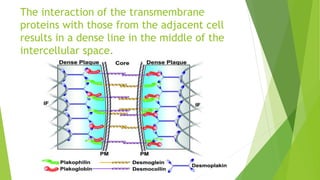
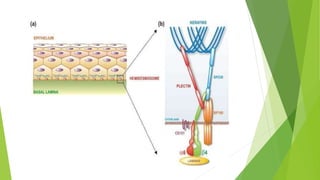
Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes are cell junctions that connect adjacent cells or attach cells to the extracellular matrix. Desmosomes link the intermediate filaments of neighboring cells, forming strong bonds especially in tissues under mechanical stress like skin. They are composed of transmembrane proteins, plaque proteins, and intermediate filaments. Hemidesmosomes attach basal epithelial cells to the basement membrane. Loss of desmosome function can cause skin and mucous membrane fragility disorders like pemphigus.