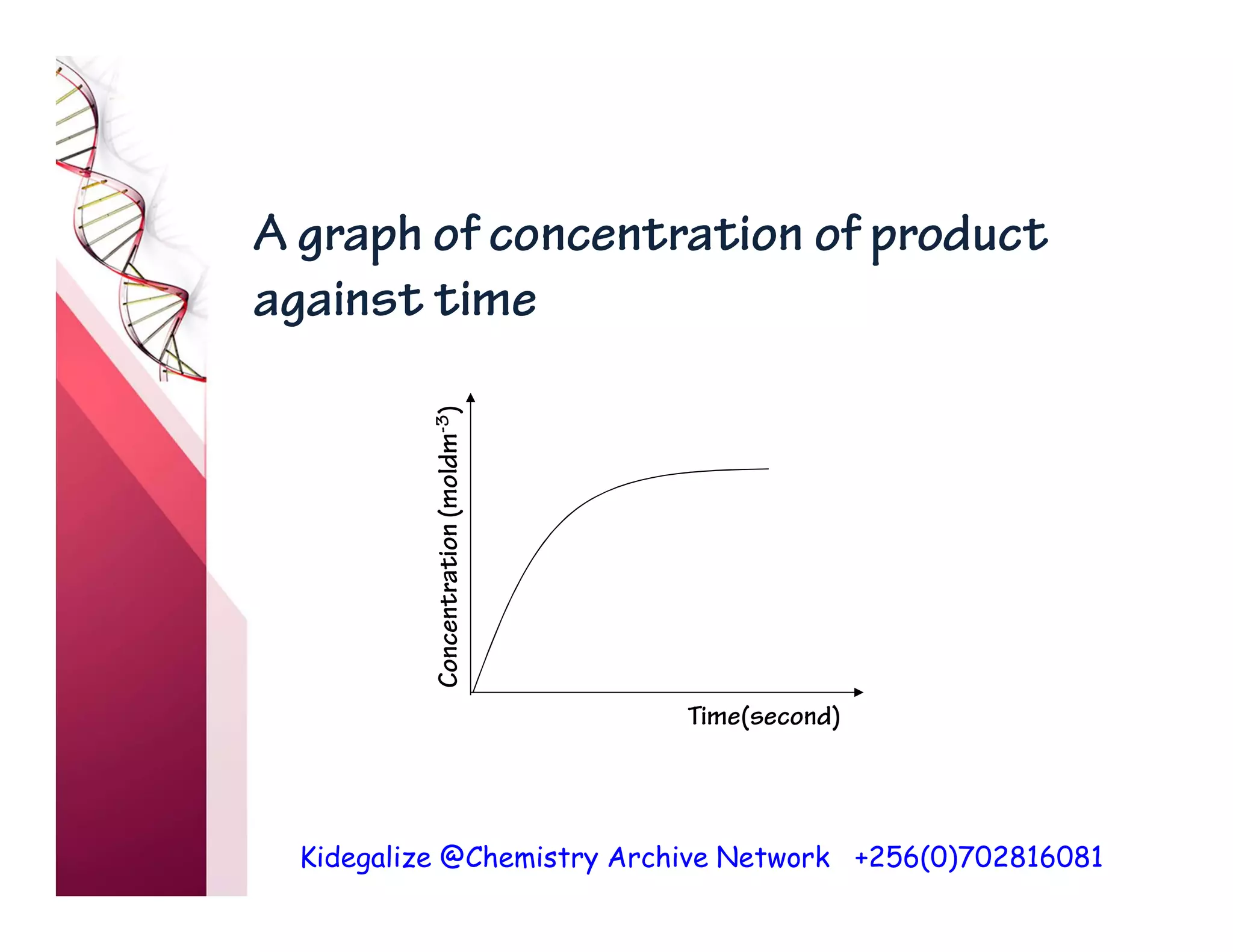
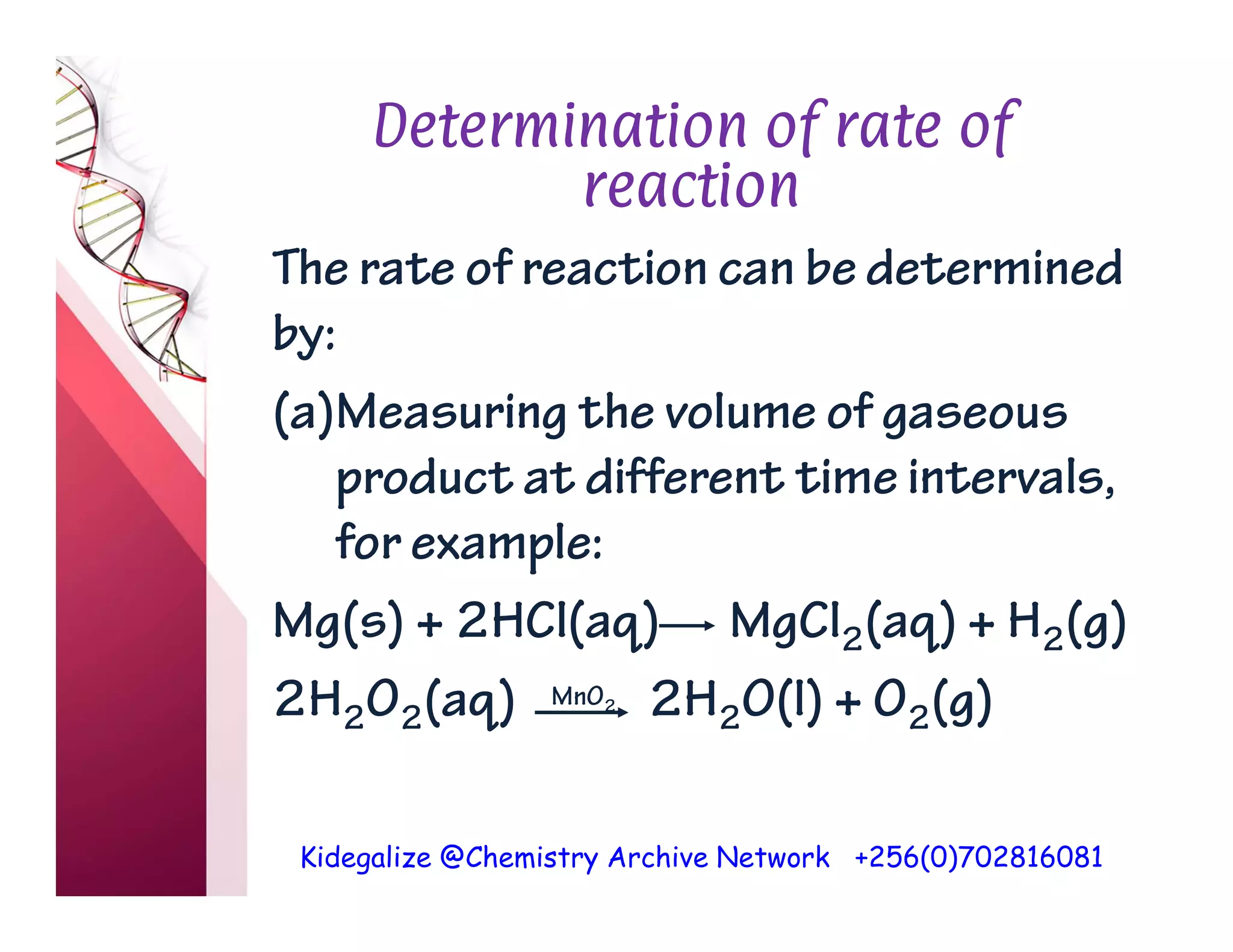
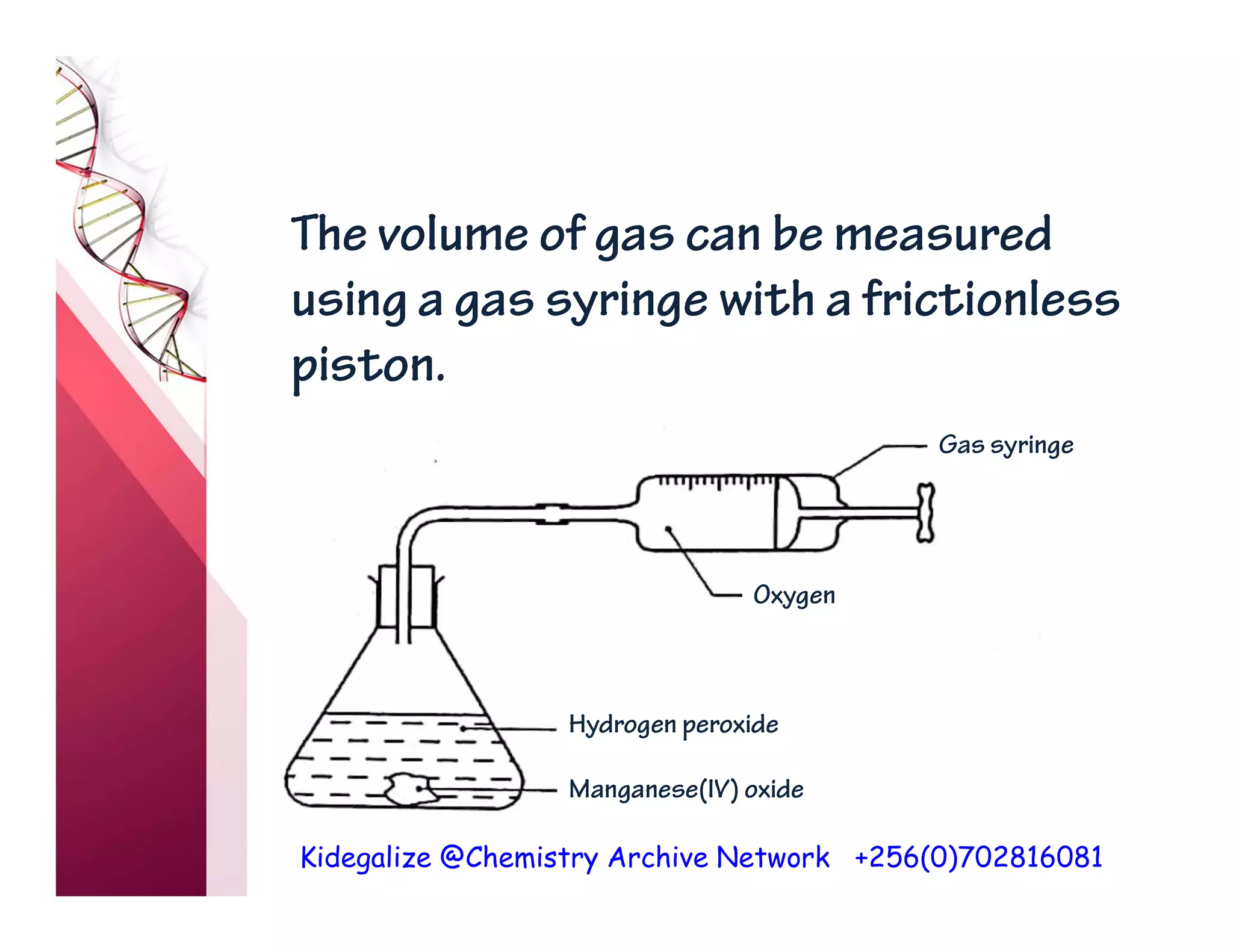
