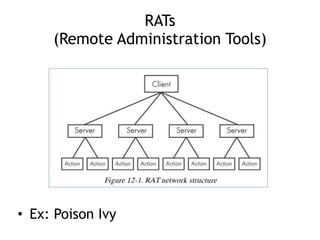
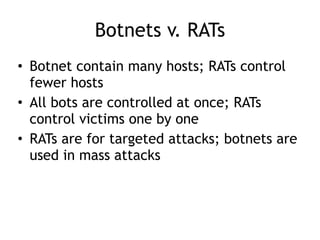
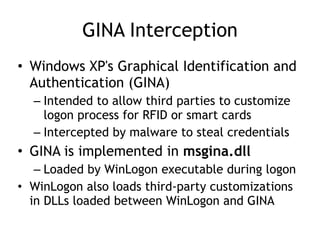
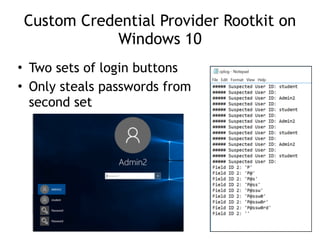
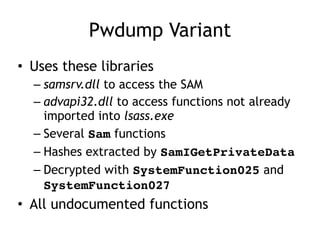
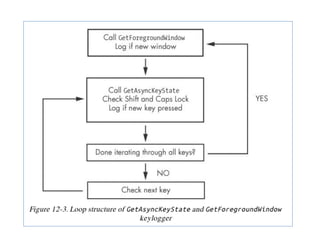
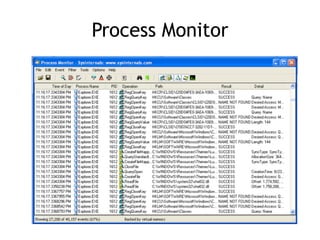
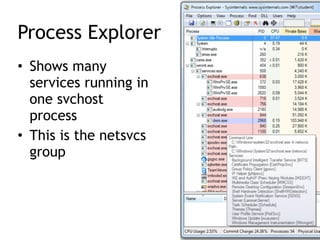
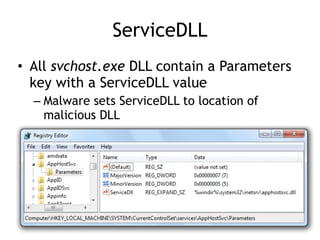
Chapter 11 of 'Practical Malware Analysis' discusses various types of malware behaviors, including downloaders, launchers, backdoors, and credential stealers. It details techniques such as GINA interception, hash dumping, and keylogging, as well as persistence mechanisms like registry modifications and DLL load-order hijacking. The chapter emphasizes the different methods malware uses to maintain control and conceal itself within systems, highlighting strategies for detecting and understanding these threats.