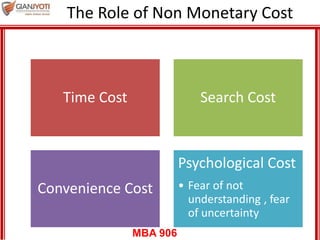
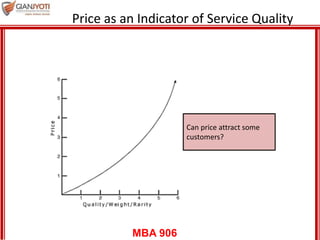
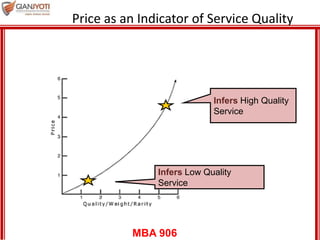
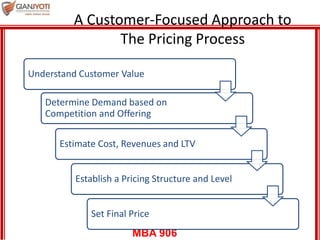
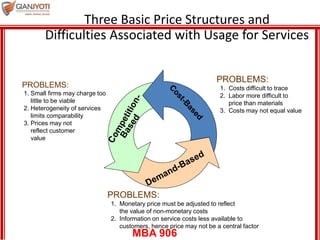
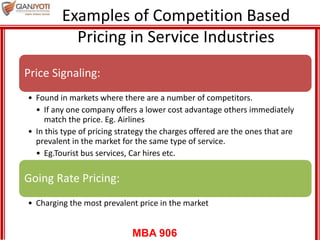
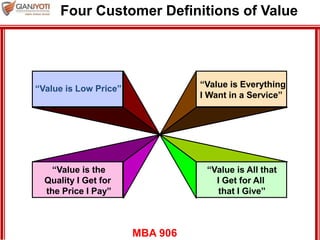
This document discusses pricing strategies for services. It outlines three key differences in how consumers understand service prices compared to product prices. Namely, service prices are more difficult for customers to know due to variability, individual needs, and non-visible nature. The role of non-monetary costs like time and uncertainty are also examined. Various approaches to determining service prices are then reviewed, including cost-based pricing, competition-based pricing, and demand-based pricing oriented around customer perceptions of value. Specific pricing techniques within each approach are defined.