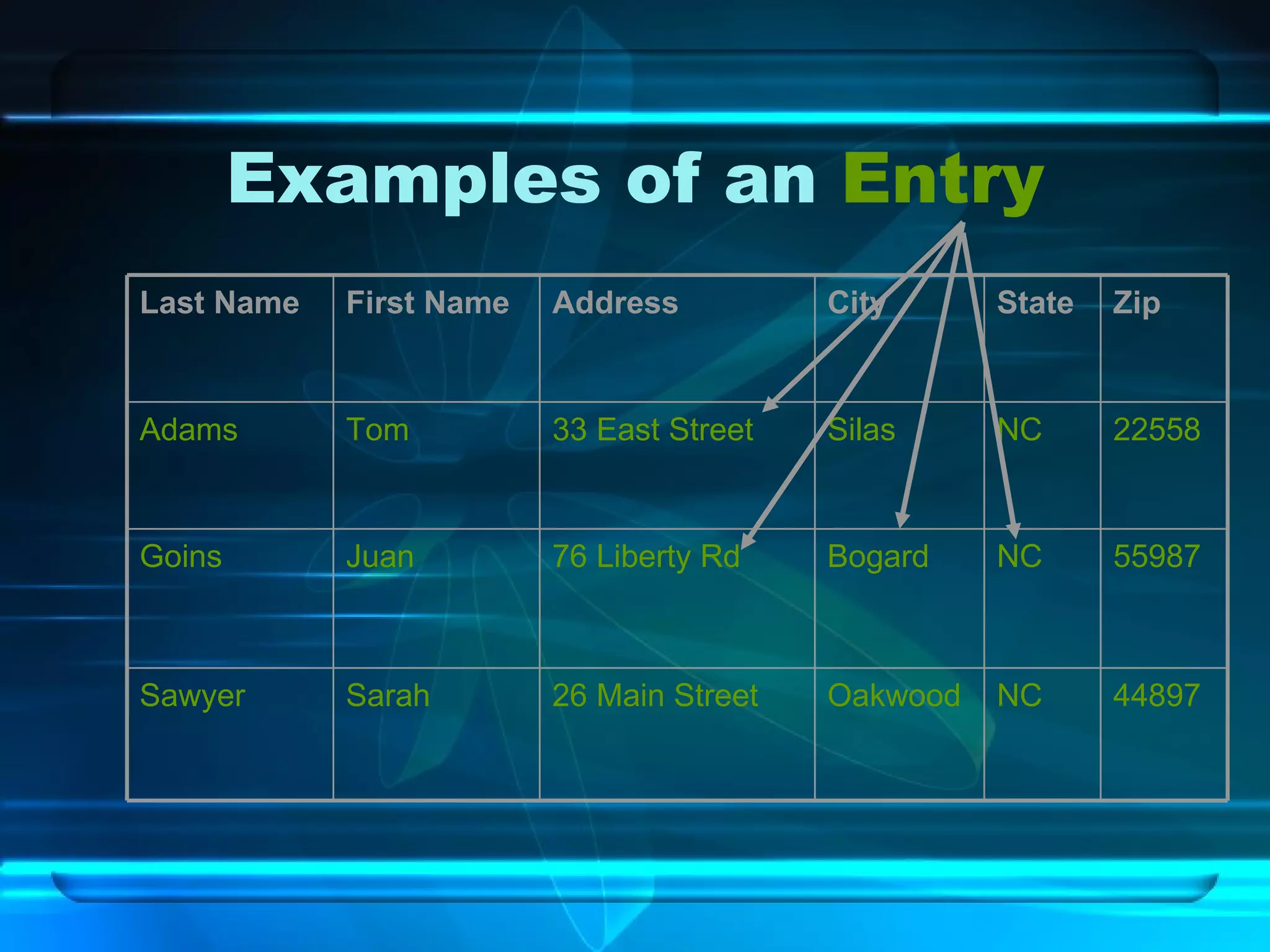
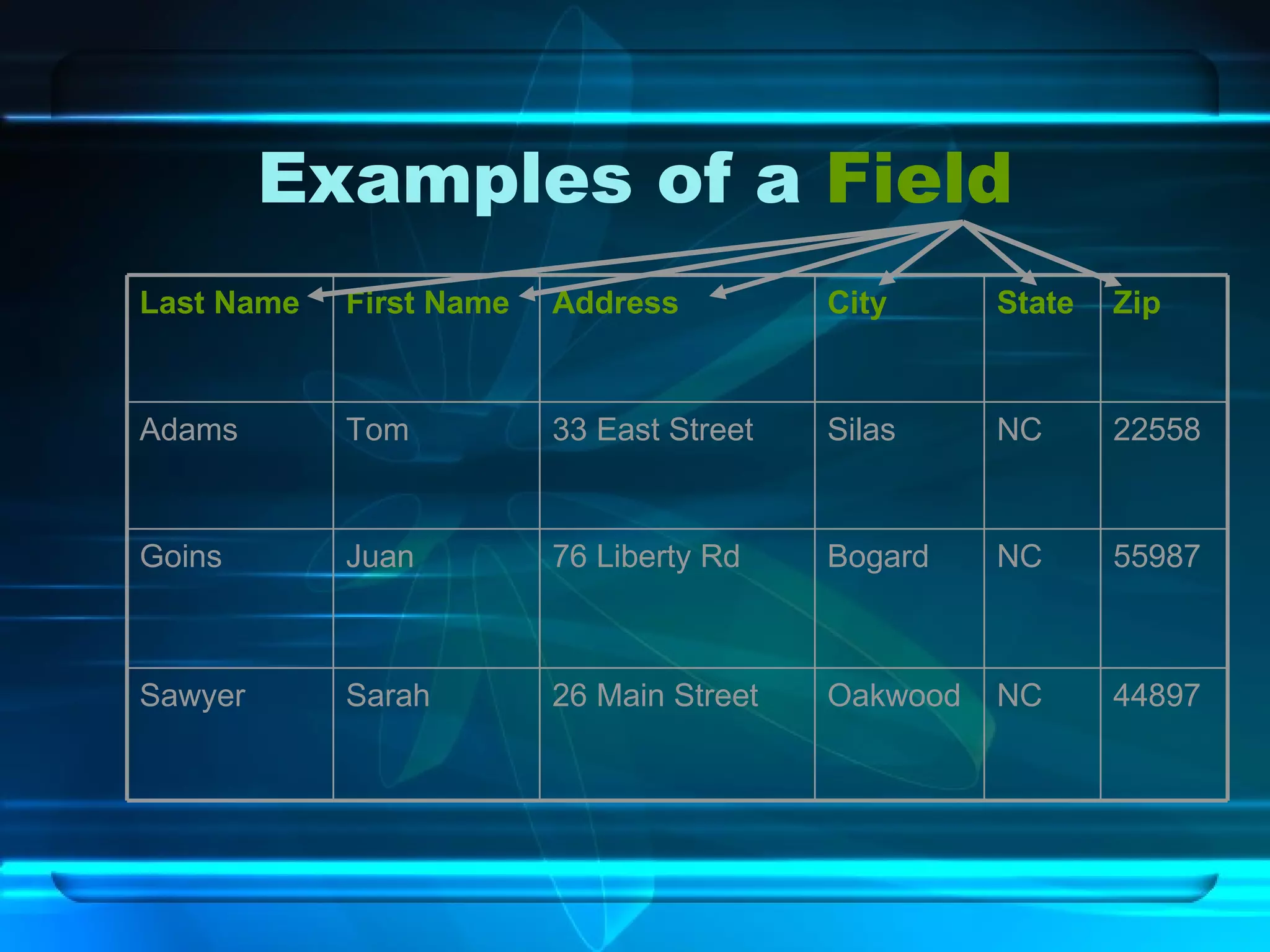
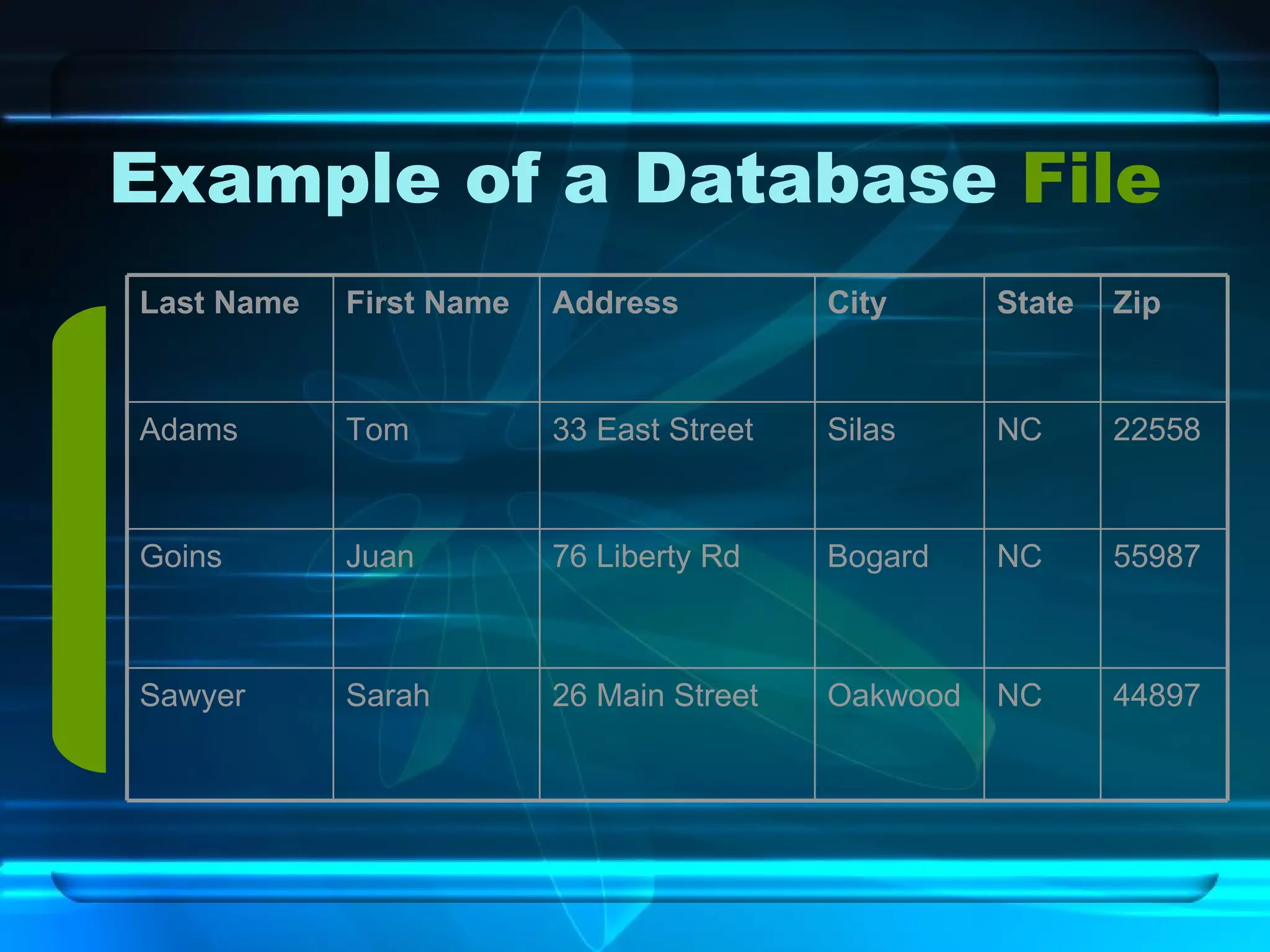
