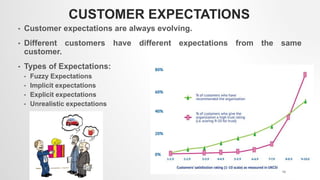
This document discusses several key challenges in services marketing. It identifies intangibility, inseparability, and heterogeneity as inherent characteristics of services that make them difficult to standardize and control quality. Other challenges include managing customer expectations, defining and measuring quality, designing effective customer organizations, and positioning services in the marketplace against competitors. Overall, the document outlines the complex nature of services and highlights areas services marketers must address, such as customization, training employees, and emphasizing quality to overcome issues related to intangibility and heterogeneity.