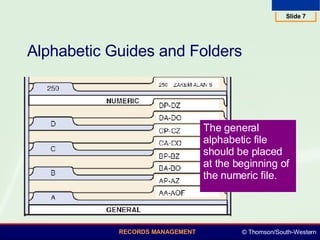
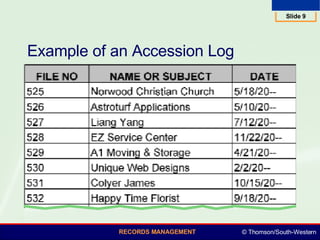
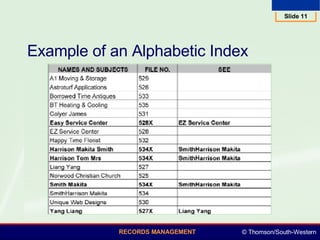
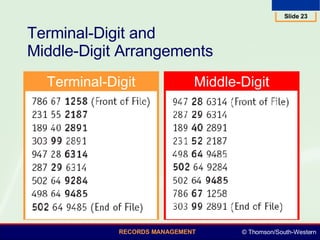
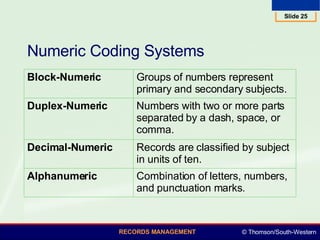
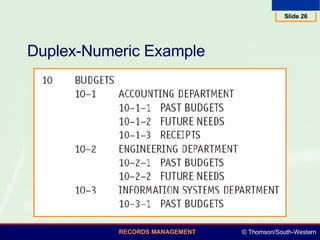
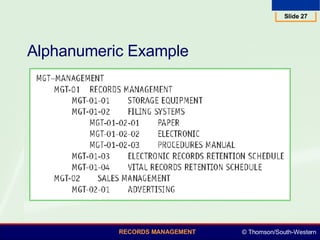
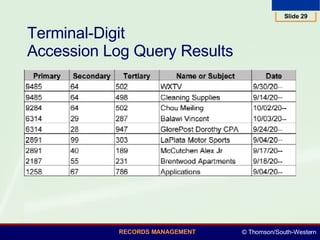
This document summarizes various numeric records management systems. It describes consecutive numbering systems and their components like numbered files, guides, and an accession log. It also describes terminal-digit and middle-digit storage methods where numbers are divided into groups separated by spaces or hyphens. Various numeric coding systems are mentioned that combine letters, numbers, and punctuation to classify records. Database software can be used to simplify creation and sorting of accession logs and alphabetic indexes for numeric storage systems.