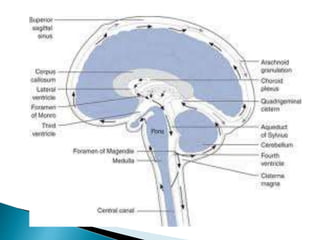
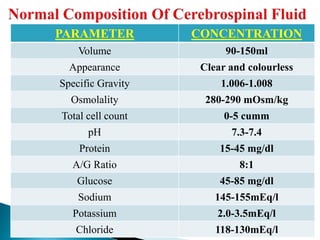
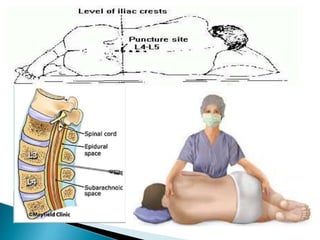
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a transcellular fluid produced mainly in the choroid plexuses of the brain, with a daily production of 500-600ml but an active volume of 120-150ml at any time. CSF serves essential functions such as acting as a shock absorber, regulating intracranial pressure, and transporting nutrients and waste. Lumbar punctures are indicated for conditions like meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and other CNS diseases.