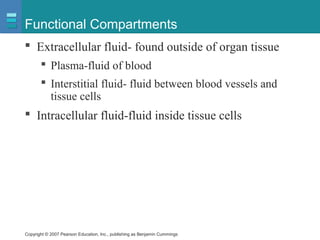
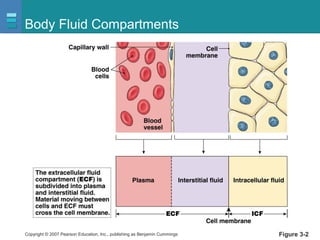
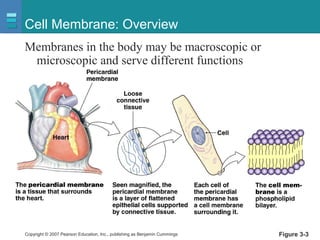
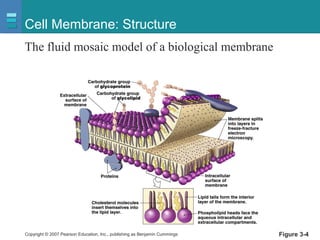
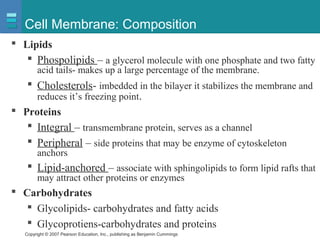
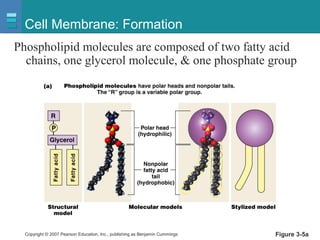
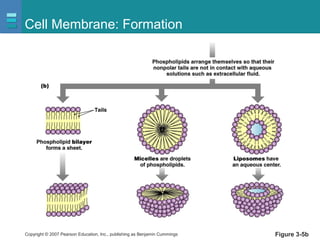
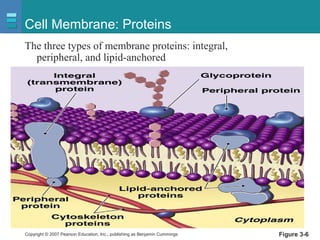
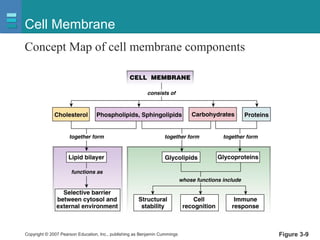
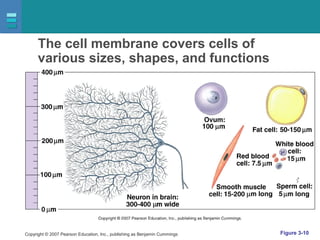
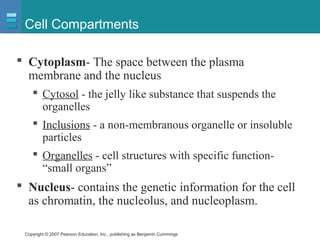
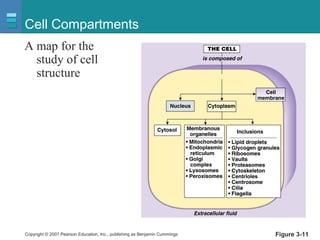
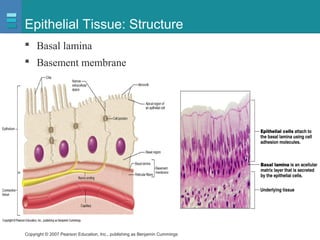
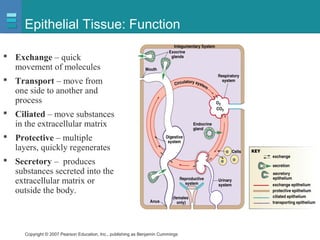
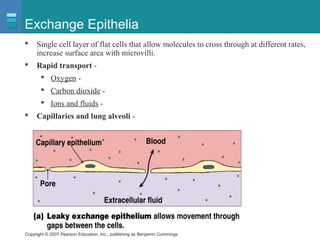
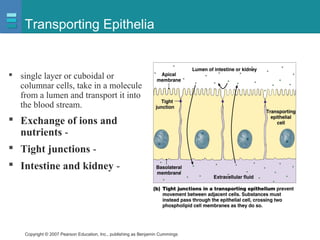
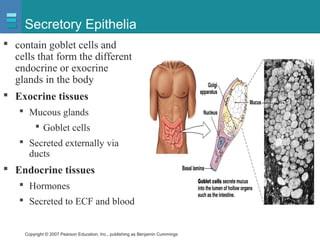
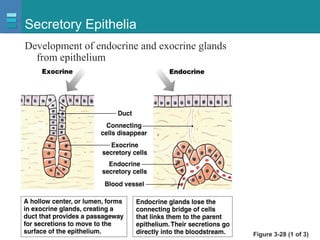
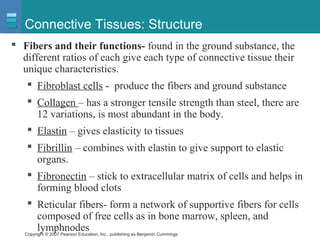
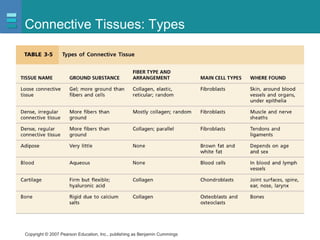
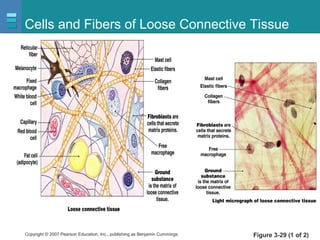
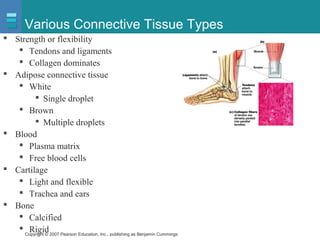
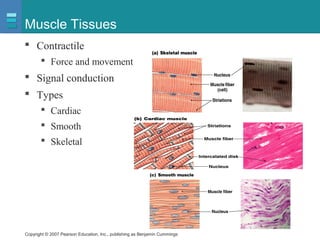
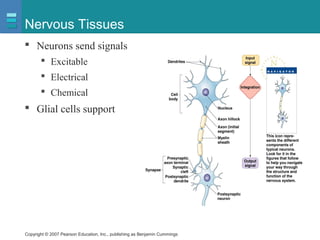
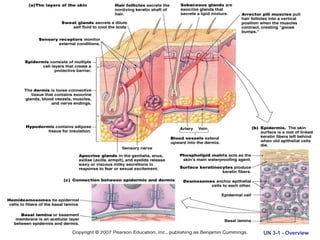
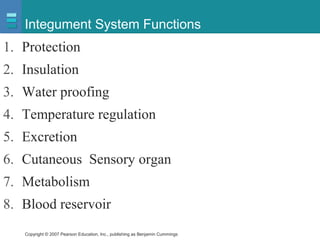
The document discusses the organization of the human body into compartments and tissues. It begins by describing the three major body cavities - the dorsal cavity, the cranial cavity, and the ventral cavity. It then discusses the different tissue types - epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It provides information on the structure and functions of cells and their membranes. The key body tissues and organs are organized into functional compartments to carry out essential processes.