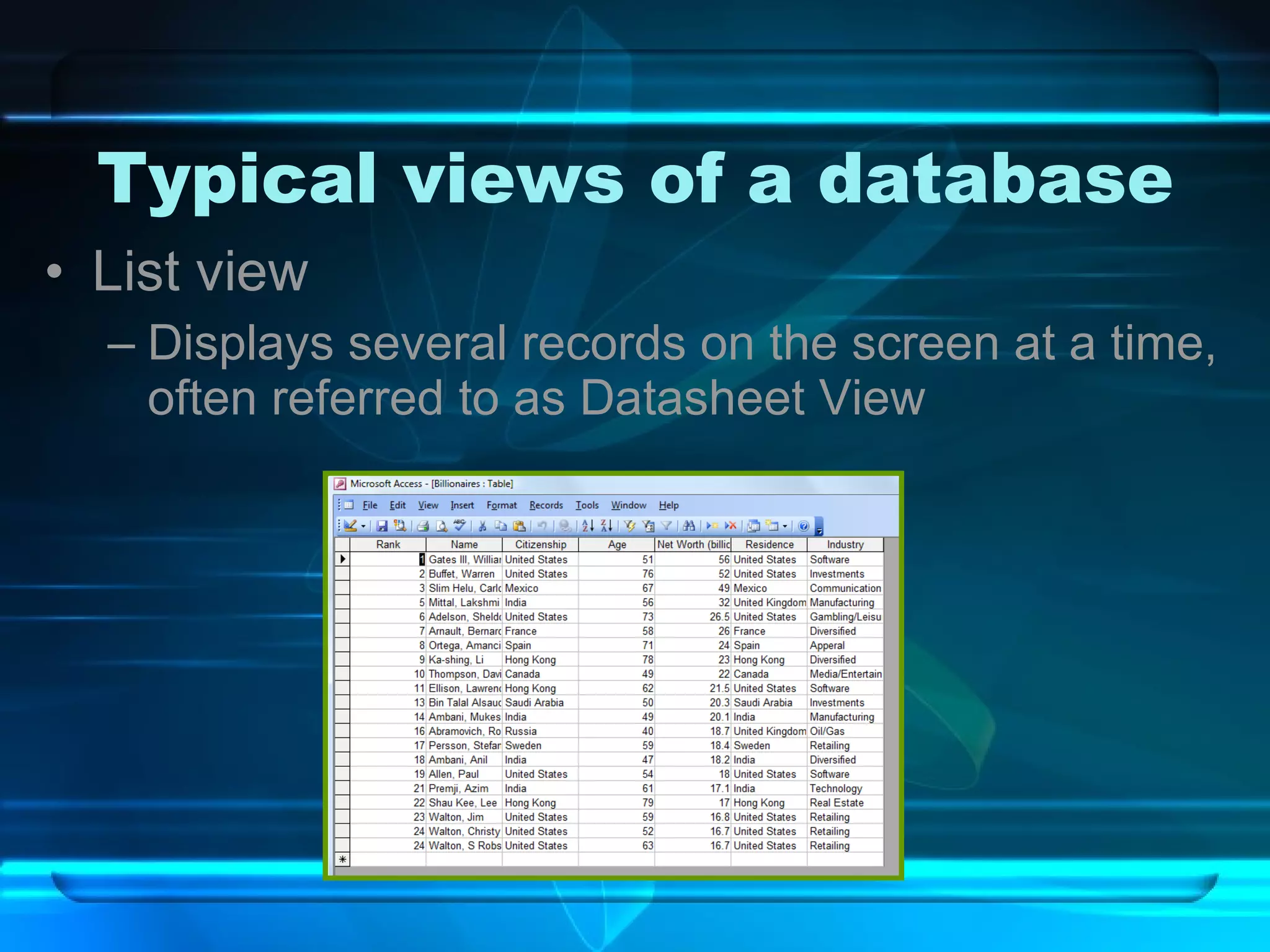
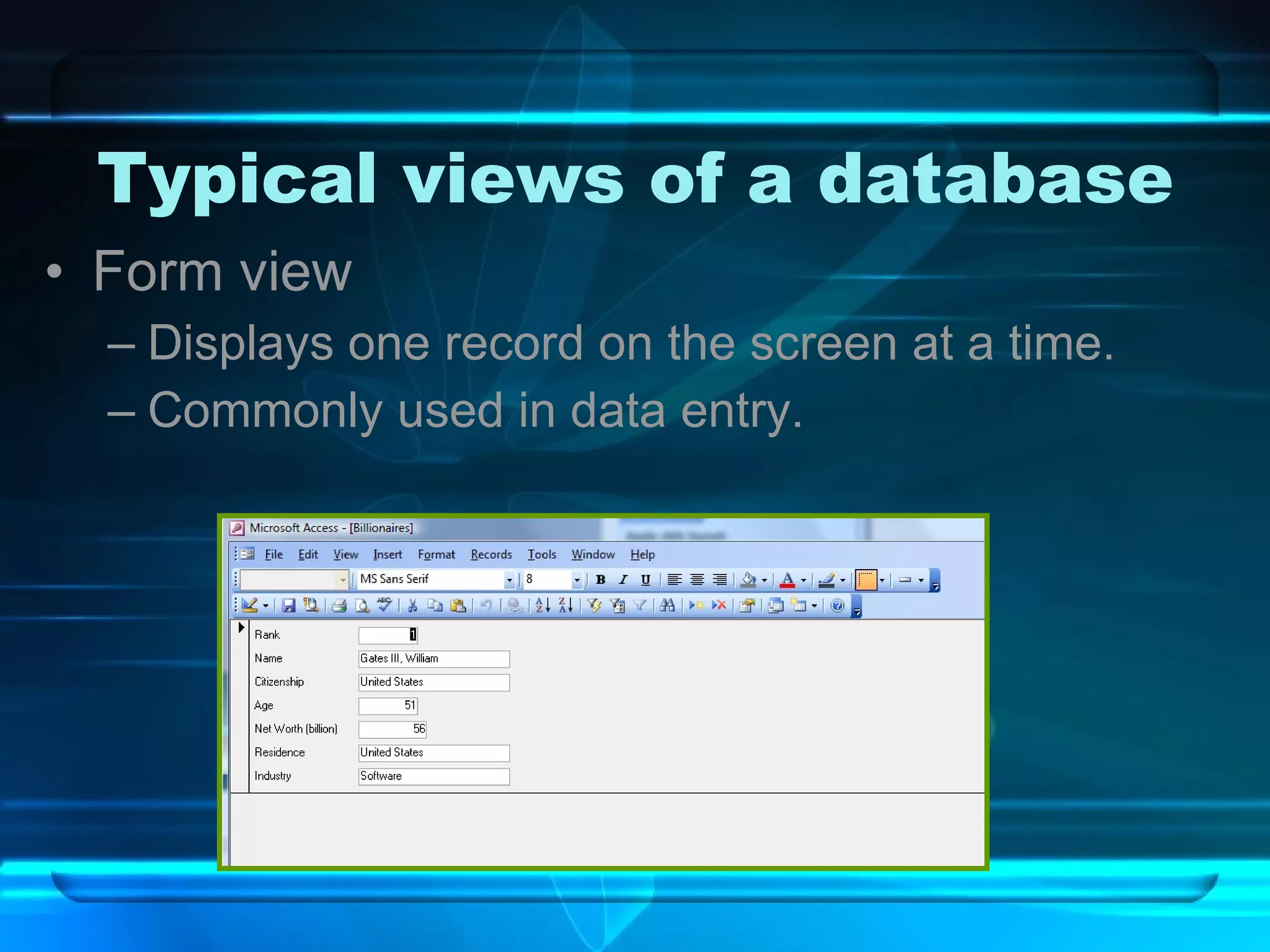
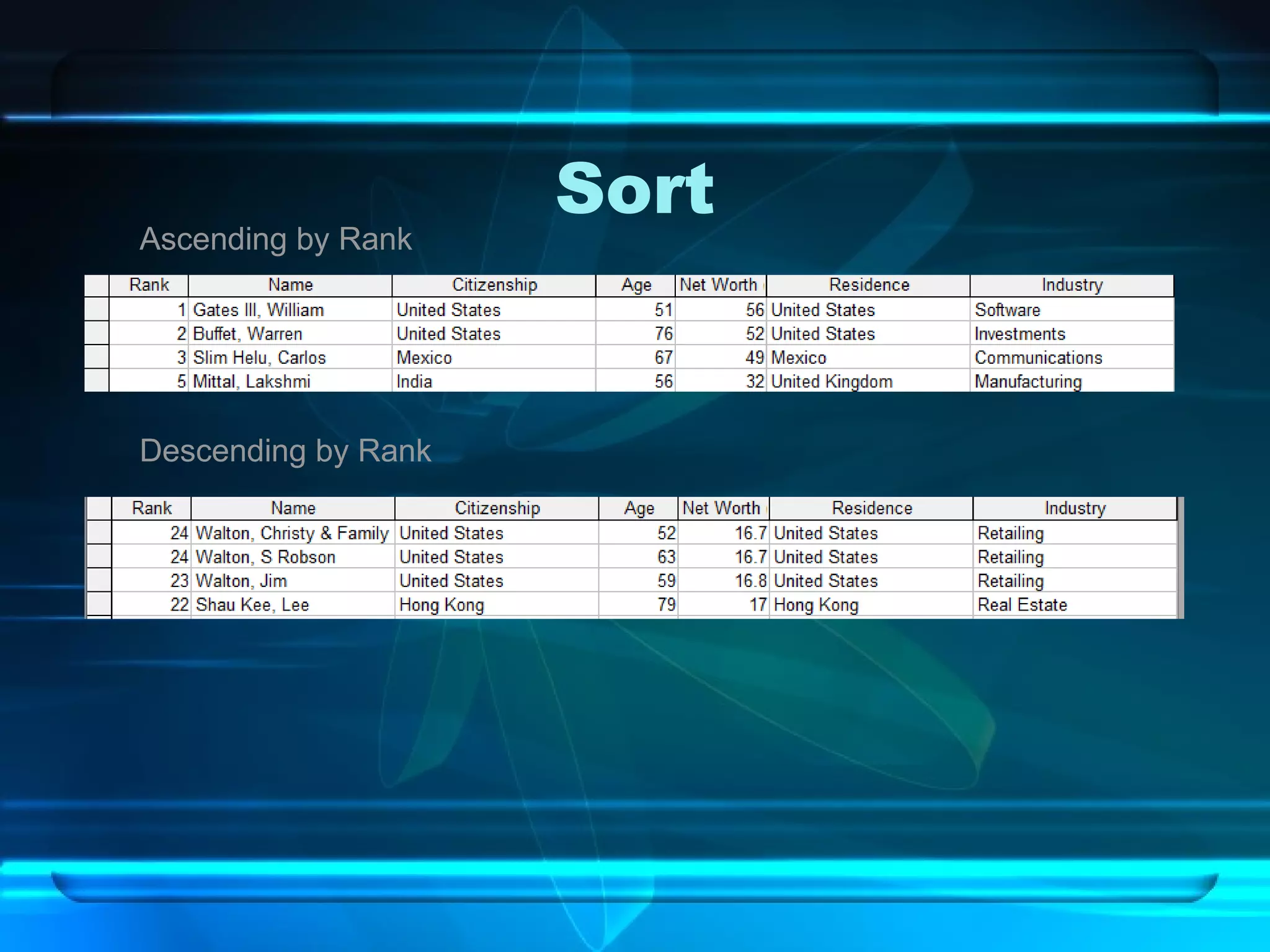
