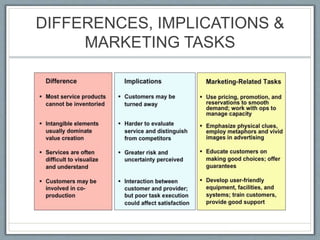
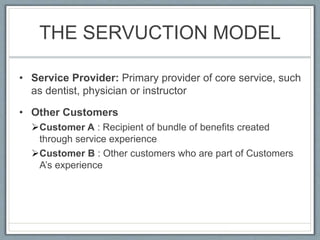
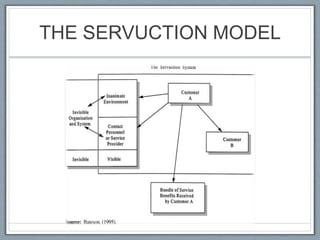
Services account for over 60% of the world's GDP and most new employment. Marketing of services differs from products in several key ways: services are intangible, perishable, inseparable from their production and delivery, and variable. The 8Ps marketing mix framework expands the traditional 4Ps to address the unique characteristics of services, including elements like process, physical environment, and people. Properly understanding customer involvement in the co-production of services is vital, as illustrated by the servuction model which maps the visible and invisible factors shaping the customer experience.