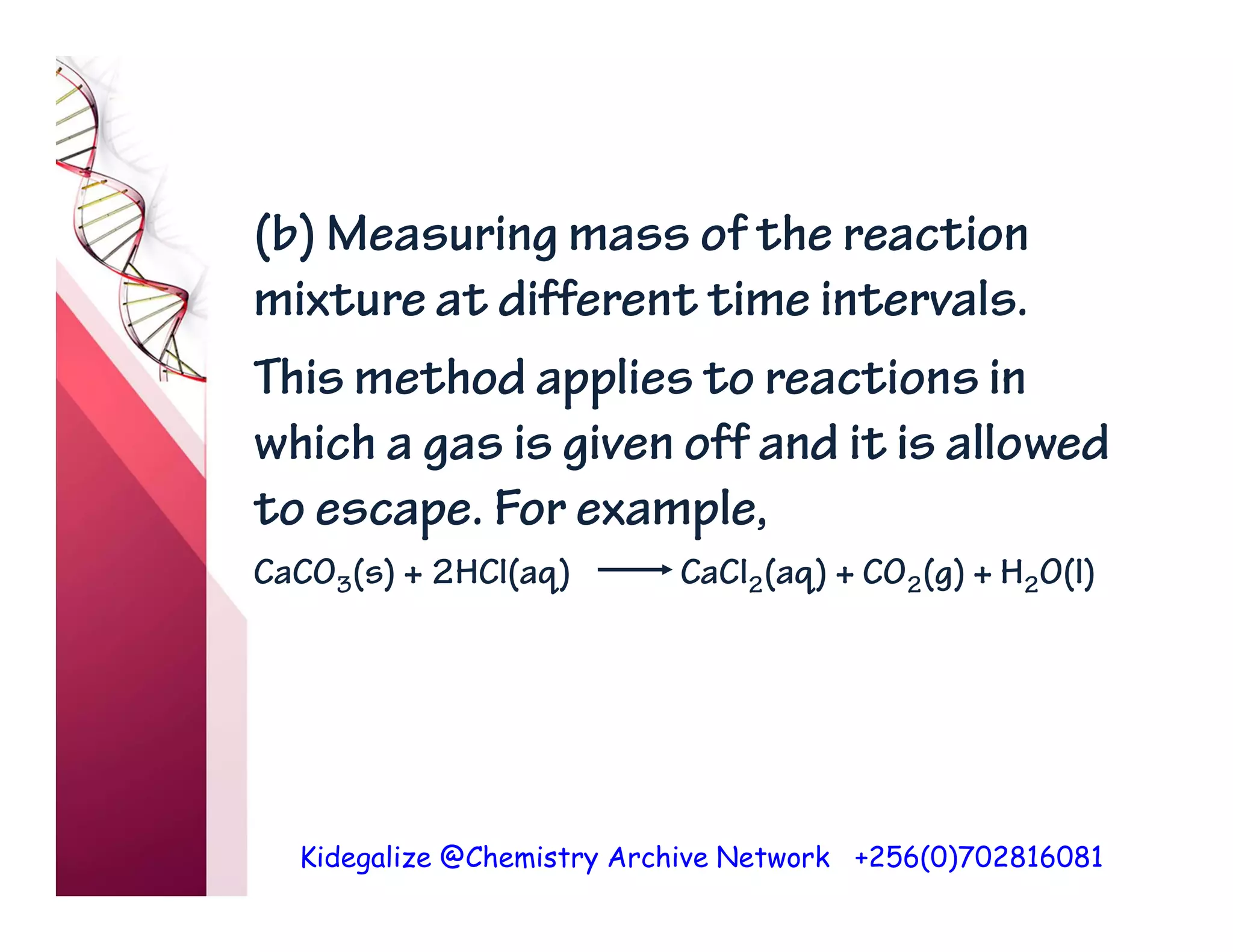
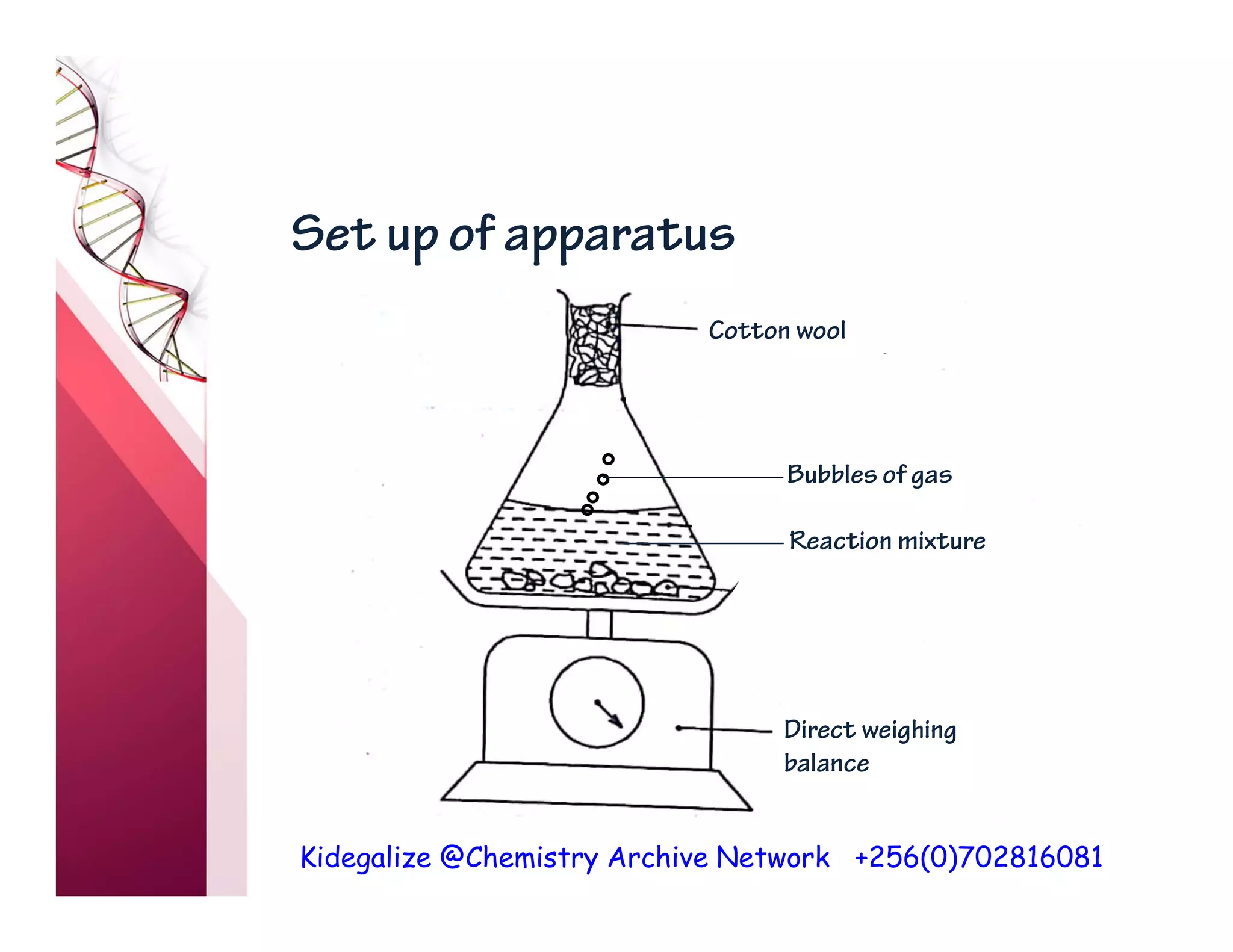
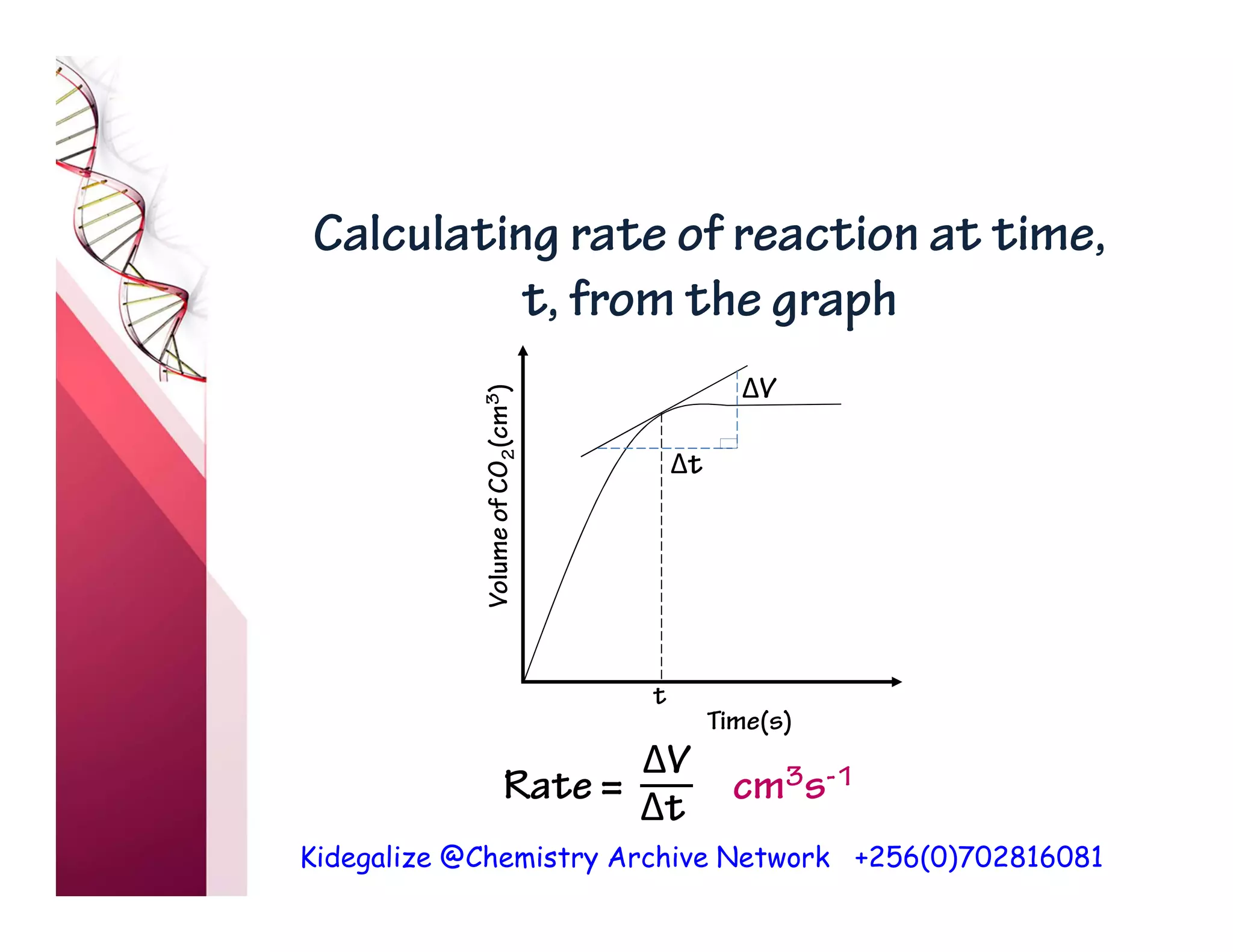
