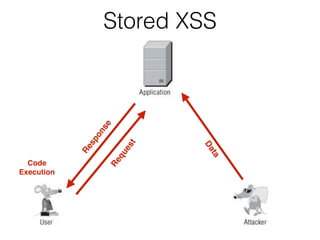
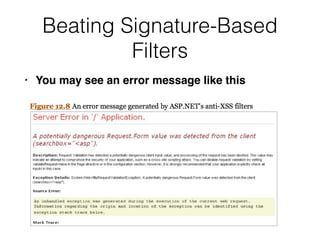
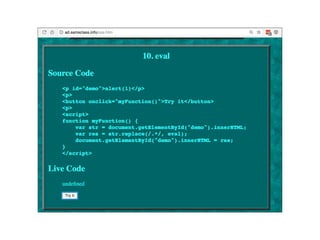
This document discusses cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks and how they work. It covers different types of XSS like reflected XSS, stored XSS, and DOM-based XSS. Reflected XSS occurs when untrusted user input is reflected back without sanitization. Stored XSS happens when malicious scripts are stored in a database or server and executed when others view the content. DOM-based XSS abuses client-side scripts that access data from the URL and display it. Real-world examples like attacks on Apache, MySpace, and Twitter are also described.