The document provides information about ceramics, including:
1. It lists the 11 group members of the ceramic group and provides a brief history of ceramics dating back to 24,000 BC.
2. It describes the main compositions of clay which are feldspar minerals comprising 60% of the earth's crust. Clays are divided into primary and secondary types.
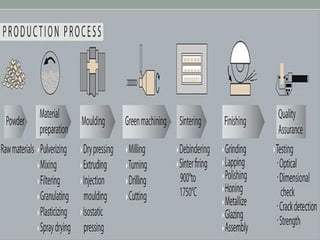
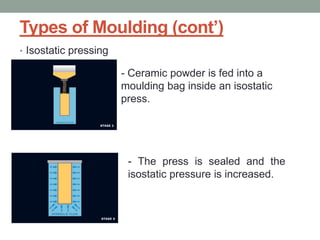
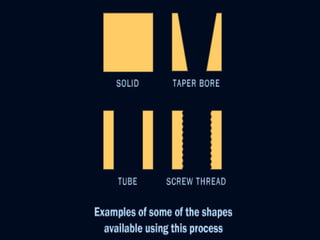
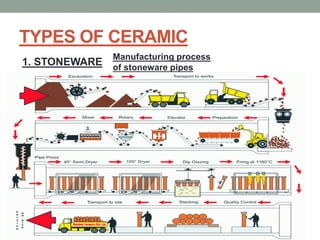
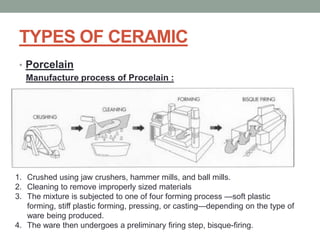
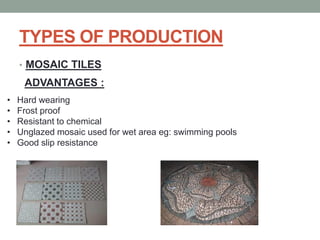
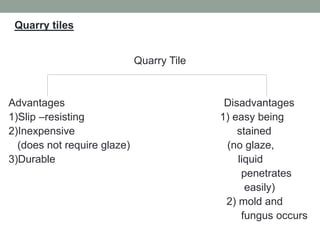
3. The manufacturing process of ceramics includes various molding techniques like injection molding and isostatic pressing. Characteristics of ceramics include high hardness, resistance to chemicals and temperatures up to 2400°C.