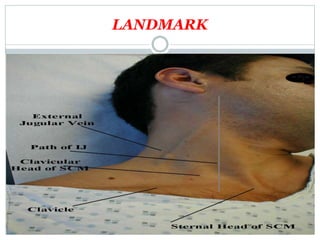
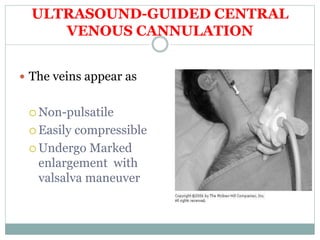
This document provides information about central venous cannulation and central venous pressure (CVP) measurement. It discusses the indications, contraindications, sites, techniques, and complications of central venous cannulation. The internal jugular vein and subclavian vein are described as common sites. Ultrasound guidance can help with visualization and decreases complications rates. CVP is measured by connecting a manometer to the central line and observing the fluid level, with normal ranges being from 3-8 cmH2O. Peripherally inserted central catheters are also discussed as an alternative approach.

![Indications for central venous Cannulation
Central venous pressure monitoring
Pulmonary artery catheterization and monitoring
Transvenous cardiac pacing
Temporary hemodialysis
Drug administration
Vasoactive drugs
Hyperalimentation [TPN]
Chemotherapy
Drugs irritating to peripheral veins
Prolonged antibiotic therapy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/centralvenouscannulation1-200828153541/85/Central-venous-cannulation-3-320.jpg)































![PROCEDURE FOR CVP MEASUREMENT IS
ZERO MANOMETER AT THE
LEVEL OF RT. ATRIUM
[level of the 4th intercostal space
in the mid-axillary line while the
patient is lying supine]
FILL MANOMETER WITH
SALINE USING A THREE
WAY TAP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/centralvenouscannulation1-200828153541/85/Central-venous-cannulation-38-320.jpg)