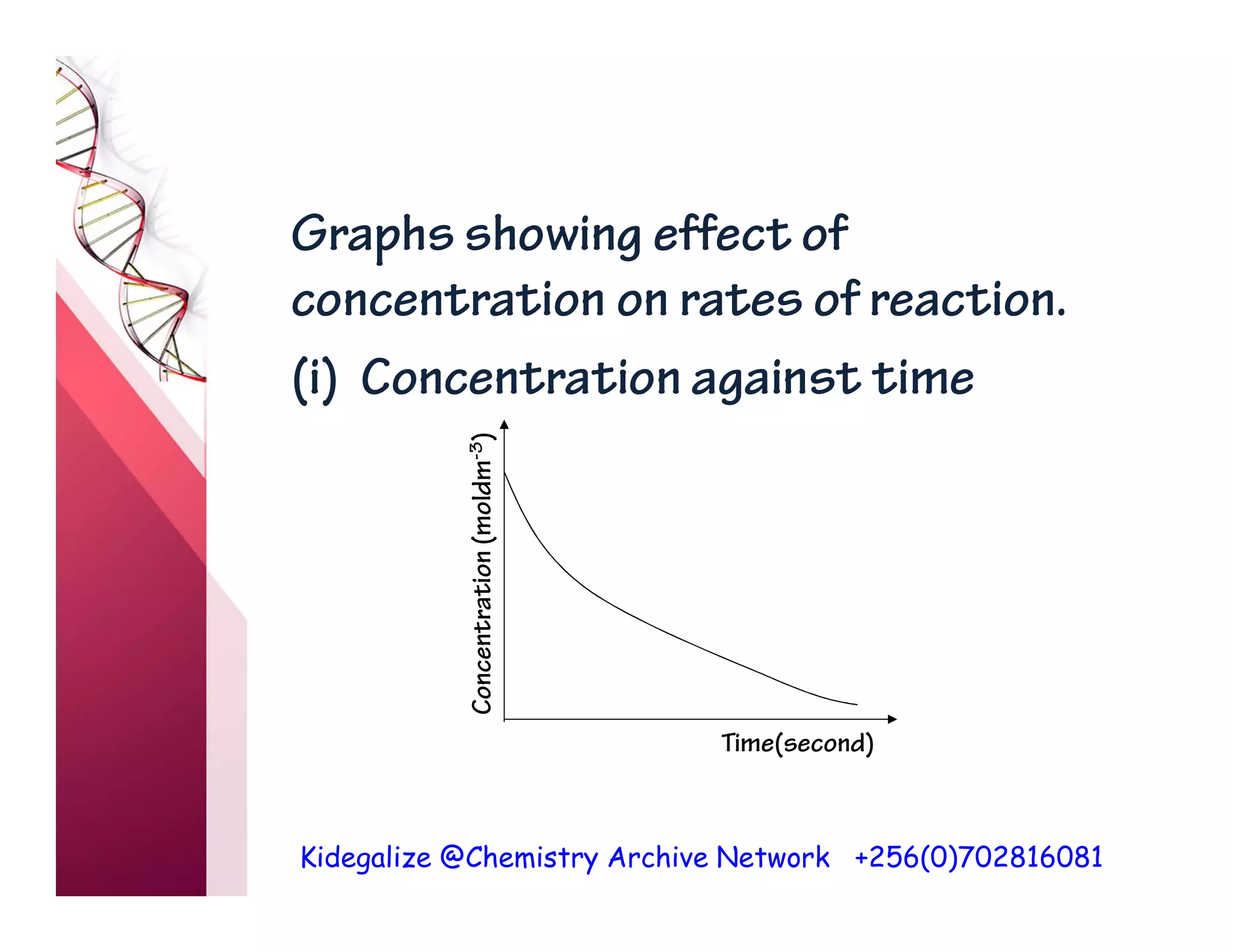
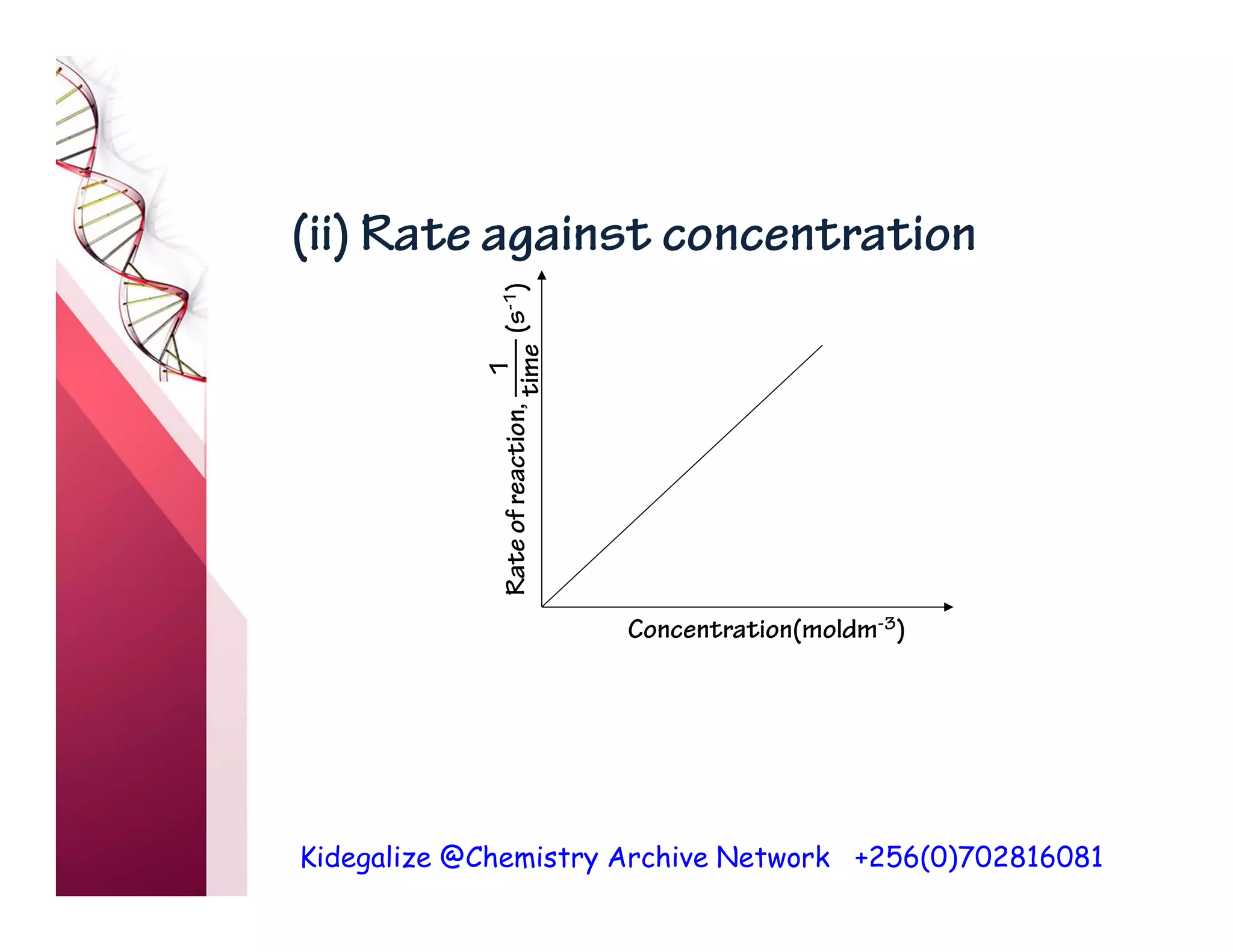
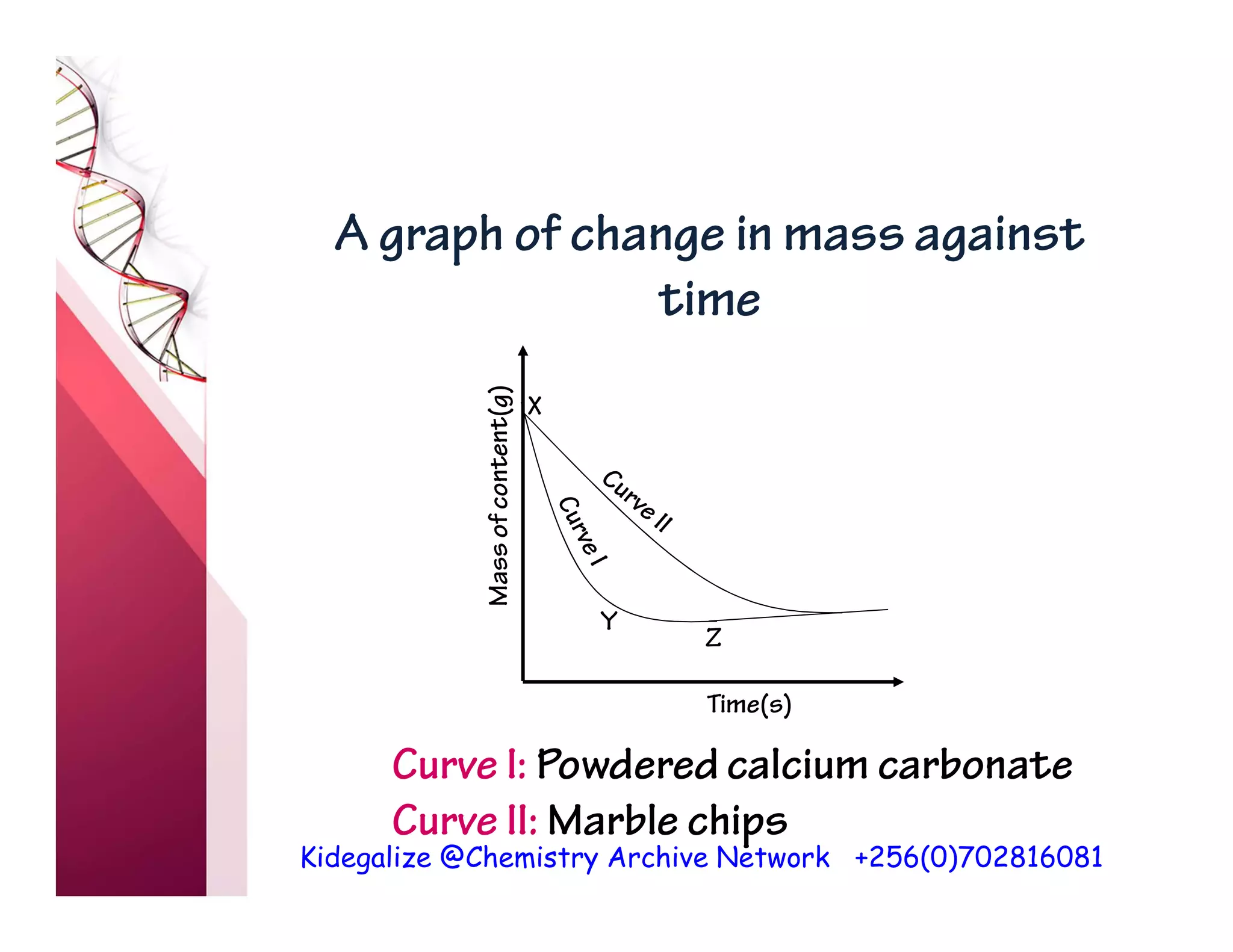
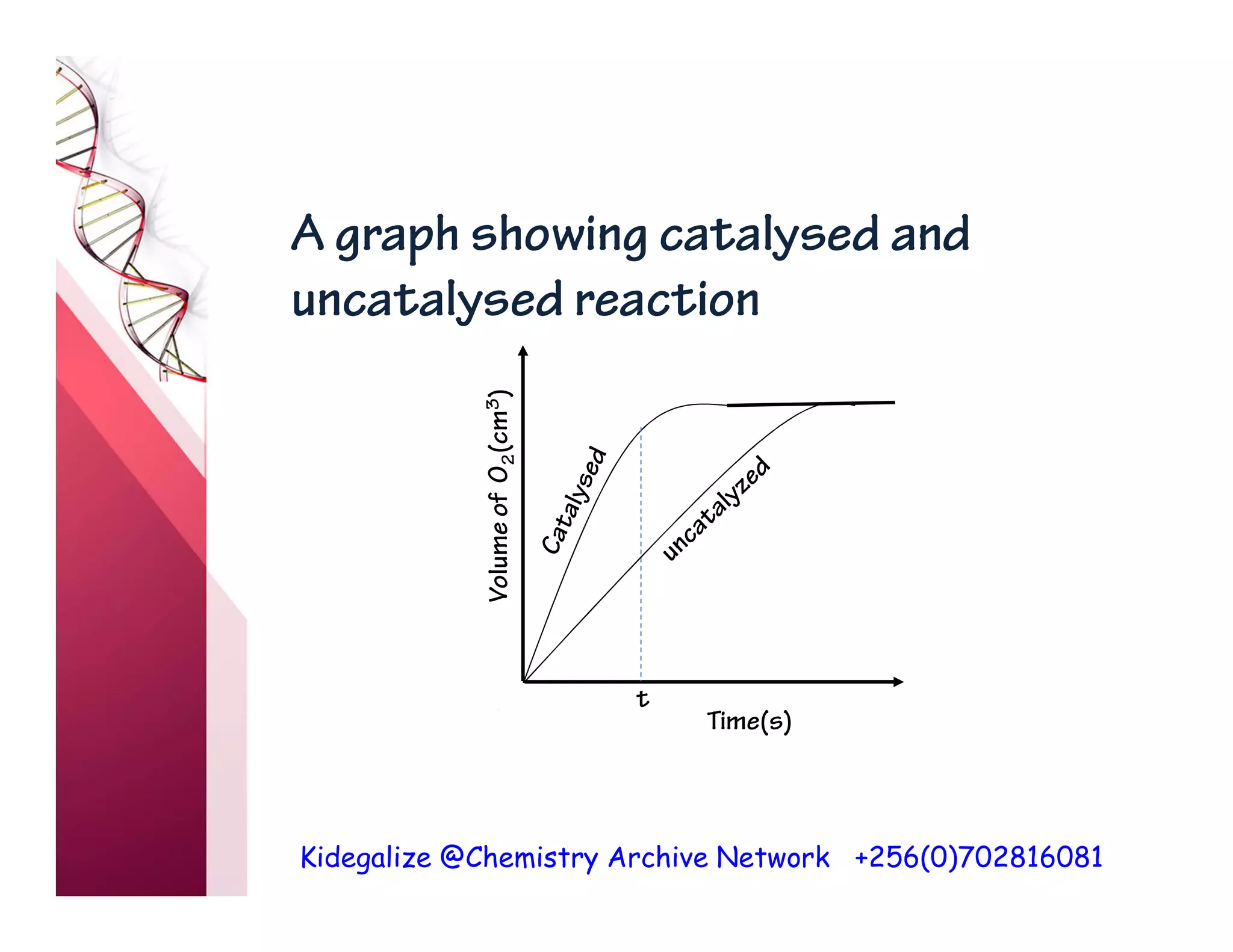
