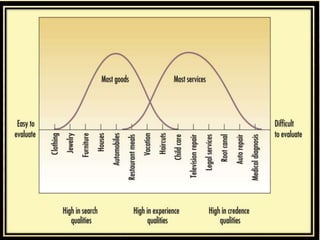
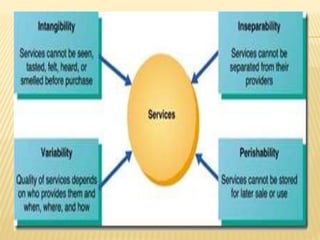
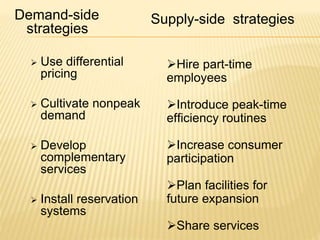
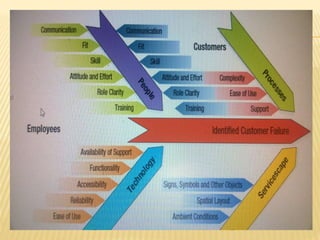
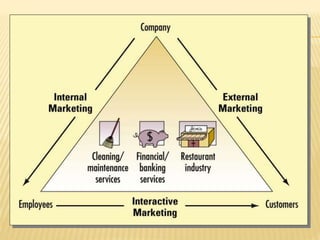
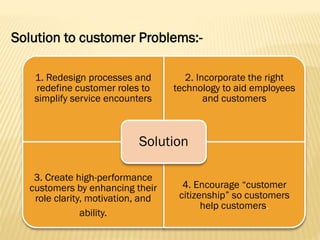
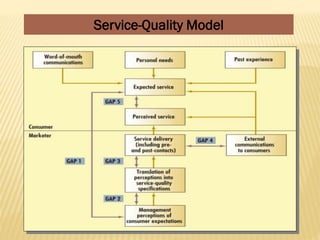
This document discusses key aspects of services marketing and management. It covers the nature of services, categories of service mixes, distinctive characteristics of services including intangibility, inseparability, variability and perishability. It also discusses the new service realities of customer empowerment, co-production and satisfying employees. Finally, it outlines marketing strategies for service firms including the service quality model and determinants of service quality.