Here are some potential solutions to optimize industrial processes to produce higher yields at lower cost:
1. Use a catalyst. Adding a catalyst can lower the activation energy of the reaction, allowing it to proceed at a faster rate even at lower temperatures and pressures. This reduces energy costs while maintaining or increasing product yields.
2. Improve reactor design. Advanced reactor designs that improve heat and mass transfer can allow reactions to reach optimum conditions more efficiently. Examples include continuous flow reactors, microreactors, and reactive distillation columns.
3. Employ process intensification techniques. Methods like ultrasound, microwave irradiation, and supercritical fluid processing can accelerate reaction kinetics, reducing processing time. Some also allow operation at lower temperatures and pressures.




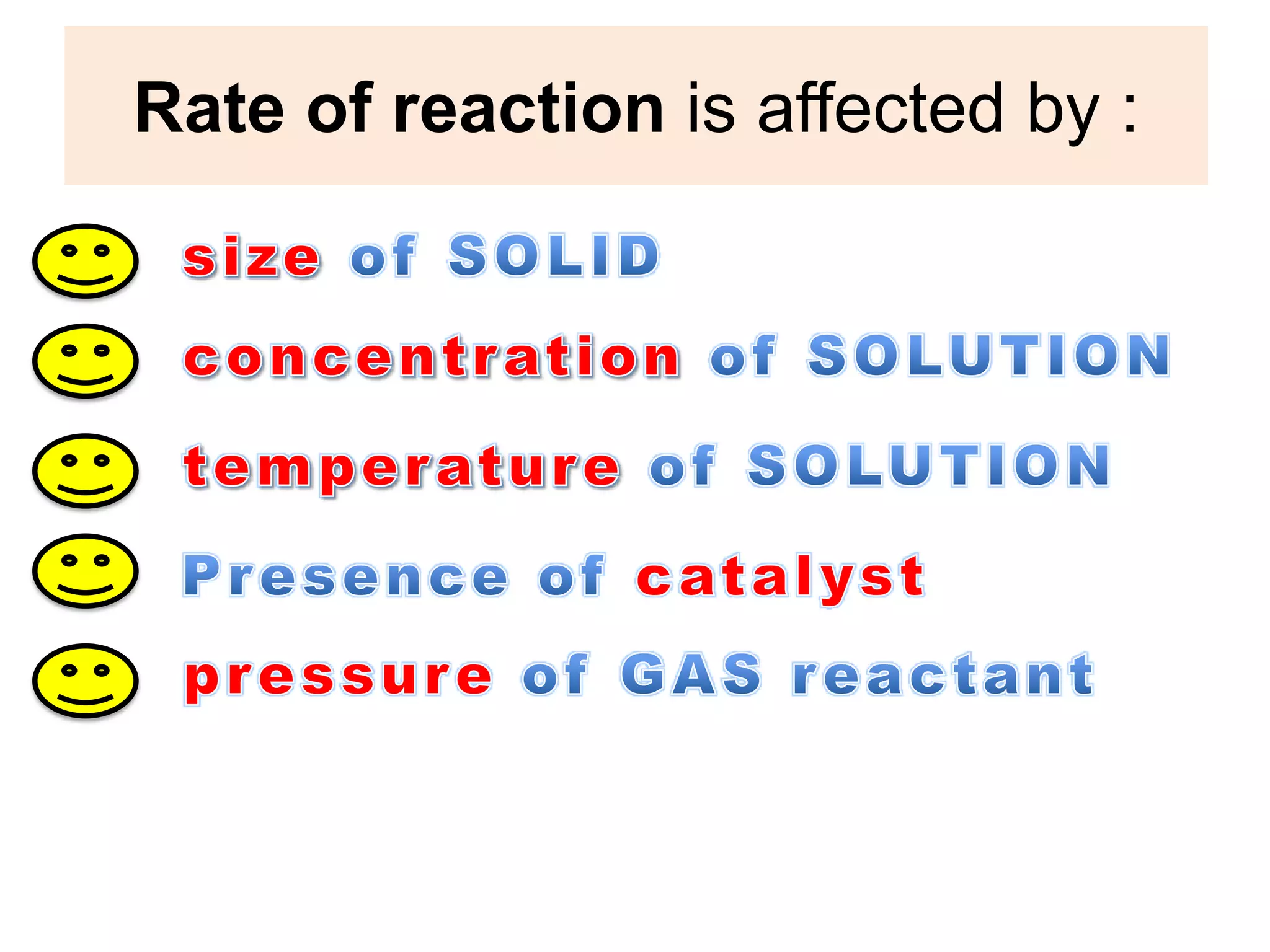


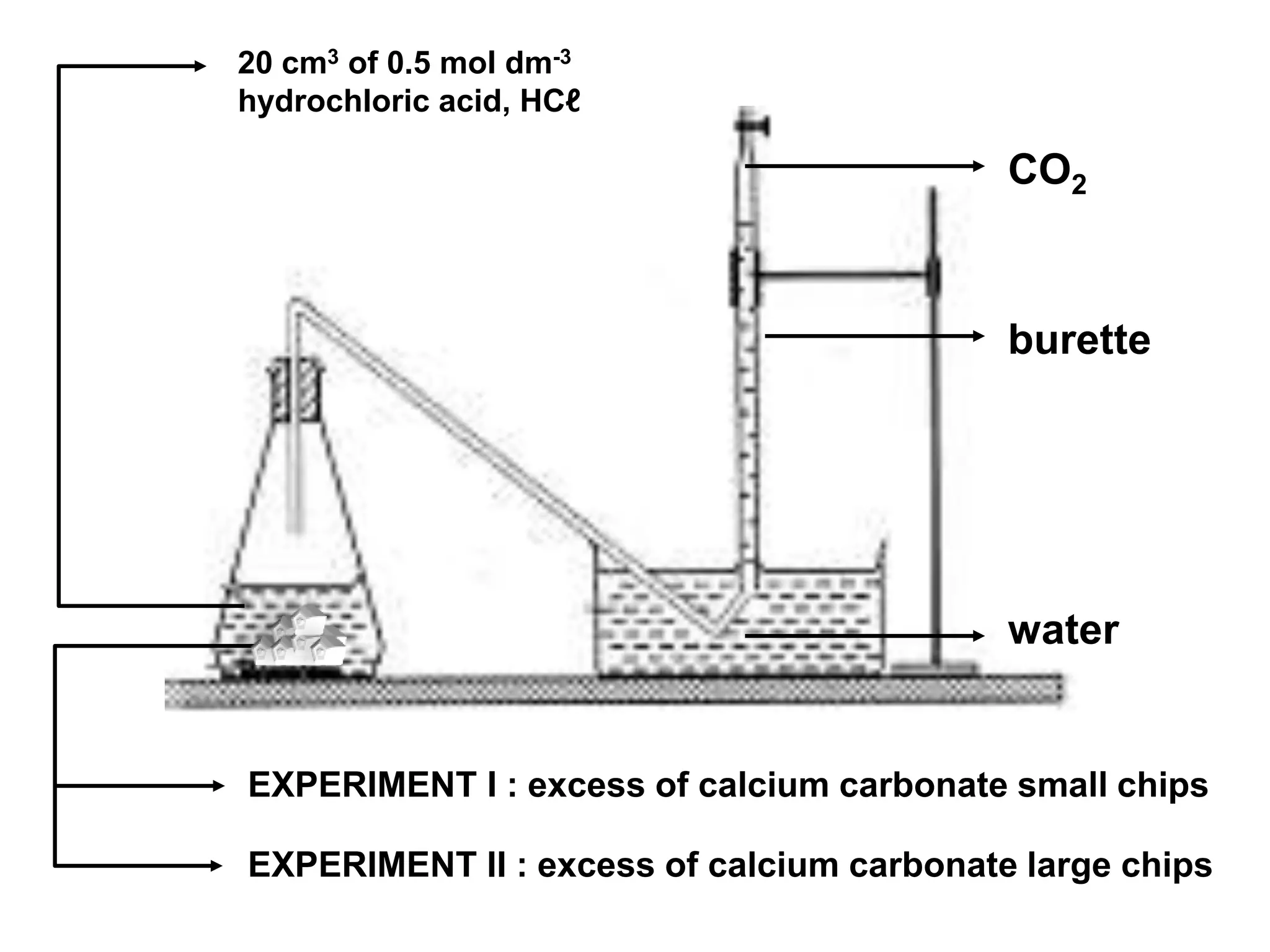


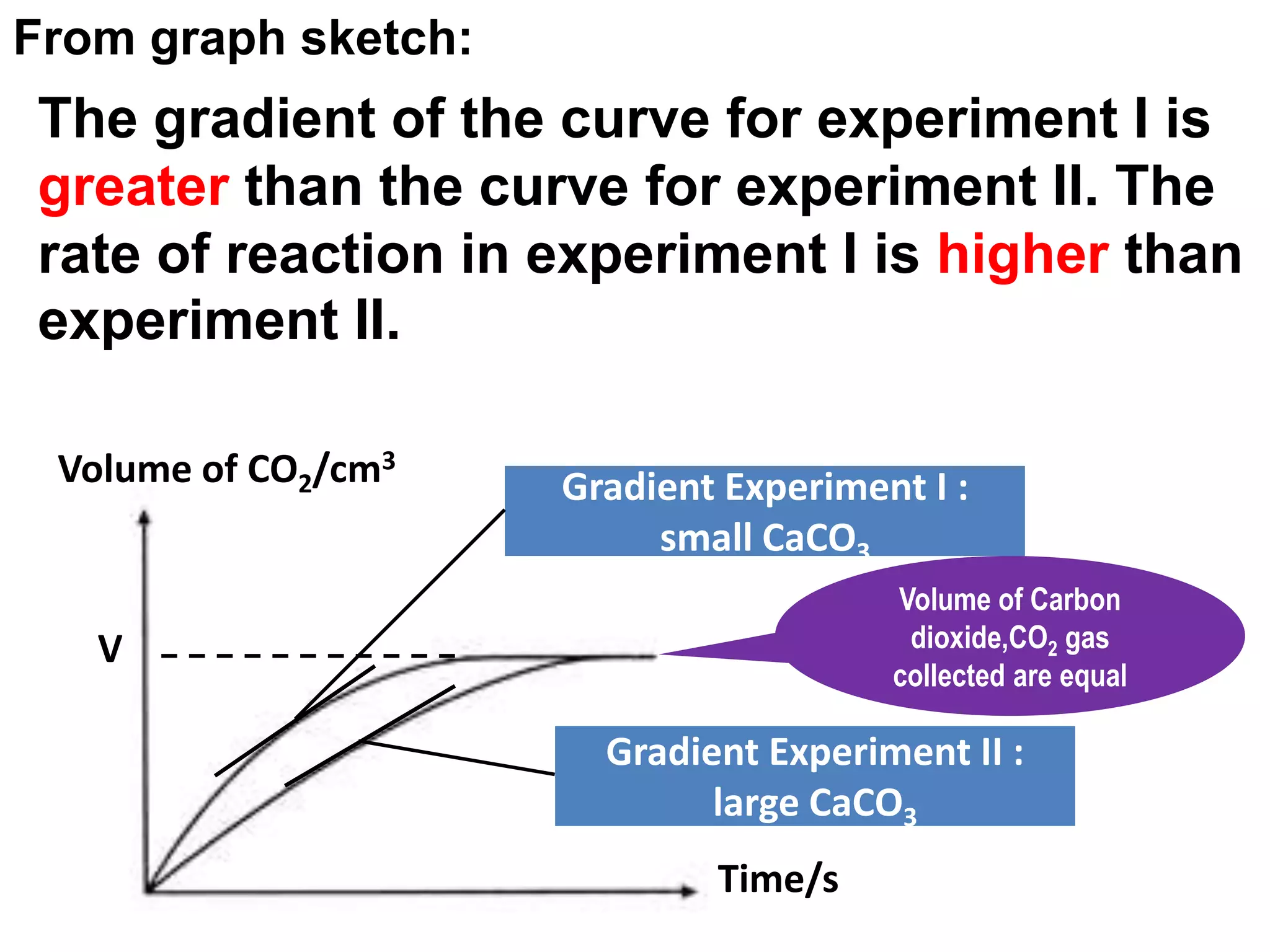
![The gradient of the curve for experiment I is greater than the curve for experiment II. The rate of reaction in experiment I is higherthan experiment II.The rate of reaction of the small calcium carbonate chips is higher.Since calcium carbonate used in excess, all hydrochloric acid has reacted. [ HCℓ reacted completed CaCO3excess].The number of mole of hydrochloric acid in both experiments:= 0.5 mol dm-3 x 20 cm3 1000= 0.01 molThe volume of carbon dioxide gas collected for both experiments are equal because number of mol of hydrochloric acid experiment I and experiment II are equal= MV 1000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rateofreation-110116112915-phpapp01/75/Rate-Of-Reaction-14-2048.jpg)

![experimentsFactor 2:concentration of SOLUTIONReactant :Differents CONCENTRATION :45 cm3 of 0.2 mol dm-3sodium thiosulphate, Na2S2O3 [diluted with different volume of distilled water]Fixed VOLUME and TEMPERATURE :5 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3sulphuric acid, H2SO4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rateofreation-110116112915-phpapp01/75/Rate-Of-Reaction-16-2048.jpg)