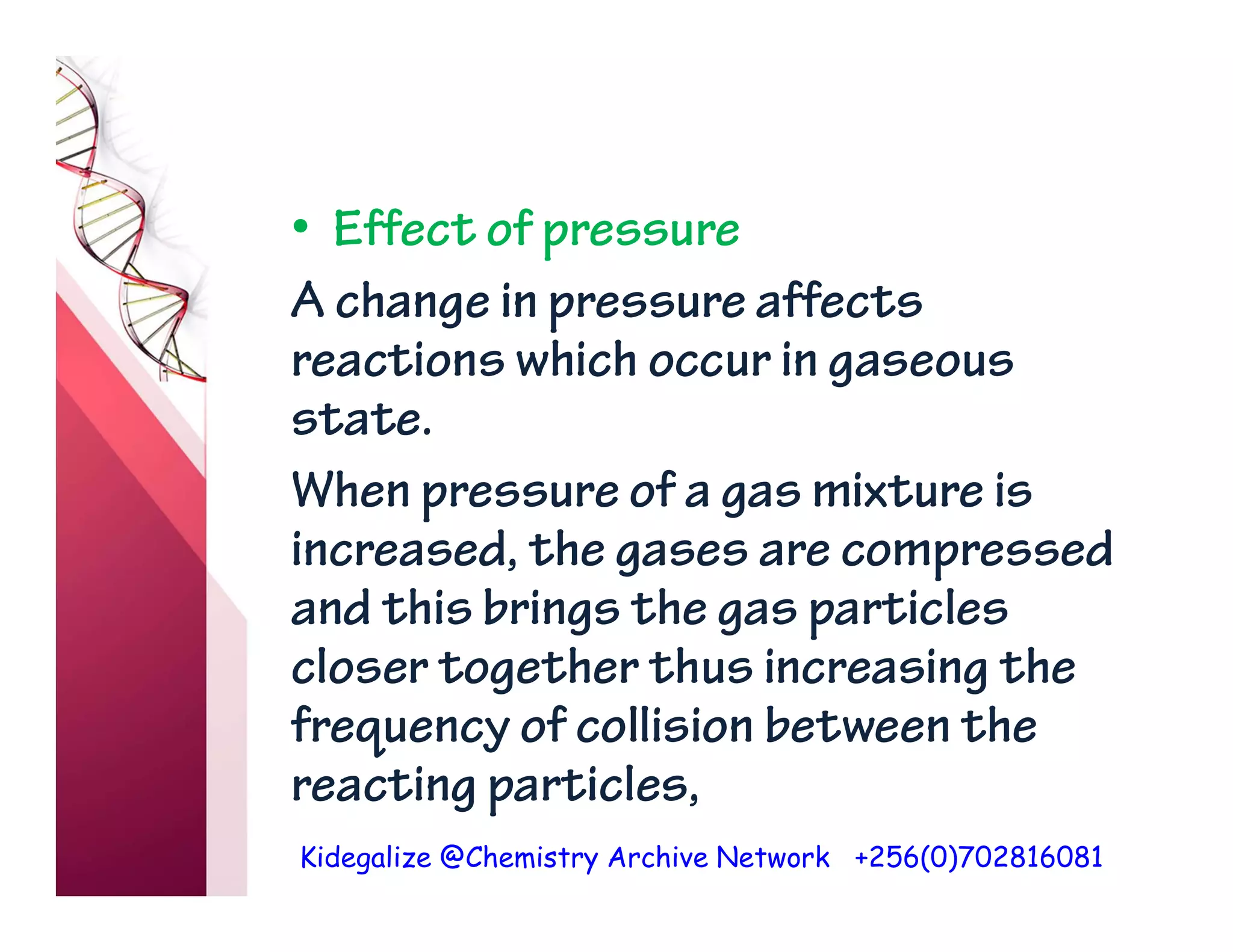
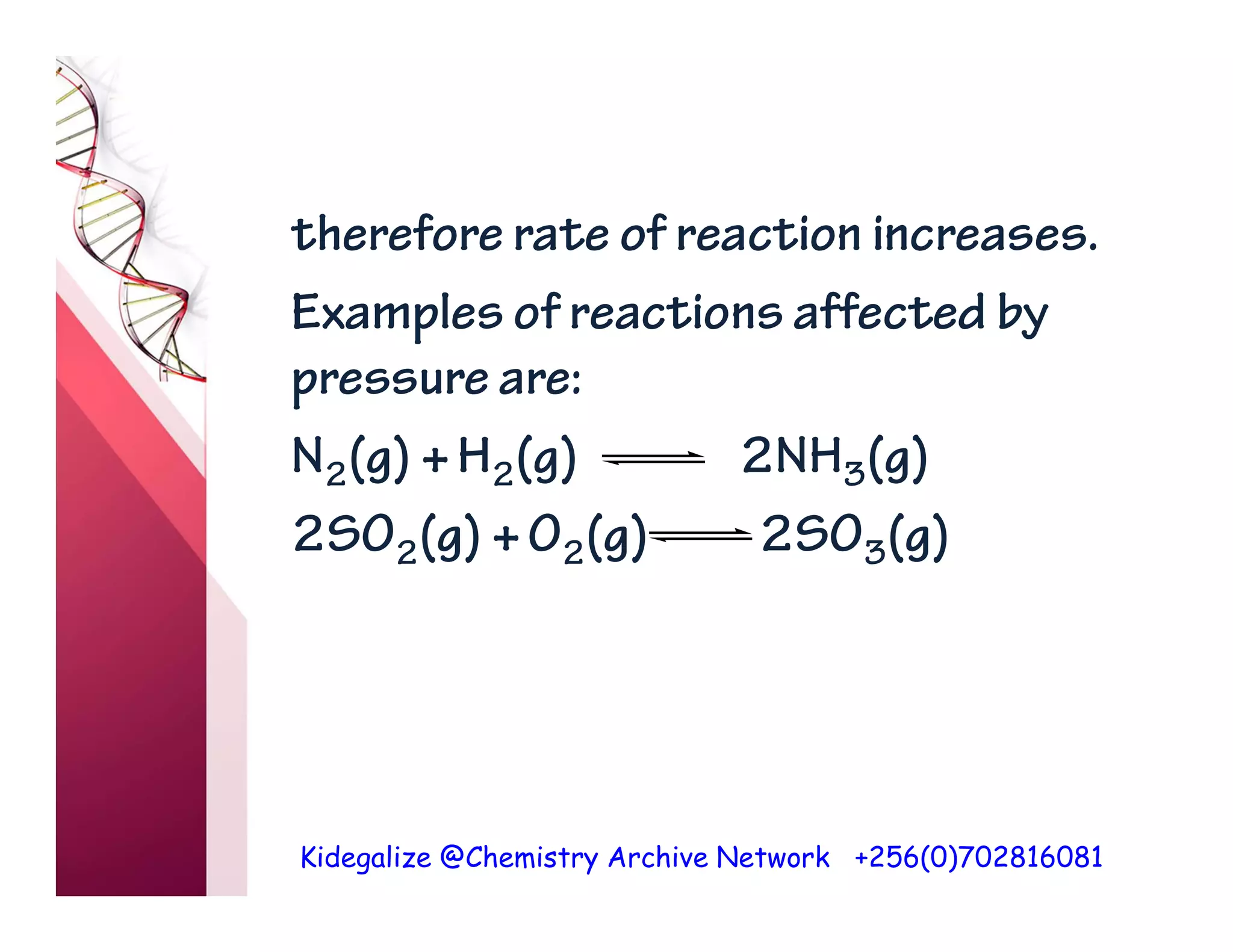
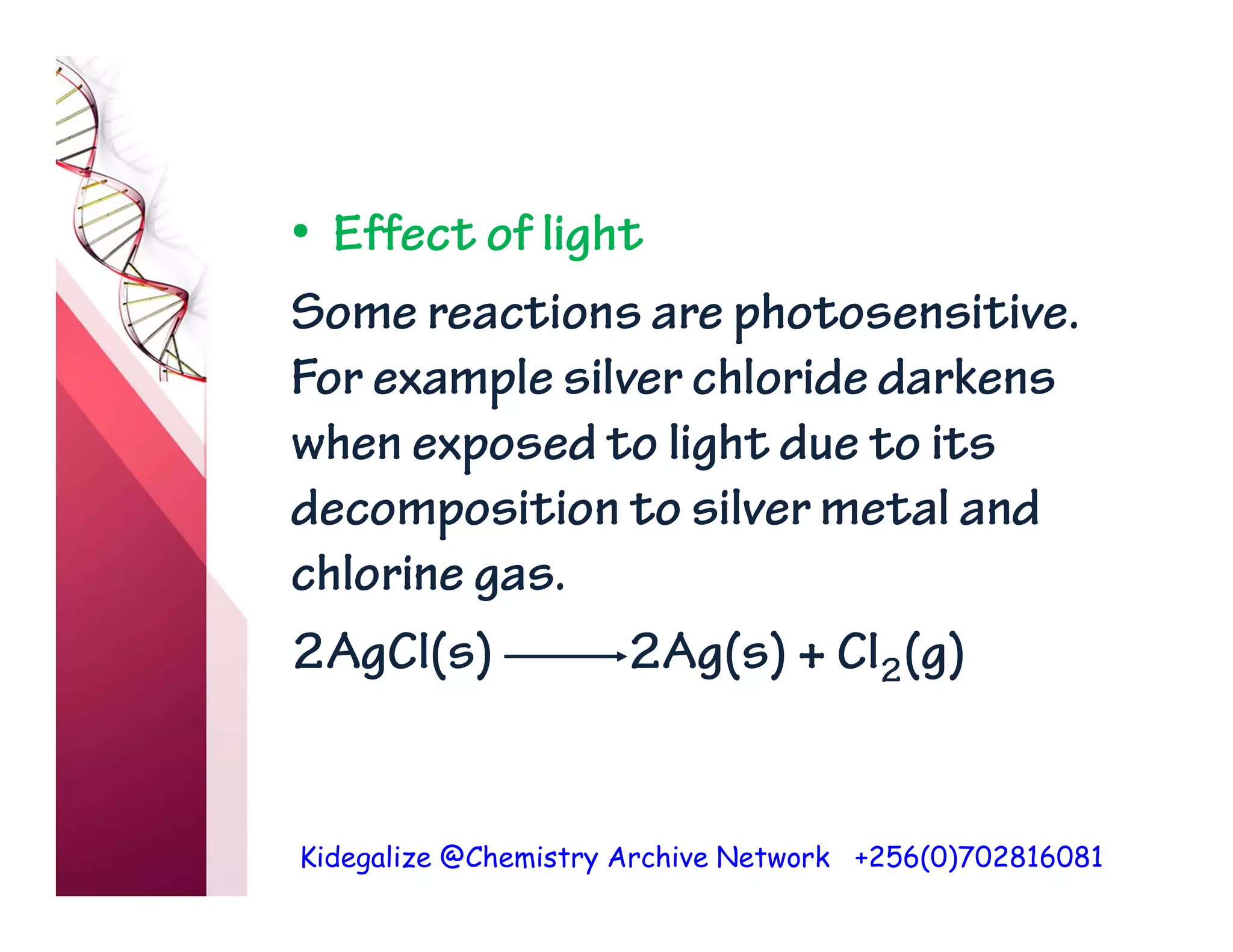
The document discusses the rate of reaction and factors that affect it. It defines rate of reaction as the change in amount of reactant or product per unit time. The rate depends on concentration, temperature, surface area, and other factors. Higher concentrations and temperatures increase the rate by increasing collisions between reactant particles. Smaller particle sizes also increase the rate by providing more surface area for reactions. Graphs and experiments are described to illustrate these relationships.