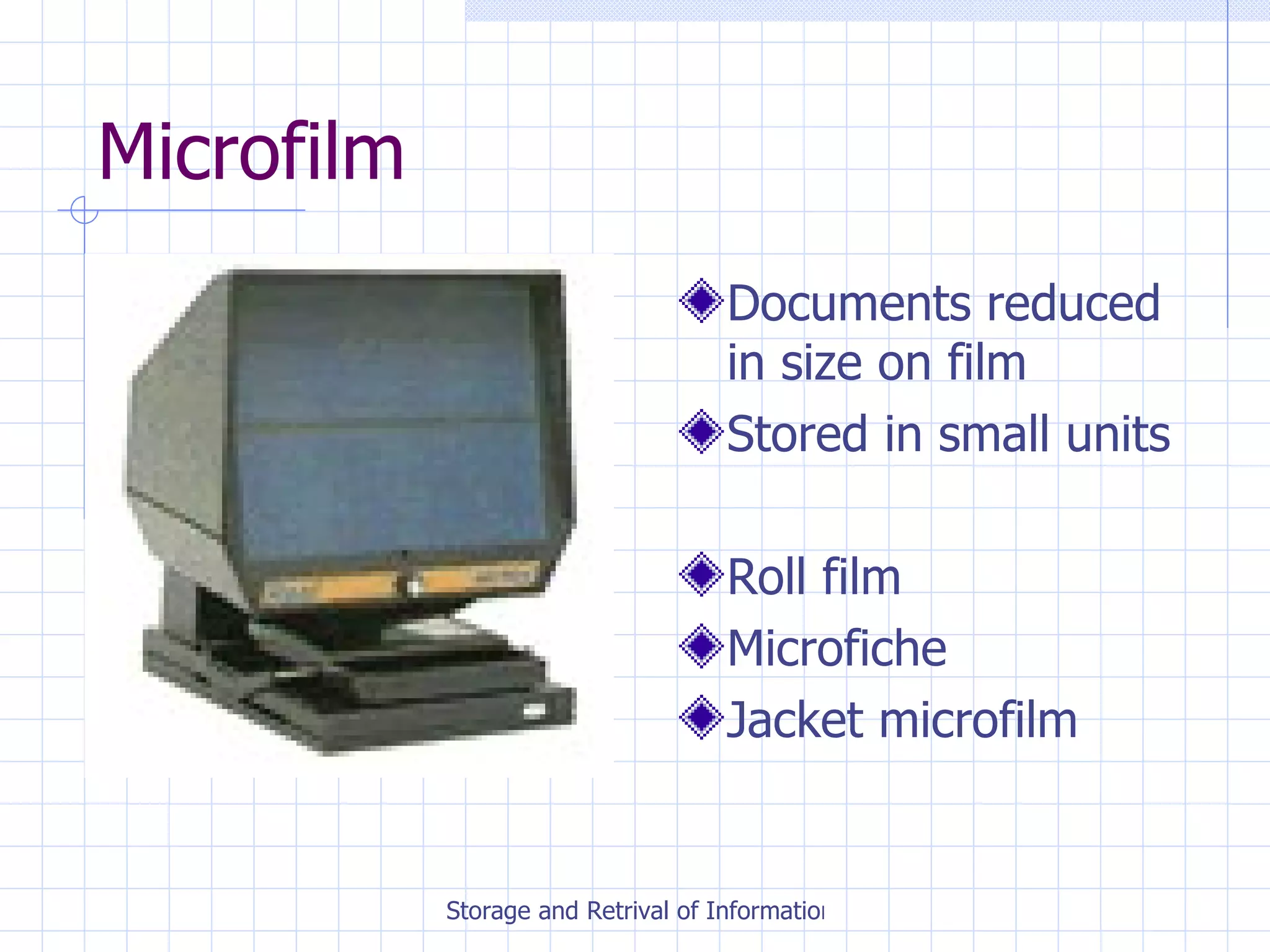
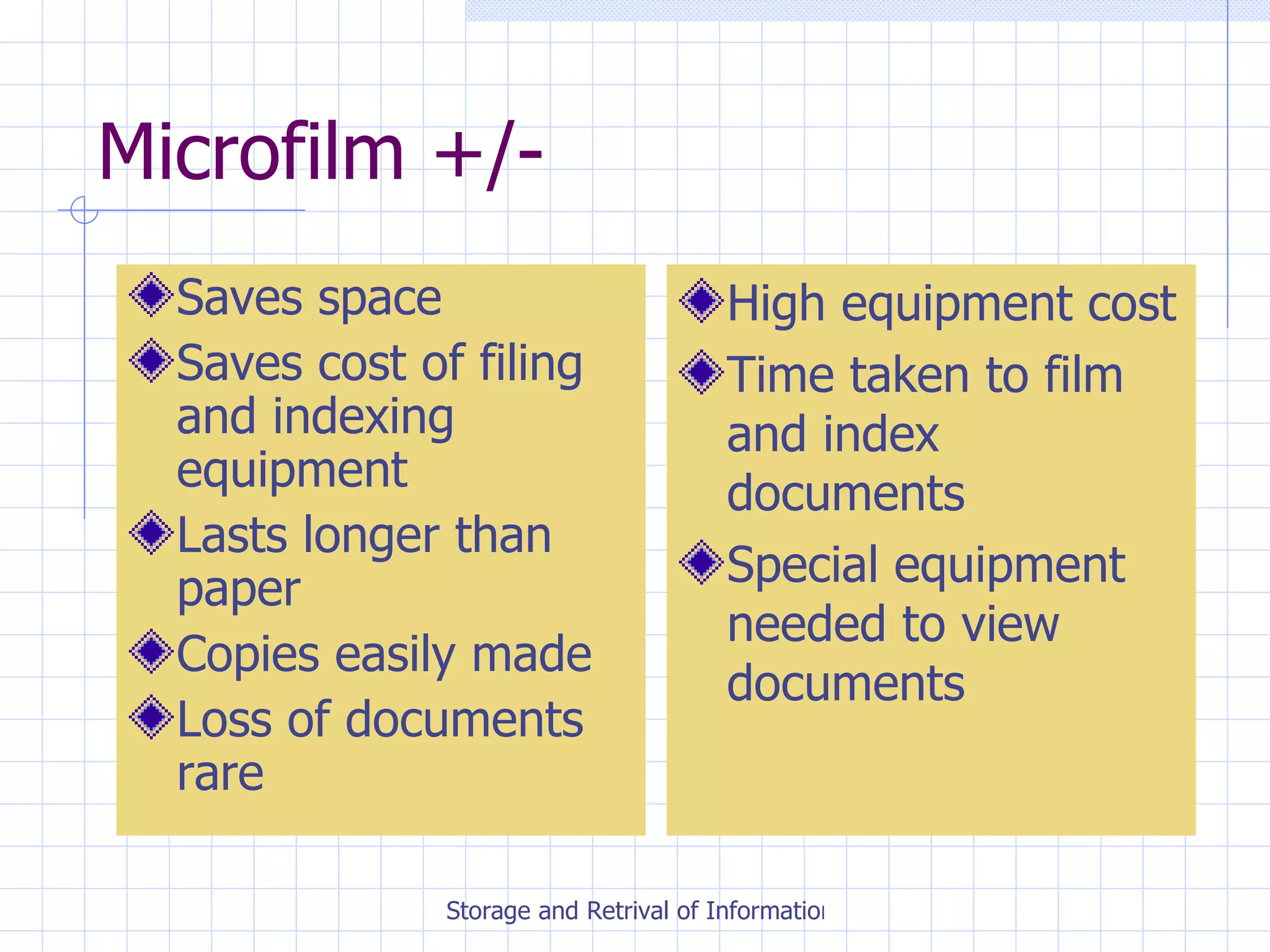
The document discusses various methods for storing and retrieving information, including manual and electronic filing systems. It provides details on setting up and maintaining different types of manual filing systems, such as alphabetical, numerical, and chronological order. Electronic filing options include using databases, spreadsheets, microfilm, and backing up files. The document also covers important considerations for evaluating different filing methods and ensuring security and compliance with data protection regulations.