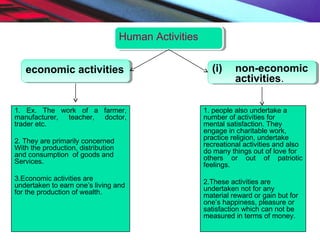
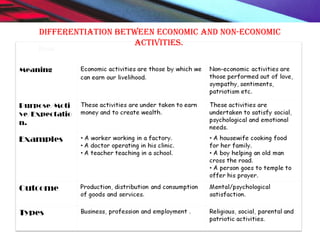
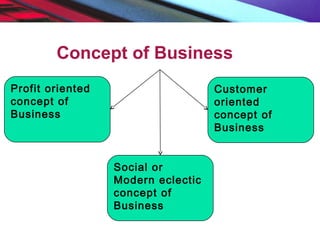
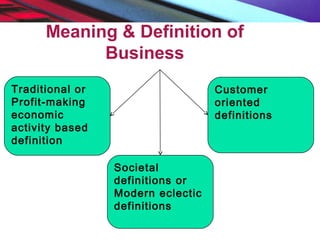
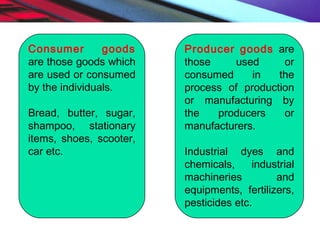
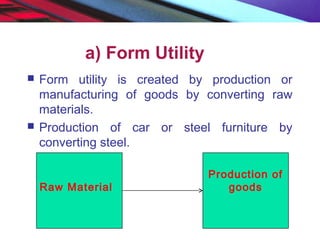
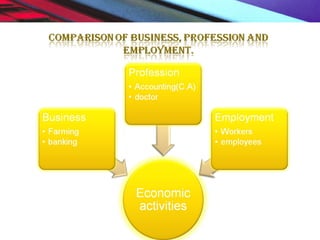
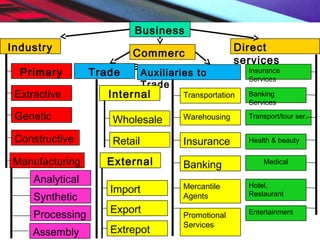
This document provides an overview of the nature and scope of business. It defines key terms like economic and non-economic activities. It discusses the traditional, customer-oriented, and societal concepts of defining business. The characteristics of business are explained, differentiating between basic/fundamental characteristics and modern characteristics. It also compares the differences between business, profession, and employment. Finally, it outlines the scope of business, categorizing business activities into industry, commerce, and direct services.