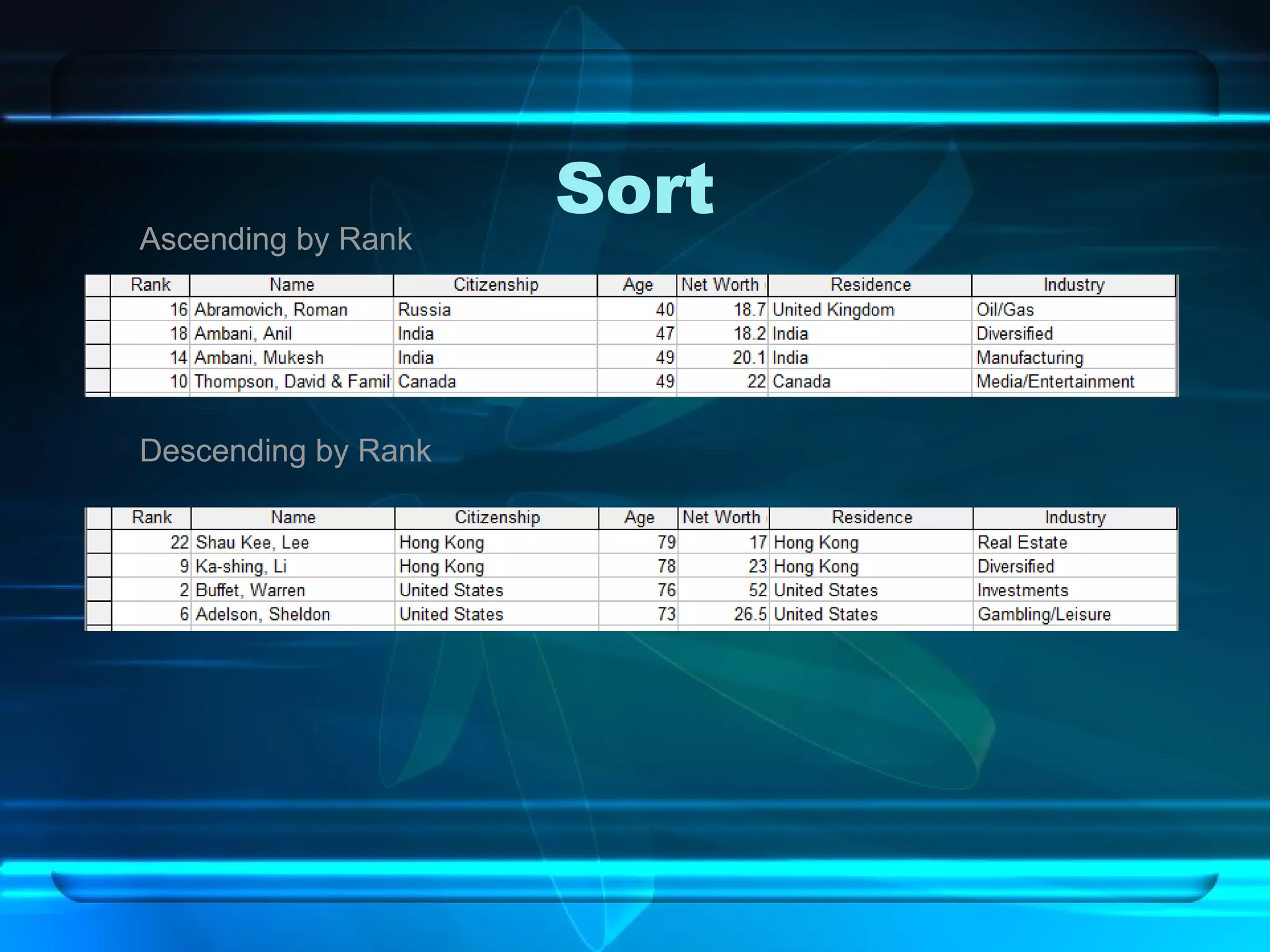
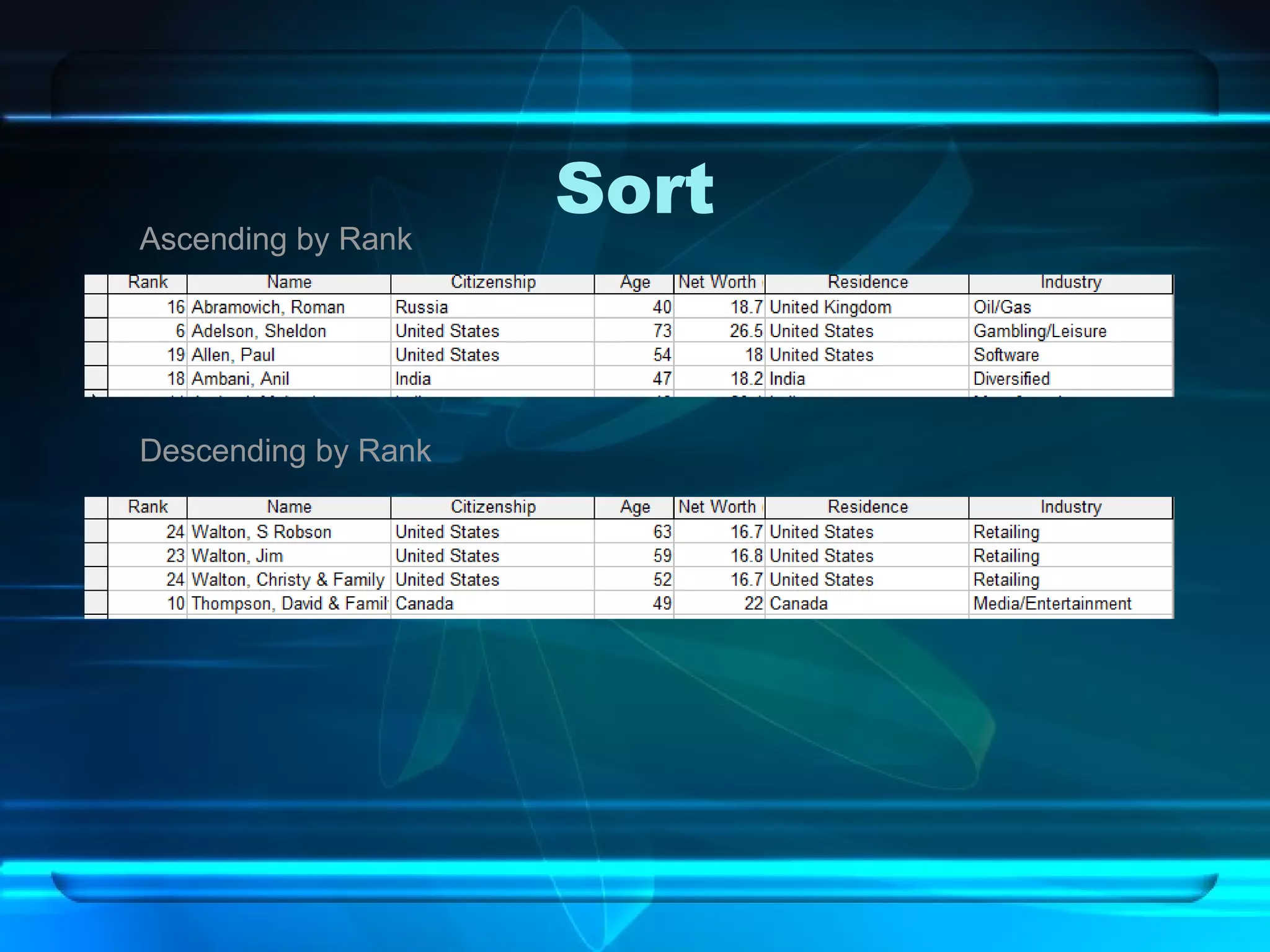
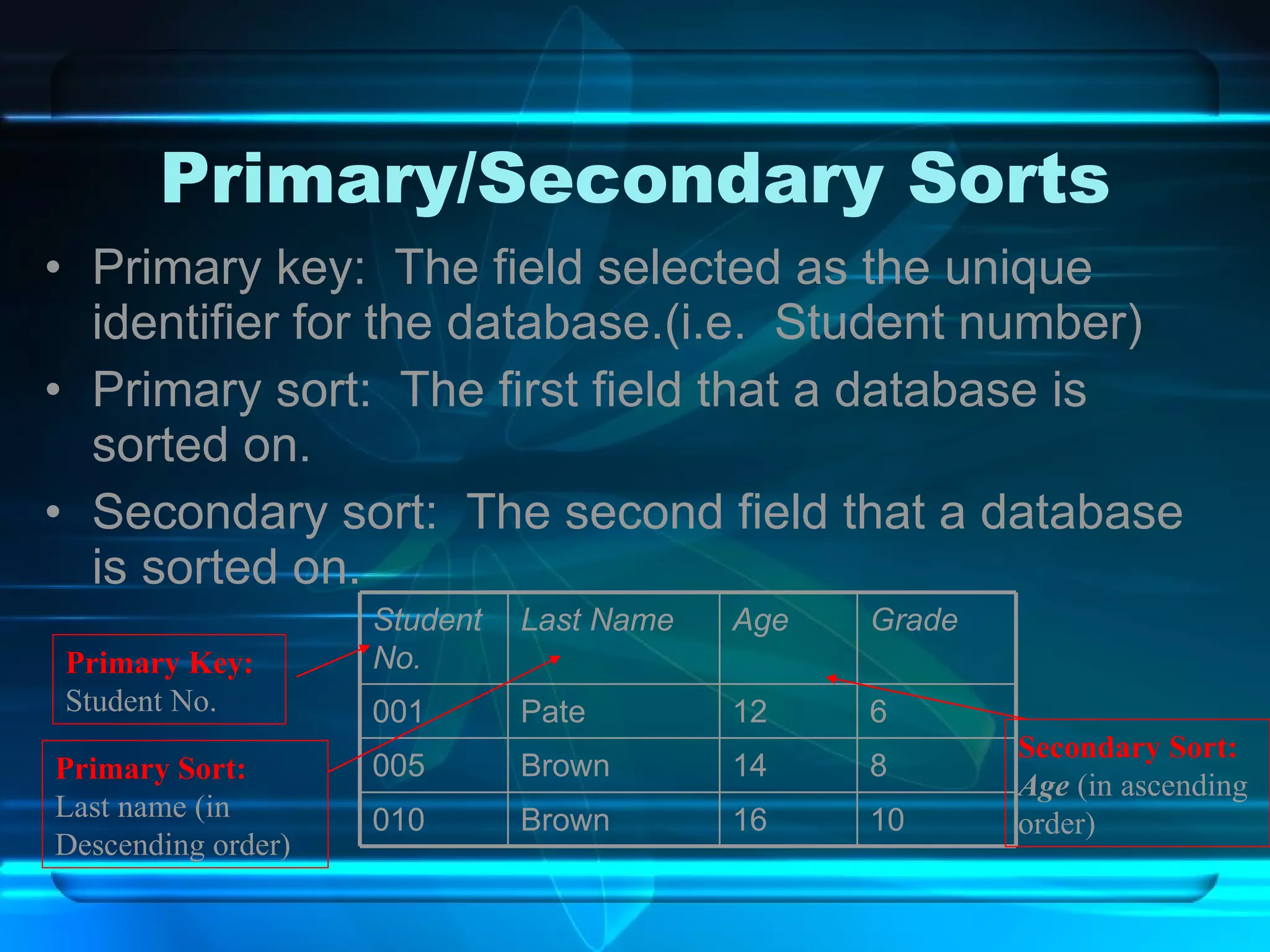
The document discusses databases, including what they are, how they are organized, and common examples. It explains that a database is an organized collection of related information and a database management system allows users to create, edit, and retrieve data. Popular databases mentioned include Netflix, cell phone contacts, medical records, and school records. The document outlines the basic components of a database like entries, fields, and records. It also describes common operations with databases like sorting, searching, filtering and generating reports.