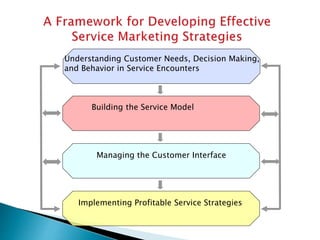
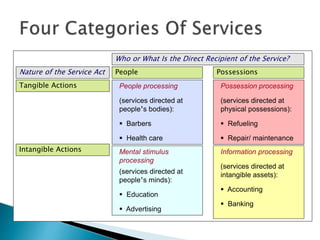
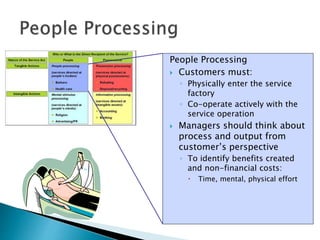
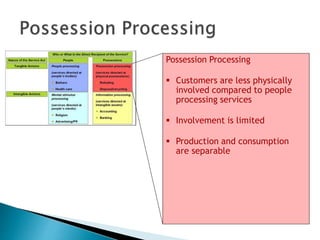
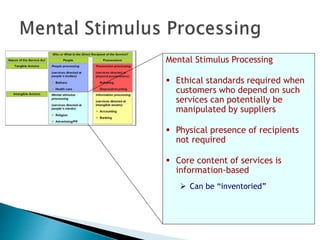
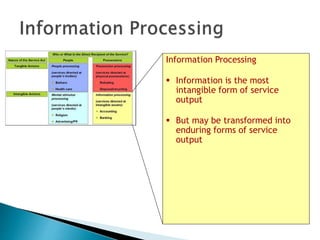
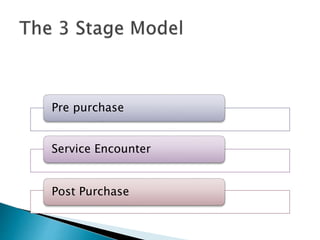
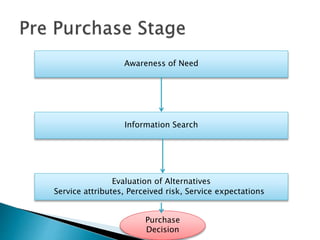
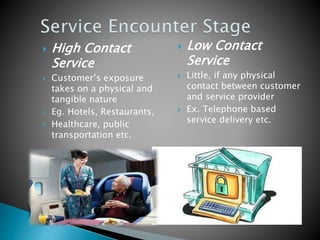
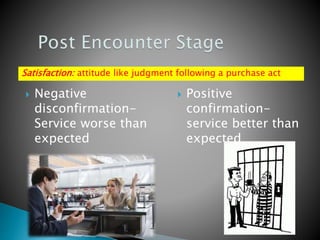
The document summarizes key aspects of customer behavior in service marketing. It discusses how consumers seek, choose, purchase, experience, and evaluate services. It outlines the three stages of the consumer decision making process - pre-purchase, service encounter, and post-purchase stages. It also categorizes services into four types based on whether the service act is tangible or intangible and whether people or possessions are the direct recipient. Finally, it examines factors that influence customer expectations and satisfaction during the different stages.